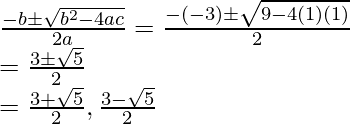多项式具有不同的类型,其中两个多项式的形式为ax 2 + bx + c,a≠0。当将此多项式等于0时,我们得到一个二次方程。在许多现实生活中都会出现这类方程式。让我们研究这些方程式,如何求解它们以及如何在现实生活中公式化它们。
例如,一个校务委员会决定为他们的学生做一个足球场。他们决定将足球场的面积定为1000m 2 。教练指示地面长度必须比地面宽度的两倍长50米。我们需要找到地面的长度和宽度。
假设地面的宽度为“ x”。则地面的长度将为“ 2x + 50”。我们知道面积必须为1000m 2 。所以,
x(2x + 50)= 1000
⇒2x 2 + 50x = 1000
⇒2x 2 + 50x – 1000 = 0
在这里,我们得到一个二次方程。让我们正式定义二次方程。
二次方程
变量“ x”中的二次方程是形式为等式的方程,
斧2 +斧+ c = 0
其中,a,b,c是实数和常数,且a≠0。
例如: 4x 2 – 5x = 0,5x 2 + 16x + 5 = 0
In general, any second-degree polynomial P(x), when put like P(x) = 0 represents a quadratic equation.
问题1:Rahul和Ravi共有45个糖果。他们俩各损失了5个糖果。现在,他们两个人拥有的糖果数的乘积为124。我们被要求找出一开始每个人拥有的糖果数。为这个问题制定二次方程。
解决方案:
Let’s say Rahul had “x” candies. Then Ravi must have “45 – x” candies because both of them had 45 candies.
Now after losing the candies, we are given that product of the number of candies they have is 124. That is,
x(45 – x) = 124
⇒ 45x – x2 = 124
⇒ 0 = x2 – 45x + 124
问题2:检查以下方程式是否为二次方程式。
(x – 2)(x +1)=(x – 1)(x + 3)
解决方案:
We know that a quadratic equation must be of degree 2.
Let’s simplify and check the given equation.
(x – 2)(x + 1) = (x – 1)(x + 3)
⇒ x2 + x – 2x – 2 = x2 + 3x – x – 3
⇒ x2 – x – 2 = x2 + 2x – 3
⇒ -x – 2 = 2x – 3
⇒ -3x + 1 = 0
This equation is of degree 1. Thus, it cannot be a quadratic equation.
求解二次方程
假设二次方程P(x)=0。满足该方程的点称为二次方程的解或零。可以找到三种方法来求解二次方程式:
- 分解法
- 完成平方方法
- Shree Dharacharya或二次方程式
让我们通过示例逐一查看这三种方法。
分解法
二次方程式可以认为是两个项的因数。像ax 2 + bx + c = 0可以写成(x – x 1 )(x – x 2 )= 0,其中x 1和x 2是二次方程的根。
解决步骤:
- 找到两个数字,以使这些数字的乘积为“ ac”,且总和为“ b”。
- 然后将x系数写为这两个数字的总和,并将它们除以得到x的两个项。
- 将前两个项作为一个组,将后两个项作为另一个组。
- 从这些中取公因数,并在取了公因数并重新排列方程后将两个表达式等于零,我们得到了根。
问题1:使用因式分解法找出给定二次方程的解。
2x 2 – 3x +1 = 0
解决方案:
2x2 – 3x + 1 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 2x – x + 1 = 0
⇒ 2x(x – 1) – 1(x -1) = 0
⇒ (2x – 1)(x-1) = 0
Now this equation will be zero when either of these two terms of both of these terms are zero
So, putting 2x – 1 = 0, we get x = ![]()
Similarly, x – 1 = 0, we get x = 1
Thus, we get two roots x = 1 and ![]()
问题2:使用相同的方法找出以下二次方程的根。
2x 2 – x – 6 = 0
解决方案:
2x2 – x – 6 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 4x. +3x – 6 = 0
⇒ 2x (x – 2) +3(x – 2) = 0
⇒ (2x + 3) (x – 2) = 0
Now,
2x + 3 = 0
x = ![]()
x – 2 = 0
x = 2
Thus, this equation has roots x = 2 and ![]()
完成平方方法
任何等式ax 2 + bx + c = 0都可以转换为(x + m) 2 – n 2 = 0的形式。之后取平方根,得到等式的根。完成平方只是重新调整给定二次方程的一种方式,使它们以完整平方的形式出现。我们来看一个例子。
问题1:通过完成平方法找到给定方程的根。
x 2 + 4x – 5 = 0
解决方案:
We are given, x2 + 4x – 5 = 0
To solve it by completing the square method, we need to bring it in the above mentioned form.
x2 + 4x – 5 = 0
⇒ x2 + 4x + 4 – 9 = 0
⇒ (x + 2)2 – 32 = 0
⇒ (x + 2)2 = 32
Taking square root both sides,
x + 2 = 3 and x + 2 = -3
This gives us x = 1, -5
问题2:通过完成平方法找到给定方程的根。
x 2 + 6x + 9 = 0
解决方案:
Given, x2 + 6x + 9 = 0
x2 + 6x + 9 = 0
⇒ x2 + 2(3x) + 32 = 0
⇒ (x + 3)2 = 0
Taking square root,
x + 3 = 0
x = – 3
Thus, this equation has only one root with multiplicity of 2.
x = -3,-3
Shree Dharacharya或二次方程式
这个公式说
For a quadratic equation in general form,
ax2 + bx + c = 0
If b2 – 4ac > 0,
Then roots are given by ![]()
问题1:找到方程3x 2 – 5x + 2 = 0的根。
解决方案:
For finding out the roots using Shree Dharacharya formula,
We need to check If b2 – 4ac > 0,
In this particular equation, a = 3, b = -5 and c = 2.
So, b2 – 4ac
⇒ (-5)2 – 4(3)(2)
⇒ 25 – 24
⇒ 1 > 0
Thus, roots are possible,
Now let’s calculate the roots by plugging in the values in the formula mentioned above.

问题2:找到方程式的根
![]()
解决方案:
We need to first simplify this equation and bring it to the quadratic form so that we can apply Dharacharya Formula.
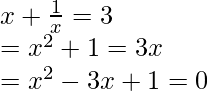
Now let’s check if b2 – 4ac > 0 first.
Here a = 1, b = -3 and c = 1
b2 – 4ac
⇒ 9. -4(1)(1)
⇒ 5 > 0
So we can apply the formula now,