Expectimax搜索算法是一种用于使期望效用最大化的博弈论算法。它是Minimax算法的一种变体。虽然Minimax假定对手(最小化器)发挥最佳效果,但Expectimax却没有。这对于建模敌对代理不是最佳或其行动是基于机会的环境的建模很有用。
期望最大vs最小最大
考虑下面的Minimax树:
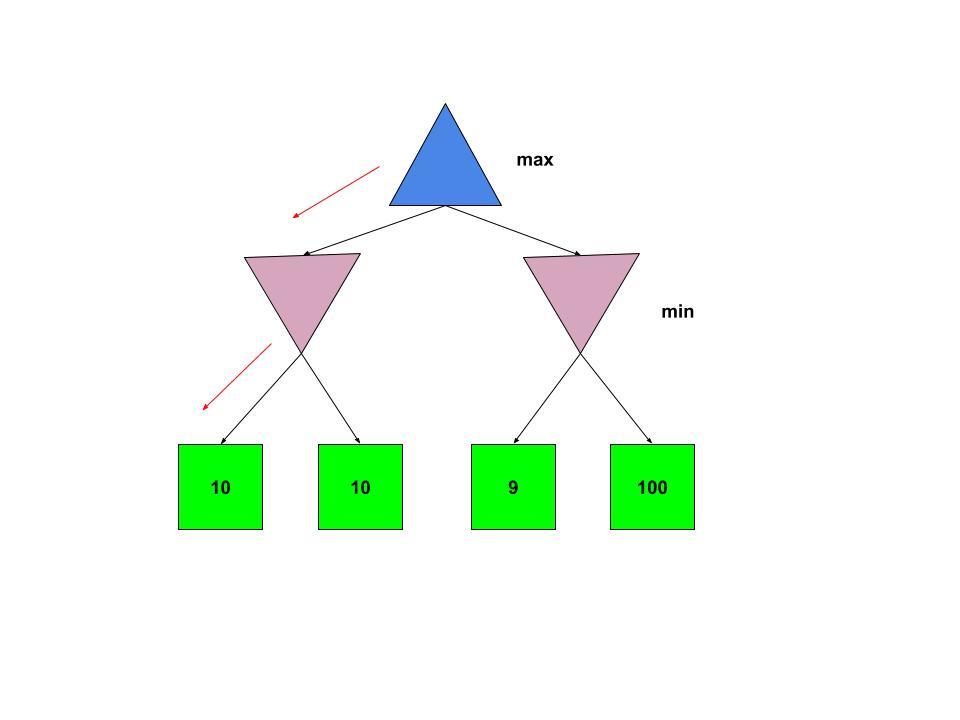
我们知道,敌方代理(最小化器)发挥了最佳作用,因此向左移动是有意义的。但是,如果最小化程序有可能犯错(或无法发挥最佳性能),该怎么办。因此,正确行事听起来可能更具吸引力,也可能会带来更好的解决方案。
在下面的Expectimax树中,我们用机会节点替换了最小化器节点。
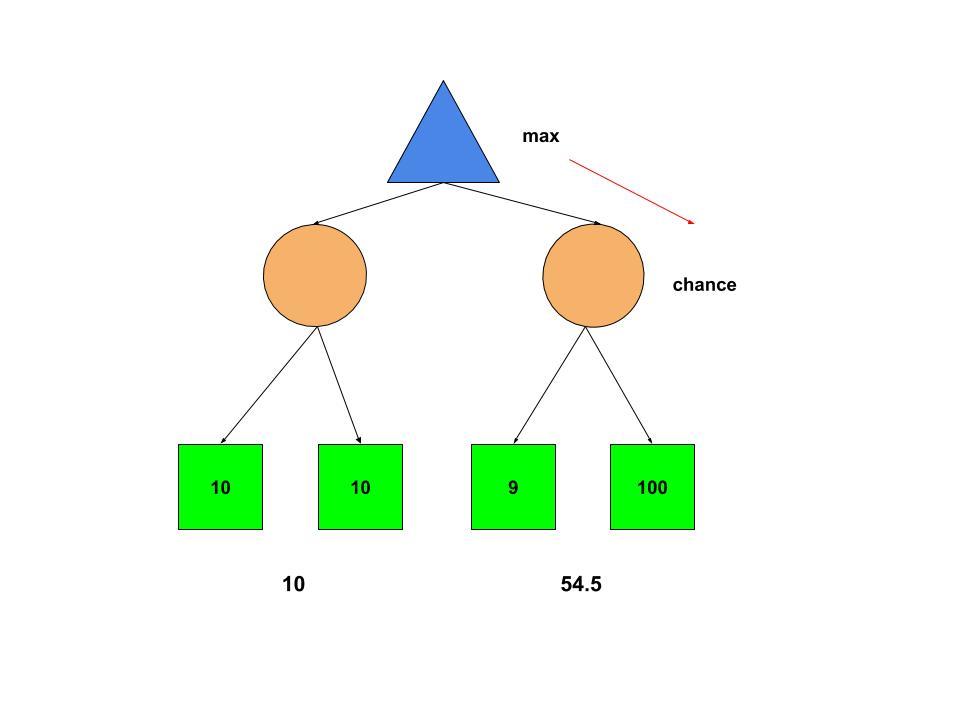
Chance节点取所有可用实用程序的平均值,为我们提供了“预期实用程序”。因此,左右子树的预期效用为(10 + 10)/ 2 = 10和(100 + 9)/2=54.5。最大化器节点选择正确的子树以最大化期望的效用。
Expectimax优于Minimax的优势:
- Expectimax算法有助于利用非最佳对手。
- 与Minimax不同,Expectimax可以“冒险”,并且由于对手是随机的(不是最优的)而最终处于效用更高的状态。
缺点:
- Expectimax不是最佳的。这可能会导致代理程序丢失(最终处于效用较小的状态)
- Expectimax要求探索整个搜索树。不能进行任何类型的修剪,因为单个未经开发的实用程序的值可能会大大改变期望值。因此,它可能很慢。
- 它对效用值的单调变换很敏感。
对于极小,如果我们有两个状态S 1和S 2,如果S1比S2中,evalaution函数值f的大小(S 1)和f(S 2)更好地不事沿为f( S 1 ) > f(S 2 ) 。
对于期望最大值,评估函数值的大小很重要。
算法: Expectimax可以使用以下递归算法来实现,
- 如果当前调用是最大化器节点,则返回节点后继者的状态值的最大值。
- 如果当前调用是机会节点,则返回节点后继者的状态值的平均值(假设所有节点具有相等的概率)。如果不同的节点具有不同的概率,则期望的效用由∑ i x i p i给出
- 我们递归地调用该函数,直到到达终端节点(没有后继的状态)为止。然后返回该状态的实用程序。
执行:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate
// Expectimax Algorithm
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure to declare
// left and right nodes
struct Node {
int value;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// Initializing Nodes to NULL
Node* newNode(int v)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->value = v;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Getting expectimax
float expectimax(Node* node, bool is_max)
{
// Condition for Terminal node
if (node->left == NULL
&& node->right == NULL) {
return node->value;
}
// Maximizer node. Chooses the max from the
// left and right sub-trees
if (is_max) {
return max(
expectimax(
node->left, false),
expectimax(node->right, false));
}
// Chance node. Returns the average of
// the left and right sub-trees
else {
return (
expectimax(node->left, true)
+ expectimax(node->right, true))
/ 2.0;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Non leaf nodes.
// If search is limited
// to a given depth,
// their values are
// taken as heuristic value.
