在数值分析领域,梯形法则用于寻找定积分的近似值。梯形法则的基本思想是假定给定函数图下的区域为梯形并计算其面积。
它遵循: ![由QuickLaTeX.com渲染 {\displaystyle \int _{a}^{b}f(x)\,dx\approx (b-a)\left[{\frac {f(a)+f(b)}{2}}\right]}](https://mangdo-1254073825.cos.ap-chengdu.myqcloud.com//front_eng_imgs/geeksforgeeks2021/Trapezoidal%20Rule%20for%20Approximate%20Value%20of%20Definite%20Integral_0.jpg)
为了获得更准确的结果,图的域分为大小相等的n个段,如下所示:
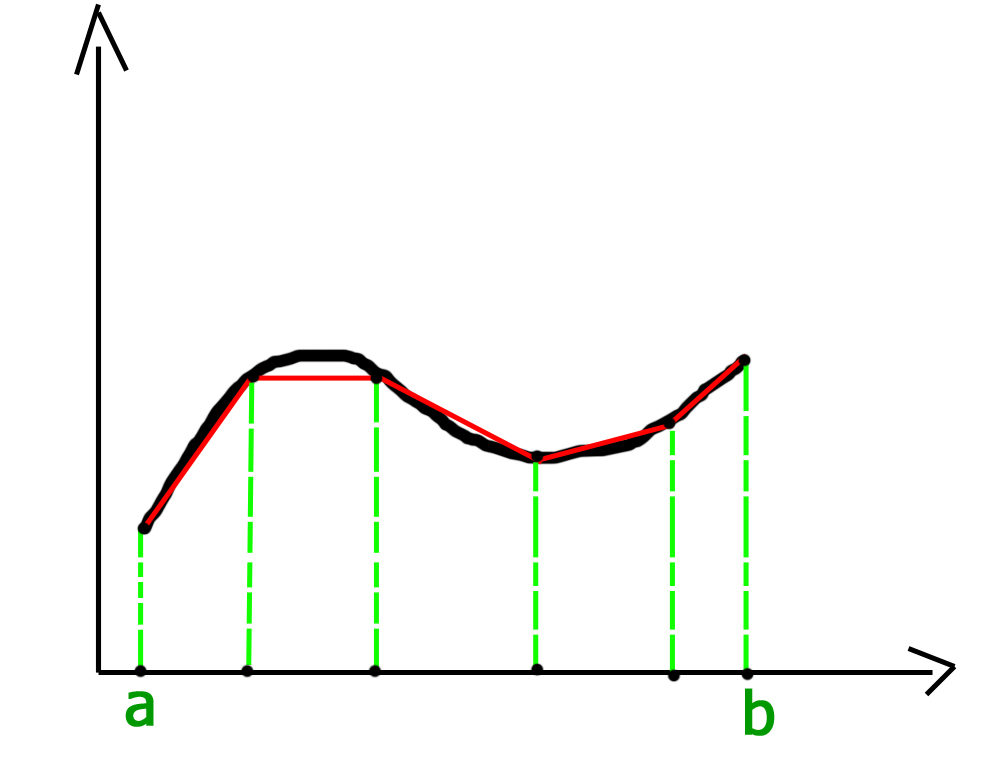
网格间距或段大小h =(ba)/ n。
因此,积分的近似值可以由下式给出: ![]()
C++
// C++ program to implement Trapezoidal rule
#include
// A sample function whose definite integral's
// approximate value is computed using Trapezoidal
// rule
float y(float x)
{
// Declaring the function f(x) = 1/(1+x*x)
return 1/(1+x*x);
}
// Function to evalute the value of integral
float trapezoidal(float a, float b, float n)
{
// Grid spacing
float h = (b-a)/n;
// Computing sum of first and last terms
// in above formula
float s = y(a)+y(b);
// Adding middle terms in above formula
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
s += 2*y(a+i*h);
// h/2 indicates (b-a)/2n. Multiplying h/2
// with s.
return (h/2)*s;
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
// Range of definite integral
float x0 = 0;
float xn = 1;
// Number of grids. Higher value means
// more accuracy
int n = 6;
printf("Value of integral is %6.4f\n",
trapezoidal(x0, xn, n));
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to implement Trapezoidal rule
class GFG
{
// A sample function whose definite
// integral's approximate value
// is computed using Trapezoidal
// rule
static float y(float x)
{
// Declaring the function
// f(x) = 1/(1+x*x)
return 1 / (1 + x * x);
}
// Function to evalute the value of integral
static float trapezoidal(float a, float b, float n)
{
// Grid spacing
float h = (b - a) / n;
// Computing sum of first and last terms
// in above formula
float s = y(a) + y(b);
// Adding middle terms in above formula
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
s += 2 * y( a + i * h);
// h/2 indicates (b-a)/2n. Multiplying h/2
// with s.
return (h / 2) * s;
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// Range of definite integral
float x0 = 0;
float xn = 1;
// Number of grids. Higher
// value means more accuracy
int n = 6;
System.out.println("Value of integral is "+
Math.round(trapezoidal(x0, xn, n)
* 10000.0) / 10000.0);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Anant Agarwal.Python3
# Python3 code to implement Trapezoidal rule
# A sample function whose definite
# integral's approximate value is
# computed using Trapezoidal rule
def y( x ):
# Declaring the function
# f(x) = 1/(1+x*x)
return (1 / (1 + x * x))
# Function to evalute the value of integral
def trapezoidal (a, b, n):
# Grid spacing
h = (b - a) / n
# Computing sum of first and last terms
# in above formula
s = (y(a) + y(b))
# Adding middle terms in above formula
i = 1
while i < n:
s += 2 * y(a + i * h)
i += 1
# h/2 indicates (b-a)/2n.
# Multiplying h/2 with s.
return ((h / 2) * s)
# Driver code to test above function
# Range of definite integral
x0 = 0
xn = 1
# Number of grids. Higher value means
# more accuracy
n = 6
print ("Value of integral is ",
"%.4f"%trapezoidal(x0, xn, n))
# This code is contributed by "Sharad_Bhardwaj".C#
// C# program to implement Trapezoidal
// rule.
using System;
class GFG {
// A sample function whose definite
// integral's approximate value
// is computed using Trapezoidal
// rule
static float y(float x)
{
// Declaring the function
// f(x) = 1/(1+x*x)
return 1 / (1 + x * x);
}
// Function to evalute the value
// of integral
static float trapezoidal(float a,
float b, float n)
{
// Grid spacing
float h = (b - a) / n;
// Computing sum of first and
// last terms in above formula
float s = y(a) + y(b);
// Adding middle terms in above
// formula
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
s += 2 * y( a + i * h);
// h/2 indicates (b-a)/2n.
// Multiplying h/2 with s.
return (h / 2) * s;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main ()
{
// Range of definite integral
float x0 = 0;
float xn = 1;
// Number of grids. Higher
// value means more accuracy
int n = 6;
Console.Write("Value of integral is "
+ Math.Round(trapezoidal(x0, xn, n)
* 10000.0) / 10000.0);
}
}
// This code is contributed by nitin mittal.PHP
Javascript
输出:
Value of integral is 0.7842参考:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trapezoidal_rule