考虑一个长度为L的管道。该管道在其中N个不同的位置上有N个水滴。每个水滴以不同的速率向管道末端移动(x = L)。当水滴与另一水滴混合时,它将假定与之混合的水滴的速度。确定从管道末端出来的水滴数。
请参考下图:
圆圈上的数字表示水滴的速度
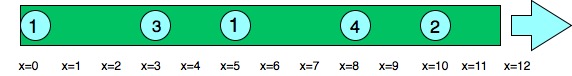
例子:
Input: length = 12, position = [10, 8, 0, 5, 3],
speed = [2, 4, 1, 1, 3]
Output: 3
Explanation:
Droplets starting at x=10 and x=8 become a droplet,
meeting each other at x=12 at time =1 sec.
The droplet starting at 0 doesn't mix with any
other droplet, so it is a drop by itself.
Droplets starting at x=5 and x=3 become a single
drop, mixing with each other at x=6 at time = 1 sec.
Note that no other droplets meet these drops before
the end of the pipe, so the answer is 3.
Refer to the figure below
Numbers on circles indicates speed of water droplets.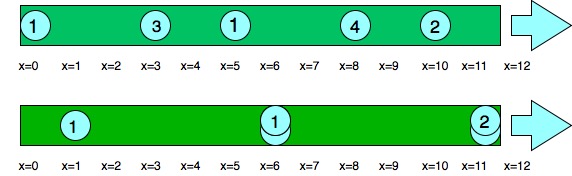
方法:
此问题使用贪婪技术。
如果满足两个条件,则一滴水将与另一滴水混合:
1.如果液滴比与其混合的液滴快,
2.如果快速下降的位置在慢速下降的后面。
我们使用成对的数组来存储位置和第i个下降到达管道末端所需的时间。然后,我们根据墨滴的位置对数组进行排序。现在我们有了一个好主意,哪些液滴在后面,哪些液滴以及到达终点所需的时间。时间越多意味着速度越慢,时间越少意味着速度越快。现在,所有较慢滴之前的滴都将与它混合。以及在较慢滴之后的所有滴与下一个较慢滴的混合,依此类推。
例如,如果到达终点的时间是:12、3、7、8、1(根据位置排序)
0滴最慢,不会与下一个滴混合
第一滴比第二滴快,因此它们将混合,第二滴比第三滴快,因此所有三个将混合在一起。他们不能与第四滴混合,因为这样更快。
局部最大值+残基数(最后一个局部最大值之后的液滴数)=液滴总数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the number
// of the drops that come out of the
// pipe
int drops(int length, int position[],
int speed[], int n)
{
// stores position and time
// taken by a single
// drop to reach the end as a pair
vector > m(n);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// calculates distance needs to be
// covered by the ith drop
int p = length - position[i];
// inserts initial position of the
// ith drop to the pair
m[i].first = position[i];
// inserts time taken by ith
// drop to reach
// the end to the pair
m[i].second = p * 1.0 / speed[i];
}
// sorts the pair according to increasing
// order of their positions
sort(m.begin(), m.end());
int k = 0; // counter for no of final drops
int curr_max = m[n-1].second;
// we traverse the array demo
// right to left
// to determine the slower drop
for (i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
// checks for next slower drop
if (m[i].second > curr_max)
{
k++;
curr_max=m[i].second;
}
}
// calculating residual
// drops in the pipe
k++;
return k;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// length of pipe
int length = 12;
// position of droplets
int position[] = { 10, 8, 0, 5, 3 };
// speed of each droplets
int speed[] = { 2, 4, 1, 1, 3 };
int n = sizeof(speed)/sizeof(speed[0]);
cout << drops(length, position, speed, n);
return 0;
} Python3
# Function to find the number
# of the drops that come out of the
# pipe
def drops(length, position, speed, n):
# Stores position and time
# taken by a single drop to
# reach the end as a pair
m = []
for i in range(n):
# Calculates distance needs to be
# covered by the ith drop
p = length - position[i]
# Inserts initial position of the
# ith drop to the pair
# inserts time taken by ith
# drop to reach
# the end to the pair
m.append([position[i], (p * 1.0) / speed[i]])
# Sorts the pair according to increasing
# order of their positions
m.sort()
# Counter for no of final drops
k = 0
curr_max = m[n - 1][1]
# We traverse the array demo
# right to left
# to determine the slower drop
for i in range(n - 2, -1, -1):
# Checks for next slower drop
if (m[i][1] > curr_max):
k += 1
curr_max = m[i][1]
# Calculating residual
# drops in the pipe
k += 1
return k
# Driver Code
# Length of pipe
length = 12
# Position of droplets
position = [ 10, 8, 0, 5, 3 ]
# Speed of each droplets
speed = [ 2, 4, 1, 1, 3 ]
n = len(speed)
print(drops(length, position, speed, n))
# This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Function to find the number
// of the drops that come out of the
// pipe
static int drops(int length, int[] position,
int[] speed, int n)
{
// stores position and time
// taken by a single
// drop to reach the end as a pair
List> m = new List>();
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// calculates distance needs to be
// covered by the ith drop
int p = length - position[i];
// inserts initial position of the
// ith drop to the pair
// inserts time taken by ith
// drop to reach
// the end to the pair
m.Add(new Tuple(position[i], p * 1.0 / speed[i]));
}
// sorts the pair according to increasing
// order of their positions
m.Sort();
int k = 0; // counter for no of final drops
int curr_max = (int)m[n - 1].Item2;
// we traverse the array demo
// right to left
// to determine the slower drop
for (i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
// checks for next slower drop
if (m[i].Item2 > curr_max)
{
k++;
curr_max = (int)m[i].Item2;
}
}
// calculating residual
// drops in the pipe
k++;
return k;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
// length of pipe
int length = 12;
// position of droplets
int[] position = { 10, 8, 0, 5, 3 };
// speed of each droplets
int[] speed = { 2, 4, 1, 1, 3 };
int n = speed.Length;
Console.WriteLine(drops(length, position, speed, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019 输出
3如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。