// But because the entire tree
// is searched their
// values don't matter
Node* root = newNode(0);
root->left = newNode(0);
root->right = newNode(0);
// Assigning values to Leaf nodes
root->left->left = newNode(10);
root->left->right = newNode(10);
root->right->left = newNode(9);
root->right->right = newNode(100);
float res = expectimax(root, true);
cout << "Expectimax value is "
<< res << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to illustrate
// Expectimax Algorithm
class GFG{
// Structure to declare
// left and right nodes
static class Node {
int value;
Node left, right;
};
// Initializing Nodes to null
static Node newNode(int v)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.value = v;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Getting expectimax
static float expectimax(Node node, boolean is_max)
{
// Condition for Terminal node
if (node.left == null
&& node.right == null) {
return node.value;
}
// Maximizer node. Chooses the max from the
// left and right sub-trees
if (is_max) {
return Math.max(
expectimax(
node.left, false),
expectimax(node.right, false));
}
// Chance node. Returns the average of
// the left and right sub-trees
else {
return (float) ((
expectimax(node.left, true)
+ expectimax(node.right, true))
/ 2.0);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Non leaf nodes.
// If search is limited
// to a given depth,
// their values are
// taken as heuristic value.
// But because the entire tree
// is searched their
// values don't matter
Node root = newNode(0);
root.left = newNode(0);
root.right = newNode(0);
// Assigning values to Leaf nodes
root.left.left = newNode(10);
root.left.right = newNode(10);
root.right.left = newNode(9);
root.right.right = newNode(100);
float res = expectimax(root, true);
System.out.print("Expectimax value is "
+ res +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992Python3
# Python3 program to illustrate
# Expectimax Algorithm
# Structure to declare
# left and right nodes
class Node:
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Initializing Nodes to None
def newNode(v):
temp = Node(v);
return temp;
# Getting expectimax
def expectimax(node, is_max):
# Condition for Terminal node
if (node.left == None and node.right == None):
return node.value;
# Maximizer node. Chooses the max from the
# left and right sub-trees
if (is_max):
return max(expectimax(node.left, False), expectimax(node.right, False))
# Chance node. Returns the average of
# the left and right sub-trees
else:
return (expectimax(node.left, True)+ expectimax(node.right, True))/2;
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
# Non leaf nodes.
# If search is limited
# to a given depth,
# their values are
# taken as heuristic value.
# But because the entire tree
# is searched their
# values don't matter
root = newNode(0);
root.left = newNode(0);
root.right = newNode(0);
# Assigning values to Leaf nodes
root.left.left = newNode(10);
root.left.right = newNode(10);
root.right.left = newNode(9);
root.right.right = newNode(100);
res = expectimax(root, True)
print("Expectimax value is "+str(res))
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# program to illustrate
// Expectimax Algorithm
using System;
class GFG{
// Structure to declare
// left and right nodes
class Node {
public int value;
public Node left, right;
};
// Initializing Nodes to null
static Node newNode(int v)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.value = v;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Getting expectimax
static float expectimax(Node node, bool is_max)
{
// Condition for Terminal node
if (node.left == null
&& node.right == null) {
return node.value;
}
// Maximizer node. Chooses the max from the
// left and right sub-trees
if (is_max) {
return Math.Max(
expectimax(
node.left, false),
expectimax(node.right, false));
}
// Chance node. Returns the average of
// the left and right sub-trees
else {
return (float) ((
expectimax(node.left, true)
+ expectimax(node.right, true))
/ 2.0);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Non leaf nodes.
// If search is limited
// to a given depth,
// their values are
// taken as heuristic value.
// But because the entire tree
// is searched their
// values don't matter
Node root = newNode(0);
root.left = newNode(0);
root.right = newNode(0);
// Assigning values to Leaf nodes
root.left.left = newNode(10);
root.left.right = newNode(10);
root.right.left = newNode(9);
root.right.right = newNode(100);
float res = expectimax(root, true);
Console.Write("Expectimax value is "
+ res +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by sapnasingh4991输出:
Expectimax value is 54.5时间复杂度:O(b m )
空间复杂度:O(b * m),其中b是分支因子, m是树的最大深度。
应用程序: Expectimax可以用于其中一个代理的动作是随机的环境中。以下是一些示例,
- 在Pacman中,如果我们有随机的重影,则可以将Pacman建模为最大化器,将重影建模为机会节点。效用值将是最终状态(获胜,失败或平局)的值或给定深度处一组可能状态的评估函数值。
- 我们可以通过将玩家代理建模为最大化器并将地雷建模为机会节点来创建扫雷AI。