考虑以下情况:我们有一组间隔,并且需要有效执行以下操作:
- 添加间隔
- 删除间隔
- 给定间隔x,请确定x是否与任何现有间隔重叠。
间隔树可以实现为增强型二分搜索树(最好是自平衡),从而使我们能够以O(logN)时间复杂度执行所需的操作。
树的每个节点将存储以下信息:
- 间隔i :表示为一对[低,高]。
- 右端点的最大元数据:存储在以该节点为根的子树中的所有时间间隔的右端点的最大值。存储此元数据是我们扩充树的方式。
间隔树中使用的示例间隔树|第一组:
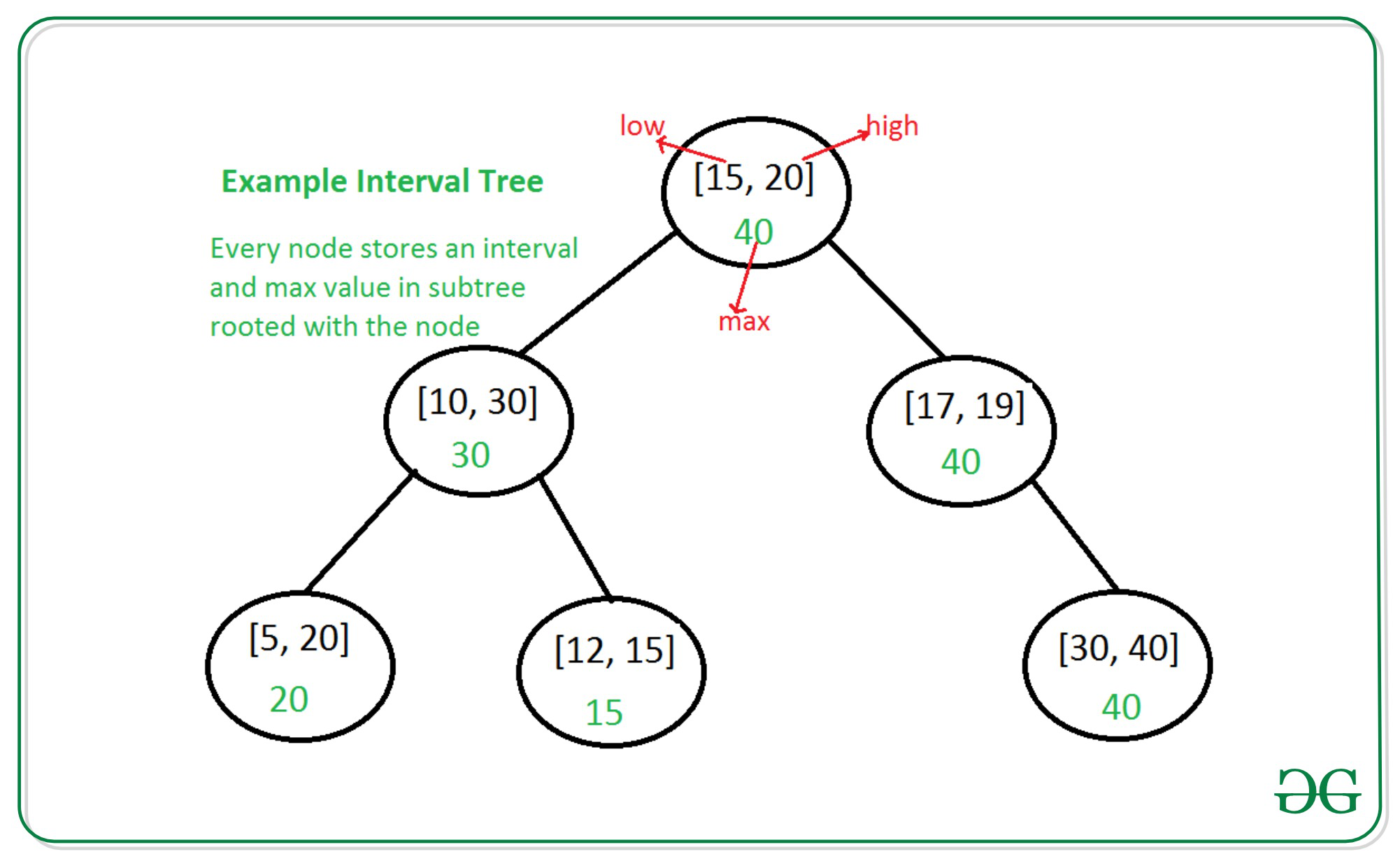
在间隔树中|第一组,我们看到了如何使用简单的BST(不是自平衡)实现间隔树。在本文中,我们将使用内置的基于GNU树的容器来实现“间隔树”。这样做的好处是:
- 我们不必编写我们自己的树数据结构。
- 我们可以直接使用默认操作,例如插入和删除。
- 我们将使用内置的Red-Black树实现,这意味着我们的树将是自平衡的。
我们将使用基于GNU策略的树数据结构实现。
g ++中基于策略的数据结构一文介绍了基于GNU策略的数据结构以及所需的头文件。
我们将定义自己的Node_update策略,以便我们可以将子树中间隔的最大右端点作为元数据保留在树的节点中。
定义自定义Node_policy的语法为:
CPP
template <
typename Const_Node_Iterator,
typename Node_Iterator,
typename Cmp_Fn_,
typename Allocator_>
;
struct custom_node_update_policy {
typedef type_of_our_metadata
metadata_type;
void operator()(
node_iterator it,
const_node_iterator end_it)
{
// ...
