溶液浓度
浓度是化学和其他相关领域中常用的术语。它是一种确定一种物质与另一种物质混合多少的方法。这可以适用于任何类型的化学组合,尽管它最常用于溶液的上下文中,它指的是溶解在溶剂中的溶质的量。浓度,可以用定性(非正式)或定量(数字)术语来表示。
溶液浓度:
- 确定溶解在单位量溶剂中的溶质量,
- 可以定性和定量地表示,并且
- 是一种宏观性质(散装物质的特性称为宏观性质)
浓度的定性表达
To qualitatively express concentration, a solution can be classified as a, dilute solution or a concentrated solution.
- 稀释溶液:与溶剂的比例相比,稀释溶液含有的溶质比例较小。
- 浓缩溶液:与溶剂的比例相比,稀溶液含有更多比例的溶质。
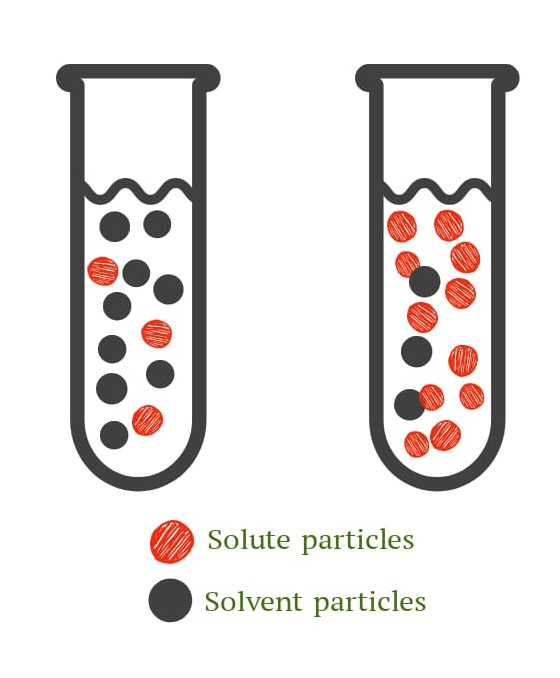
图 1. 稀释(左)和浓缩(右)溶液
浓度的半定性表达
To semi-qualitatively express concentration, a solution can be classified as an, saturated solution or a unsaturated solution.
- 饱和溶液:溶剂具有溶解某些类型溶质的能力。饱和溶液是在给定温度下可以溶解在溶剂中的最大量的溶质。当溶液达到饱和时,它不再溶解任何溶质。未溶解的化学物质沉到底部。饱和点被确定为不再有溶质可以溶解在溶剂中的点。
- 不饱和溶液:不饱和溶液是指溶质含量低于最大值的溶液,即在溶液达到饱和水平之前。底部无残留物质,说明溶质已全部溶解在溶剂中。不饱和溶液是一种化学溶液,其中溶质浓度小于相应的平衡溶解度。
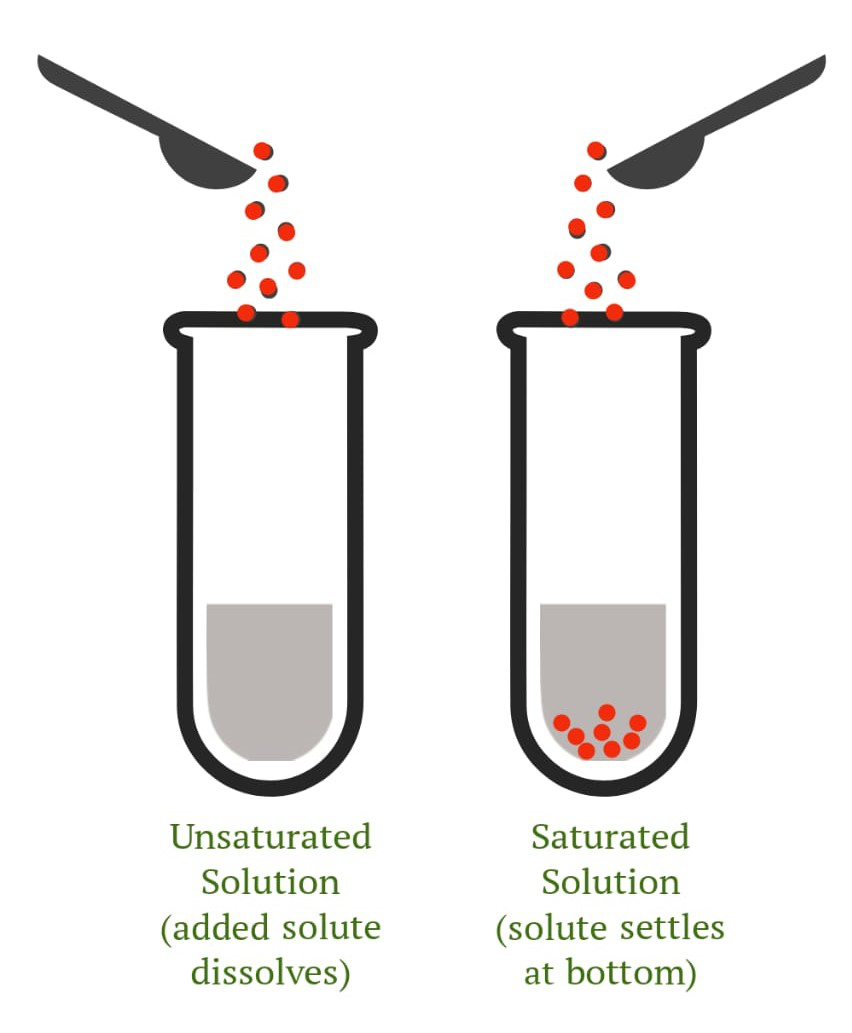
图 2. 不饱和(左)和饱和(右)溶液
从上述术语我们可以定义溶解度:
Solubility is defined as the greatest amount of solute that may dissolve in a certain quantity of solvent at a given temperature.
