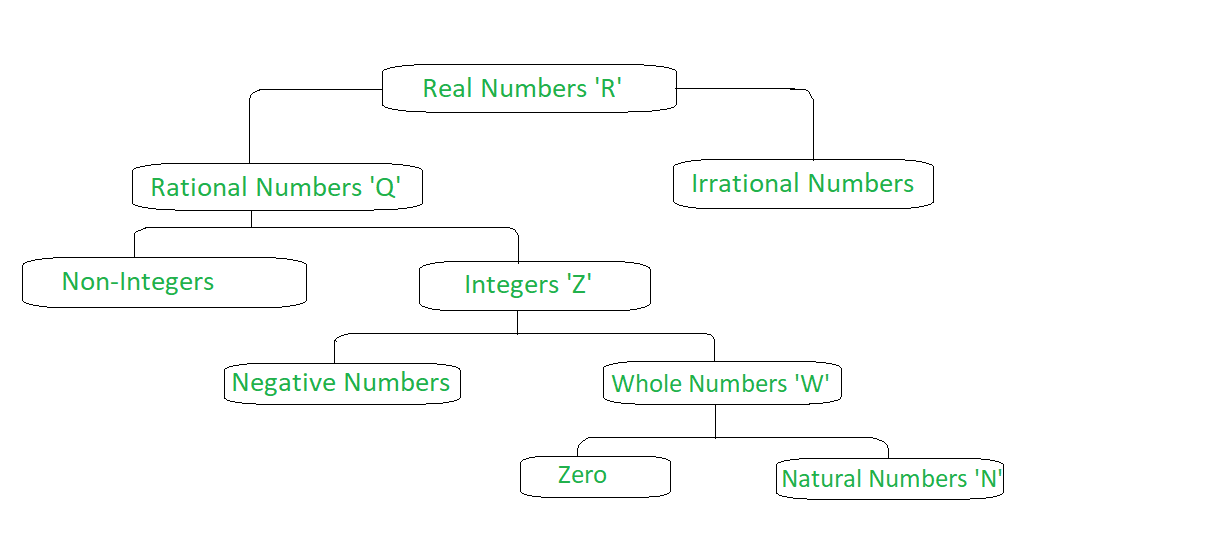
一组有理数和无理数的组合称为实数。所有实数都可以在数字行上表示。不能在数字行上表示的除实数以外的数字称为虚数(虚数)。它们用于表示复数。下面是实数的分类图。
十进制展开
在介绍有理数的十进制扩展之前,让我们了解什么是有理数。有理数是可以p / q形式写的数字,其中p,q是整数,q!=0。例如: 2 / 3、1 / 4、4 / 5等。有理数用Q表示。由于每个整数都可以p / q形式表示,因此所有整数都是有理数。
示例: -1,-2,-6、4、5可以表示为-1 / 1,-2 / 1、4 / 1、5 / 1
十进制扩展通常有3种类型:
- 终止
- 非终止重复
- 不终止不重复

终止小数
终止小数点是指那些位数有限的十进制数。这意味着在重复一定次数后,该数字在小数点后结束。
例如: 0.5、0.678、14.123445、1.23、0.00024等。
非终结小数
无终止小数是指具有无限位数的那些十进制数字。这里的数字并没有结束。
例如: 1.33333…..,52.36363636…,2.343537684904…,3.1415926535897…等。
重复小数:重复小数是指其中特定数字在小数点后均匀重复的数字。
例如: 0.5555…,13.262626…,1.8769876…等。
Note: Non terminating and repeating decimals are rational numbers. They can be expressed in p/q form, where q != 0.
不重复的小数:在不重复的小数中,没有统一的数字重复。
例如: 4.34527238…,1.61803398…,2.718281828459 ..,1342.53352567545…等。
Note: Non terminating and nonrepeating decimals are irrational numbers. They cannot be expressed in p/q form.
将重复的小数转换为分数
情况1:类型为0.yyyyy…或0.xyxyxyxy……或0.xyzxyzxyz…的分数。等等
示例1:转换0.4444…。几分之一?
解决方案:
Let x = 0.4444…. — eq(1)
as only one term(4) is repeating multiply eq(1) with 10.
10x = 4.4444…. — eq(2)
Now substract eq(1) from eq(2) [eq(2) – eq(1)]
9x = 4
=> x = 4/9
示例2:转换0.45454545…。几分之一?
解决方案:
Formula = Repeated term/number of 9’s for repeated term
0.45454545… = 45 (repeated term)/99 (Two 9’s as only two terms are repeating) = 45/99
情况2:形式为0.abcxyxyxyxyxy…的分数(重复和非重复的组合)
Formula: 0.abcxyxyxyxy…. = abcxy – (xy/number of 9’s for repeating term and number of 0’s for nonrepeating term)
示例1:将0.45232323…转换为分数?
解决方案:
Here 45 is nonrepeating and 23 is repeating. So in the numerator, we subtract the nonrepeating term(45) from the number and as we have two terms as repeating(2, 3). In the denominator, we place two 9’s followed by two zeros, as we have two non-repeating terms(45).
0.45232323… = 4523 – (45/9900)
示例2:将0.000456456…转换为分数?
解决方案:
Here 000 is nonrepeating and 456 is repeating. So in Numerator, we subtract 000 from 000456. In the denominator, as we have three repeating terms we place three 9’s followed by three 0’s for three non-repeating terms.
0.000456456…. = 000456 – (000/999000)
= 456/999000
有理数的性质
关闭属性
如果我们将两个有理数相加,相减或相乘,则结果为有理数。闭包属性不适用于除法,因为任何数字除以零(有理数)均未定义。除零外,它均适用。
例子:
2/3 + 3/4 = 17/12
3/4 – 2/6 = 5/12
4/5 * 3/2 = 12/10
交换性质
对于任何两个有理数,加法和乘法都是可交换的,而除法和减法则不遵循可交换性。
Commutative law of addition: a + b = b + a
Example: 1/2 + 4/3 = 4/3 + 1/2 = 11/6
Commutative law of Multiplication: a * b = b * a
Example: 2/7 * 5/8 = 5/8 * 2/7 = 10/56
关联财产
对于加法和乘法,关联属性后跟有理数。令a,b,c为三个有理数,
Associative property of addition: a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c
Associative property of multiplication: a * (b * c) = (a * b) * c
分配财产
根据分布性质,令a,b,c为三个有理数,则a *(b + c)= a * b + a * c。
例子:
1/2 * (2/3 + 1/3) = 3/6
=> 1/2 * 2/3 + 1/2 * 1/3 = 3/6
身份属性
有理数的加和标识为0
Example: 5/9 + 0 = 5/9
有理数的乘法身份为1
Example: 7/8 * 1 = 7/8
逆属性
有理数a / b的加和逆是-a / b
Example: 4/6 additive inverse is -4/6
有理数a / b的乘法逆是b / a
Example: 3/8 multiplicative inverse is 8/3