}
// ...other methods that we need
}C++
// CPP program for above approach
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
typedef pair Interval;
// An invalid interval, used as
// return value to denote that no
// matching interval was found
const Interval NO_INTERVAL_FOUND = { 1, 0 };
// interval update policy struct
template
struct interval_node_update_policy {
// Our metadata is maximum of
// right-endpoints of intervals in the
// sub-tree, which is of type int
typedef int metadata_type;
// An utility function to check
// if given two intervals overlap
bool doOverlap(Interval i1,
Node_CItr i2)
{
return (i1.first <= (*i2)->second
&& (*i2)->first <= i1.second);
}
// Search for any interval that
// overlaps with Interval i
Interval overlapSearch(Interval i)
{
for (Node_CItr it = node_begin();
it != node_end();) {
if (doOverlap(i, it)) {
return { (*it)->first,
(*it)->second };
}
if (it.get_l_child() != node_end()
&& it.get_l_child()
.get_metadata()
>= i.first) {
it = it.get_l_child();
}
else {
it = it.get_r_child();
}
}
return NO_INTERVAL_FOUND;
}
// To restore the node-invariance
// of the node pointed to by
// (it). We need to derive the
// metadata for node (it) from
// its left-child and right-child.
void operator()(Node_Itr it,
Node_CItr end_it)
{
int max_high = (*it)->second;
if (it.get_l_child() != end_it) {
max_high = max(
max_high,
it.get_l_child()
.get_metadata());
}
if (it.get_r_child() != end_it) {
max_high = max(
max_high,
it.get_r_child()
.get_metadata());
}
// The max of right-endpoint
// of this node and the max
// right-endpoints of children.
const_cast(
it.get_metadata())
= max_high;
}
virtual Node_CItr node_begin() const = 0;
virtual Node_CItr node_end() const = 0;
virtual ~interval_node_update_policy() {}
};
// IntervalTree data structure
// rb_tree_tag: uses red-black search tree
// interval_node_update_policy:
// our custom Node_update policy
typedef tree,
rb_tree_tag,
interval_node_update_policy>
IntervalTree;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
IntervalTree IT;
Interval intvs[] = { { 15, 20 },
{ 10, 30 },
{ 17, 19 },
{ 5, 20 },
{ 12, 15 },
{ 30, 40 } };
for (Interval intv : intvs) {
IT.insert(intv);
}
Interval toSearch = { 25, 29 };
cout << "\nSearching for interval ["
<< toSearch.first << ", "
<< toSearch.second << "]";
Interval res = IT.overlapSearch(toSearch);
if (res == NO_INTERVAL_FOUND)
cout << "\nNo Overlapping Interval\n";
else
cout << "\nOverlaps with ["
<< res.first << ", "
<< res.second << "]\n";
Interval toErase = { 10, 30 };
IT.erase(toErase);
cout << "\nDeleting interval ["
<< toErase.first << ", "
<< toErase.second
<< "]\n";
cout << "\nSearching for interval ["
<< toSearch.first << ", "
<< toSearch.second << "]";
res = IT.overlapSearch(toSearch);
if (res == NO_INTERVAL_FOUND)
cout << "\nNo Overlapping Interval\n";
else
cout << "\nOverlaps with ["
<< res.first << ", "
<< res.second << "]\n";
return 0;
} - type_of_our_metadata:在我们的情况下为int ,因为我们要存储元数据“子树中间隔的右端点的最大值”。
- 无效运算符()(node_iterator it,const_node_iterator end_it):内部调用该方法以恢复节点不变性,即在不变性无效后保持正确的元数据。
- 它: node_iterator到我们需要恢复其不变性的节点。
- end_it :指向后一个节点的const_node_iterator。
有关更多详细信息,请参见基于GNU树的容器。
我们还将定义一个方法overlaySearch ,它搜索树中与给定间隔i重叠的任何间隔。
// pseudocode for overlapSearch
Interval overlapSearch(Interval i) {
// start from root
it = root_node
while (it not null) {
if (doOVerlap(i, it->interval)) {
// overlap found
return it->inteval