A solution is a liquid that is a homogeneous combination of one or more solutes and a solvent. A typical example of a solution is, sugar cubes added to a cup of tea or coffee. Here, solubility is the characteristic that allows sugar molecules to dissolve.
As a result, the term solubility may be defined as a substance’s (solute’s) ability to dissolve in a particular solvent.
浓度的定量表达
定量地 表达浓度,我们使用以下术语:
- 溶液的质量百分比
- 溶液的质量体积百分比
浓度的定性表达是相对术语,不提供溶液的准确浓度。为了以准确和精确的方式表征我们周围各种溶液的浓度,我们需要浓度的定量表达。
Generally, concentration is represented in both ways:
- Concentration = Quantity of Solute / Quantity of Solution
or
- Concentration = Quantity of Solute / Quantity of Solvent
质量百分比 (w/w%):它描述了 100 克溶液中存在的溶质量(克)。
在这里,溶质的质量和溶液的质量都将以克为单位。
质量比 % = (溶质质量 / 溶液质量) × 100
质量百分比没有单位。
质量体积百分比 (w/v%):它描述了 100 mL 溶液中存在的溶质量(克)。
体积质量% =(溶质质量/溶液体积)×100
在这里,溶质的质量以克为单位,溶液的体积以毫升为单位。
质量体积百分比的单位为 g/mL。
浓度定量表达的温度依赖性
Temperature Dependence of Quantitative Expressions of Concentration | ||
|---|---|---|
Expression of Concentration | Required Parameters | Dependence on Temperature |
| Mass by Mass percentage (w/w%) | Mass of solute and mass of solution | No (mass is not affected by temperature) |
| Mass by Volume percentage (w/v%) | Mass of solute and volume of solution | Yes (volume is affected by temperature) |
示例问题
问题1:15克食盐溶于400克水中。通过以质量百分比 (w/w%) 表示溶液来计算溶液的浓度。
回答:
Given that,
Mass of solute (common salt) = 15 g …(1)
Mass of Solvent (water) = 400 g …(2)
It is known that,
Mass of Solution = Mass of Solute + Mass of Solvent …(3)
So,
Substituting (1) and (2) in (3), we obtain the following,
Mass of Solution = 15 g + 400 g = 415 g …(4)
From Figure 4, we know
Mass by Mass Percentage = ( Mass of Solute / Mass of Solution ) × 100 …(5)
Substituting (1) and (4) in (5), we obtain the following,
Mass by Mass Percentage = ( 15 g / 415 g ) × 100 = ( 0.0361 ) × 100 = 3.61
Answer is:
( w / w % ) = 3.61
问题 2:将 15 g 食盐溶解在 300 mL 溶液中,计算质量体积百分比 (w/v%)。
回答:
Given that,
Mass of solute (common salt) = 15 g …(1)
Mass of Solution (salt solution) = 300 mL …(2)
From Figure 5, we know
Mass by Volume Percentage = ( Mass of Solute / Volume of Solution ) × 100 …(3)
Substituting (1) and (2) in (3), we obtain the following,
Mass by Volume Percentage = ( 15 g / 300 mL ) × 100 = ( 0.05 ) × 100 = 5 g/mL
Answer is:
( w / v % ) = 5 g/mL
问题 3:定义溶解度。
回答:
Solubility is defined as the greatest amount of solute that may dissolve in a certain quantity of solvent at a given temperature.
问题 4:理查德将 70 克糖溶解在 750 毫升糖溶液中。按体积百分比计算质量 (w/v%)。
回答:
Given that,
Mass of solute (common salt) = 70 g …(1)
Mass of Solution (salt solution) = 750 mL …(2)
From Figure 5, we know
Mass by Volume Percentage = ( Mass of Solute / Volume of Solution ) × 100 …(3)
Substituting (1) and (2) in (3), we obtain the following,
Mass by Volume Percentage = ( 70 g / 750 mL ) * 100 = ( 0.933 ) × 100 = 93.3 g/mL
Answer is:
( w / v % ) = 93.3 g/mL
问题5:什么是稀溶液?
回答:
A dilute solution is solution which contains a smaller proportion of solute as compared to the proportion of solvent.
问题 6:Mass by Mass % 是否取决于温度?
回答:
No, mass by mass % is not dependent on temperature as mass is no effected by temperature changes.
问题 7:质量体积百分比是否取决于温度?
回答:
Solution:
Yes, mass by volume % is dependent on temperature as volume is effected by temperature changes.