给定两个整数N和K ,任务是对最多N个数字进行计数,以使没有两个零相邻且数字范围从0到K-1。
例子:
Input: N = 2, K = 3
Output: 8
Explanation:
There are 8 such numbers such that digits are from 0 to 2 only, without any adjacent 0s: {1, 2, 10, 11, 12, 20, 21, 22}
Input: N = 3, K = 3
Output: 22
方法:想法是使用动态编程来解决此问题。
令DP [i] [j]为所需数字的数量,直到该数字的第i位,其最后一位为j 。
观察结果:
- 填补一个地方的方法是
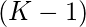
- 众所周知,零不能相邻。因此,当我们的最后一个元素为0时,意味着前一个索引将以1的方式填充,即0。因此,当前位置只能由(K-1)个数字填充。
- 如果最后一位用(K-1)位填充,则当前位可以用0或(K-1)位填充。
基本情况:
- 如果n == 1并且最后一个== K,那么我们可以用(K-1)个数字填充该位置,然后返回(K-1)
- 否则,返回1
递归关系:
When last digit place is not filled by zero then
![]()
When Last digit place is filled by zero then
![]()
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation to count the
// numbers upto N digits such that
// no two zeros are adjacent
#include
using namespace std;
int dp[15][10];
// Function to count the
// numbers upto N digits such that
// no two zeros are adjacent
int solve(int n, int last, int k)
{
// Condition to check if only
// one element remains
if (n == 1) {
// If last element is non
// zero, return K-1
if (last == k) {
return (k - 1);
}
// If last element is 0
else {
return 1;
}
}
// Condition to check if value
// calculated already
if (dp[n][last])
return dp[n][last];
// If last element is non zero,
// then two cases arise,
// current element can be either
// zero or non zero
if (last == k) {
// Memoize this case
return dp[n][last]
= (k - 1)
* solve(n - 1, k, k)
+ (k - 1)
* solve(n - 1, 1, k);
}
// If last is 0, then current
// can only be non zero
else {
// Memoize and return
return dp[n][last]
= solve(n - 1, k, k);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given N and K
int n = 2, k = 3;
// Function Call
int x = solve(n, k, k)
+ solve(n, 1, k);
cout << x;
} Java
// Java implementation to count the
// numbers upto N digits such that
// no two zeros are adjacent
class GFG{
static int[][] dp = new int[15][10];
// Function to count the numbers
// upto N digits such that
// no two zeros are adjacent
static int solve(int n, int last, int k)
{
// Condition to check if only
// one element remains
if (n == 1)
{
// If last element is non
// zero, return K-1
if (last == k)
{
return (k - 1);
}
// If last element is 0
else
{
return 1;
}
}
// Condition to check if
// value calculated already
if (dp[n][last] == 1)
return dp[n][last];
// If last element is non zero,
// then two cases arise, current
// element can be either zero
// or non zero
if (last == k)
{
// Memoize this case
return dp[n][last] = (k - 1) *
solve(n - 1, k, k) +
(k - 1) *
solve(n - 1, 1, k);
}
// If last is 0, then current
// can only be non zero
else
{
// Memoize and return
return dp[n][last] = solve(n - 1, k, k);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given N and K
int n = 2, k = 3;
// Function Call
int x = solve(n, k, k) +
solve(n, 1, k);
System.out.print(x);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Ritik BansalPython3
# Python3 implementation to count the
# numbers upto N digits such that
# no two zeros are adjacent
dp = [[0] * 10 for j in range(15)]
# Function to count the numbers
# upto N digits such that no two
# zeros are adjacent
def solve(n, last, k):
# Condition to check if only
# one element remains
if (n == 1):
# If last element is non
# zero, return K-1
if (last == k):
return (k - 1)
# If last element is 0
else:
return 1
# Condition to check if value
# calculated already
if (dp[n][last]):
return dp[n][last]
# If last element is non zero,
# then two cases arise, current
# element can be either zero or
# non zero
if (last == k):
# Memoize this case
dp[n][last] = ((k - 1) *
solve(n - 1, k, k) +
(k - 1) *
solve(n - 1, 1, k))
return dp[n][last]
# If last is 0, then current
# can only be non zero
else:
# Memoize and return
dp[n][last] = solve(n - 1, k, k)
return dp[n][last]
# Driver code
# Given N and K
n = 2
k = 3
# Function call
x = solve(n, k, k) + solve(n, 1, k)
print(x)
# This code is contributed by himanshu77C#
// C# implementation to count the
// numbers upto N digits such that
// no two zeros are adjacent
using System;
class GFG{
public static int [,]dp = new int[15, 10];
// Function to count the numbers
// upto N digits such that
// no two zeros are adjacent
public static int solve(int n, int last, int k)
{
// Condition to check if only
// one element remains
if (n == 1)
{
// If last element is non
// zero, return K-1
if (last == k)
{
return (k - 1);
}
// If last element is 0
else
{
return 1;
}
}
// Condition to check if
// value calculated already
if (dp[n, last] == 1)
return dp[n, last];
// If last element is non zero,
// then two cases arise, current
// element can be either zero
// or non zero
if (last == k)
{
// Memoize this case
return dp[n, last] = (k - 1) *
solve(n - 1, k, k) +
(k - 1) *
solve(n - 1, 1, k);
}
// If last is 0, then current
// can only be non zero
else
{
// Memoize and return
return dp[n, last] = solve(n - 1, k, k);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Given N and K
int n = 2, k = 3;
// Function Call
int x = solve(n, k, k) +
solve(n, 1, k);
Console.WriteLine(x);
}
}
// This code is contributed by SoumikMondalJavascript
输出:
8时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N * 10)
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。