矩阵知识对于数学的各个分支都是必不可少的。矩阵是数学中最强大的工具之一。行列式来自矩阵。现在,我们在本文中看到行列式的属性之一。在本文中,我们看到了如何找到矩阵的伴随。要了解矩阵的伴随,我们必须了解矩阵的辅因子。
矩阵的辅因子
辅因子是在矩阵中删除指定元素的列和行时得到的数字。这意味着从矩阵中取出一个元素,然后从矩阵中删除该元素的整个行和列,然后在该矩阵中删除哪些元素,称为辅因子。
例子
Let’s take a matrix, 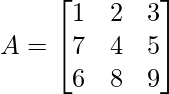
Now find the cofactor of element 3
- Step 1: Delete the entire row and column that contains element 3
- Step 2: Take the present elements as it is in the matrix after Step 1.
So, the cofactor of 3 is 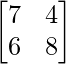
矩阵的伴随
要找到矩阵的伴随,首先,我们必须找到每个元素的辅因子,然后再找到2个步骤。请参阅以下步骤,
- 步骤1:找出矩阵中每个元素的辅因子。
- 步骤2:使用辅助因子创建另一个矩阵并展开辅助因子,然后得到一个矩阵
- 步骤3:现在找到步骤2之后的矩阵转置。
让我们通过一些例子来了解整个事情。
例子
示例1:查找给定矩阵的伴随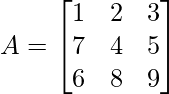 ?
?
解决方案:
Step 1: To find the cofactor of each element
To find the cofactor of each element, we have to delete the row and column of each element one by one and take the present elements after deleting.
Cofactor of element at A[0,0] = 1 :  = +(4×9 – 8×5) = -4
= +(4×9 – 8×5) = -4
Cofactor of elements at A[0,1] = 2 : 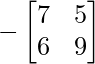 = -(7×9 – 6×5) = -33
= -(7×9 – 6×5) = -33
Cofactor of elements at A[0,2] = 3 : 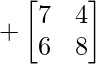 = +(7×8 – 6×4) = 32
= +(7×8 – 6×4) = 32
Cofactor of elements at A[2,0] = 7 : 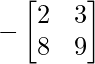 = -(2×9 – 8×3) = 6
= -(2×9 – 8×3) = 6
Cofactor of elements at A[2,1] = 4 : 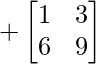 = +(1×9 – 6×3) = -9
= +(1×9 – 6×3) = -9
Cofactor of elements at A[2,2] = 5 : 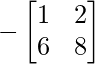 = -(1×8 – 6×2) = 4
= -(1×8 – 6×2) = 4
Cofactor of elements at A[3,0] = 6 : 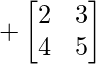 = +(2×5 – 4×3) = -2
= +(2×5 – 4×3) = -2
Cofactor of elements at A[3,1] = 8 : 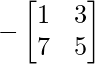 = -(1×5 – 7×3) = 16
= -(1×5 – 7×3) = 16
Cofactor of elements at A[3,2] = 9 : 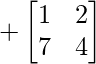 = +(1×4 – 7×2) = -10
= +(1×4 – 7×2) = -10
The matrix looks like with the cofactors:

The final cofactor matrix:
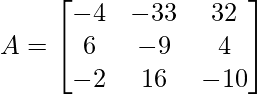
Step 2: Find the transpose of the matrix obtained in step 1
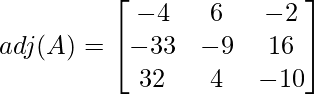
This is the Adjoint of the matrix.
示例2:查找给定矩阵的伴随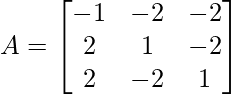 ?
?
解决方案:
Step 1: To find the cofactor of each element
To find the cofactor of each element, we have to delete the row and column of each element one by one and take the present elements after deleting.
