伯恩赛德引理有时也称为轨道计数定理。这是群体理论的结果之一。它用于计算关于对称性的不同对象。它基本上为我们提供了计算组合总数的公式,其中相对于旋转或反射彼此对称的两个对象被视为一个代表。
因此,Burnside Lemma指出不同对象的总数为: ![]()
在哪里:
- c(k)是应用第K次旋转时保持不变的组合数,并且
- N是更改N个元素的位置的总数。
例如:
让我们考虑一下,我们有一条由N块宝石组成的项链,可以用M种颜色对其进行着色。如果旋转后两条项链相似,则将两条项链视为相似并计为一个不同的组合。现在假设我们有N = 4颗宝石, M = 3种颜色,然后
因此,由于我们有N颗宝石,因此每条项链的N个旋转可能会有N种变化:
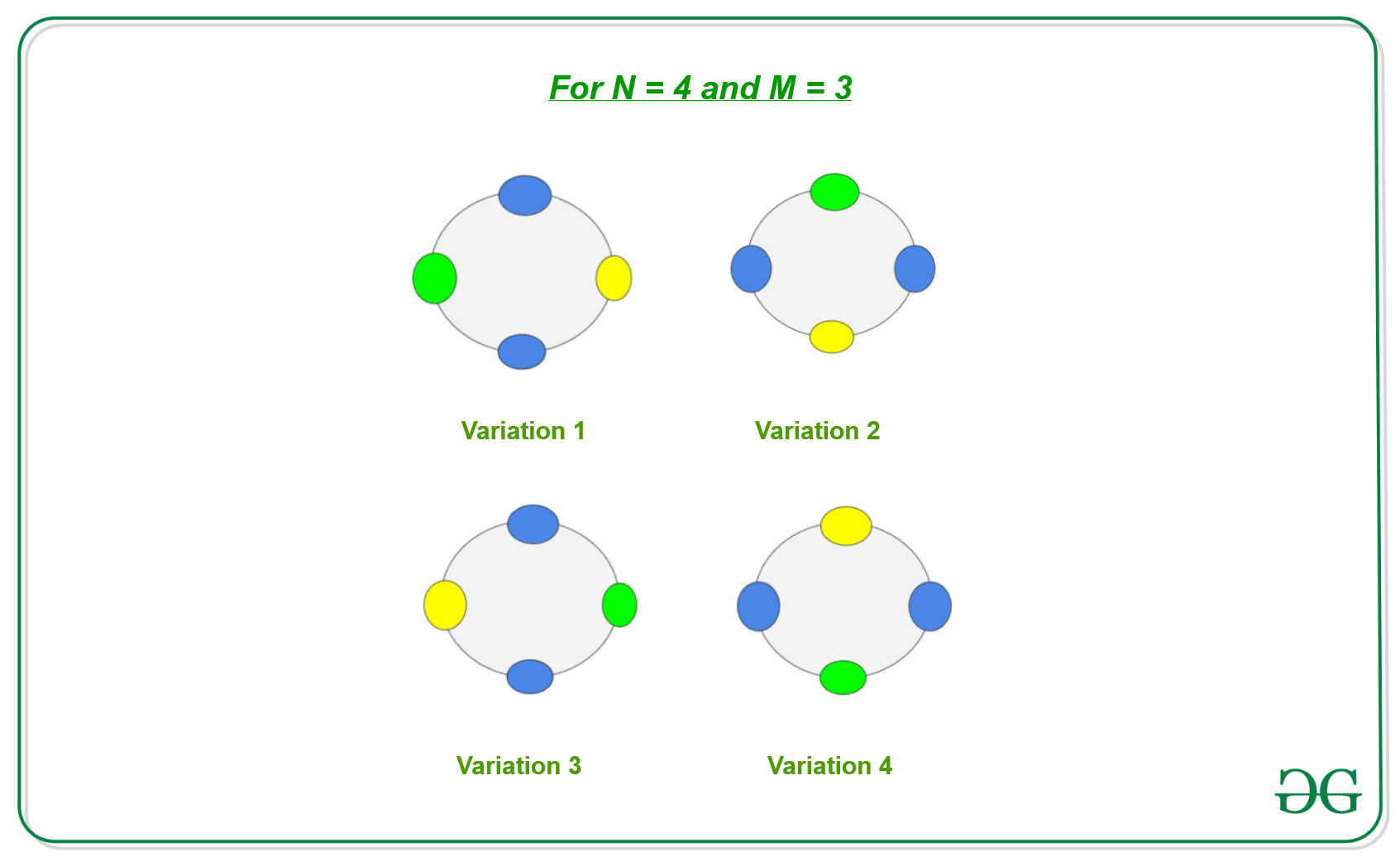
观察:有N种方法可以更改项链的位置,因为我们可以将其旋转0到N – 1次。
- 有
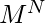 项链上色的方法。如果转数为0,则全部
项链上色的方法。如果转数为0,则全部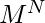 方式仍然不同。
方式仍然不同。 - 如果旋转数为1,则只有M条项链,它们在所有项链中将有所不同
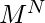 方法。
方法。 - 通常,如果转数为K ,
 项链将保持不变
项链将保持不变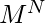 方法。
方法。
因此,对于用M种颜色着色后的N颗独特项链的总数,是每次旋转时所有独特项链的总和。它由下式给出: ![]()
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for implementing the
// Orbit counting theorem
// or Burnside's Lemma
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find result using
// Orbit counting theorem
// or Burnside's Lemma
void countDistinctWays(int N, int M)
{
int ans = 0;
// According to Burnside's Lemma
// calculate distinct ways for each
// rotation
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// Find GCD
int K = __gcd(i, N);
ans += pow(M, K);
}
// Divide By N
ans /= N;
// Print the distinct ways
cout << ans << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// N stones and M colors
int N = 4, M = 3;
// Function call
countDistinctWays(N, M);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for implementing the
// Orbit counting theorem
// or Burnside's Lemma
class GFG{
static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (a == 0)
return b;
return gcd(b % a, a);
}
// Function to find result using
// Orbit counting theorem
// or Burnside's Lemma
static void countDistinctWays(int N, int M)
{
int ans = 0;
// According to Burnside's Lemma
// calculate distinct ways for each
// rotation
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// Find GCD
int K = gcd(i, N);
ans += Math.pow(M, K);
}
// Divide By N
ans /= N;
// Print the distinct ways
System.out.print(ans);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String []args)
{
// N stones and M colors
int N = 4, M = 3;
// Function call
countDistinctWays(N, M);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# program for implementing the
// Orbit counting theorem
// or Burnside's Lemma
using System;
class GFG
{
static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (a == 0)
return b;
return gcd(b % a, a);
}
// Function to find result using
// Orbit counting theorem
// or Burnside's Lemma
static void countDistinctWays(int N, int M)
{
int ans = 0;
// According to Burnside's Lemma
// calculate distinct ways for each
// rotation
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// Find GCD
int K = gcd(i, N);
ans += (int)Math.Pow(M, K);
}
// Divide By N
ans /= N;
// Print the distinct ways
Console.Write(ans);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string []args)
{
// N stones and M colors
int N = 4, M = 3;
// Function call
countDistinctWays(N, M);
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76Javascript
输出:
24