}
if (left_child exists
AND
left_child->max_right_endpoint
>= it->left_endpoint) {
// go to left child
it = it->left_child
}
else {
// go to right child
it = it->right_child
}
}
// no overlapping interval found
return NO_INTERVAL_FOUND
}以下是间隔树的实现:
C++
// CPP program for above approach
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
typedef pair Interval;
// An invalid interval, used as
// return value to denote that no
// matching interval was found
const Interval NO_INTERVAL_FOUND = { 1, 0 };
// interval update policy struct
template
struct interval_node_update_policy {
// Our metadata is maximum of
// right-endpoints of intervals in the
// sub-tree, which is of type int
typedef int metadata_type;
// An utility function to check
// if given two intervals overlap
bool doOverlap(Interval i1,
Node_CItr i2)
{
return (i1.first <= (*i2)->second
&& (*i2)->first <= i1.second);
}
// Search for any interval that
// overlaps with Interval i
Interval overlapSearch(Interval i)
{
for (Node_CItr it = node_begin();
it != node_end();) {
if (doOverlap(i, it)) {
return { (*it)->first,
(*it)->second };
}
if (it.get_l_child() != node_end()
&& it.get_l_child()
.get_metadata()
>= i.first) {
it = it.get_l_child();
}
else {
it = it.get_r_child();
}
}
return NO_INTERVAL_FOUND;
}
// To restore the node-invariance
// of the node pointed to by
// (it). We need to derive the
// metadata for node (it) from
// its left-child and right-child.
void operator()(Node_Itr it,
Node_CItr end_it)
{
int max_high = (*it)->second;
if (it.get_l_child() != end_it) {
max_high = max(
max_high,
it.get_l_child()
.get_metadata());
}
if (it.get_r_child() != end_it) {
max_high = max(
max_high,
it.get_r_child()
.get_metadata());
}
// The max of right-endpoint
// of this node and the max
// right-endpoints of children.
const_cast(
it.get_metadata())
= max_high;
}
virtual Node_CItr node_begin() const = 0;
virtual Node_CItr node_end() const = 0;
virtual ~interval_node_update_policy() {}
};
// IntervalTree data structure
// rb_tree_tag: uses red-black search tree
// interval_node_update_policy:
// our custom Node_update policy
typedef tree,
rb_tree_tag,
interval_node_update_policy>
IntervalTree;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
IntervalTree IT;
Interval intvs[] = { { 15, 20 },
{ 10, 30 },
{ 17, 19 },
{ 5, 20 },
{ 12, 15 },
{ 30, 40 } };
for (Interval intv : intvs) {
IT.insert(intv);
}
Interval toSearch = { 25, 29 };
cout << "\nSearching for interval ["
<< toSearch.first << ", "
<< toSearch.second << "]";
Interval res = IT.overlapSearch(toSearch);
if (res == NO_INTERVAL_FOUND)
cout << "\nNo Overlapping Interval\n";
else
cout << "\nOverlaps with ["
<< res.first << ", "
<< res.second << "]\n";
Interval toErase = { 10, 30 };
IT.erase(toErase);
cout << "\nDeleting interval ["
<< toErase.first << ", "
<< toErase.second
<< "]\n";
cout << "\nSearching for interval ["
<< toSearch.first << ", "
<< toSearch.second << "]";
res = IT.overlapSearch(toSearch);
if (res == NO_INTERVAL_FOUND)
cout << "\nNo Overlapping Interval\n";
else
cout << "\nOverlaps with ["
<< res.first << ", "
<< res.second << "]\n";
return 0;
}
输出:
Searching for interval [25, 29]
Overlaps with [10, 30]
Deleting interval [10, 30]
Searching for interval [25, 29]
No Overlapping Interval
时间复杂度
所有操作的大小都是对数,即O(logN) ,其中N是存储在树中的间隔数。
我们能够实现对数最坏情况的复杂性,因为内部使用了自平衡的红黑树。
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。