Cofactor of element at A[0,0] = -1 : 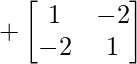 = +(1×1 – (-2)x(-2)) = -3
= +(1×1 – (-2)x(-2)) = -3
Cofactor of elements at A[0,1] = -2 : 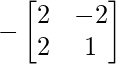 = -(2×1 – 2x(-2)) = -6
= -(2×1 – 2x(-2)) = -6
Cofactor of elements at A[0,2] = -2 : 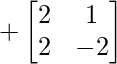 = +(2x(-2) – 2×1) = -6
= +(2x(-2) – 2×1) = -6
Cofactor of elements at A[2,0] = 2 : 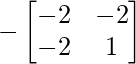 = -((-2)x1 – (-2)x(-2)) = 6
= -((-2)x1 – (-2)x(-2)) = 6
Cofactor of elements at A[2,1] = 1 : 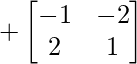 = +((-1)x1 – 2x(-2)) = 3
= +((-1)x1 – 2x(-2)) = 3
Cofactor of elements at A[2,2] = -2 : 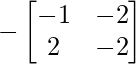 = -((-1)x(-2) – 2x(-2)) = -6
= -((-1)x(-2) – 2x(-2)) = -6
Cofactor of elements at A[3,0] = 2 : 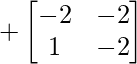 = +((-2)x(-2) – 1x(-2)) = 6
= +((-2)x(-2) – 1x(-2)) = 6
Cofactor of elements at A[3,1] = -2 : 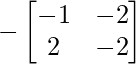 = -((-1)x(-2) – 2x(-2)) = -6
= -((-1)x(-2) – 2x(-2)) = -6
Cofactor of elements at A[3,2] = 1 : 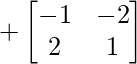 = +((-1)x(-1)- 2x(-2)) = 3
= +((-1)x(-1)- 2x(-2)) = 3
The final cofactor matrix:

Step 2: Find the transpose of the matrix obtained in Step 1
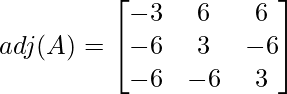
This is the Adjoint of the matrix.
奇异矩阵
如果矩阵的行列式为零,则称该矩阵为奇异矩阵。因为只有平方矩阵具有行列式,所以仅用平方矩阵就可以实现这种奇异性。同样,奇异矩阵的求逆也是不可能的,因为要找到矩阵的逆矩阵,我们需要用矩阵的行列式除以矩阵的伴随项,但是对于奇异矩阵,行列式的值为零。因此,此处不可能进行划分。要查找矩阵是否为奇数或不存在某些规则,请参见下文:
- 规则1:首先检查矩阵是否为正方形。
- 规则2:如果为正方形,则计算其行列式并检查该值是否为零。如果为零,则它是一个奇异矩阵。
例子
示例1:检查给定矩阵是否为奇数, 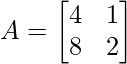 ?
?
解决方案:
Here this matrix is a square matrix, so let’s find the determinant of this matrix,
det A = (4×2 – 8×1) = 0
Here determinant of A is ZERO,
Also ![]() = inversion not possible
= inversion not possible
So we can say that matrix A is a singular matrix.
示例2:检查给定矩阵是否为奇数, 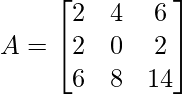 ?
?
解决方案:
det(A) = 2(0 – 16) – 4(28 – 12) + 6(16 – 0) [using 1st row]
= −2(16) + 2(16) = 0
Here determinant of A is ZERO
Also ![]() = inversion not possible
= inversion not possible
So we can say that matrix A is a singular matrix.
奇异矩阵的性质
- 所有奇异矩阵的行列式值为零。
- 所有奇异矩阵都必须是方矩阵。
- 所有奇异矩阵都不能反转。
- 奇异矩阵没有乘法逆。