给定一个无向图,任务是找到每个连接组件的大小并打印连接组件的唯一大小的数量
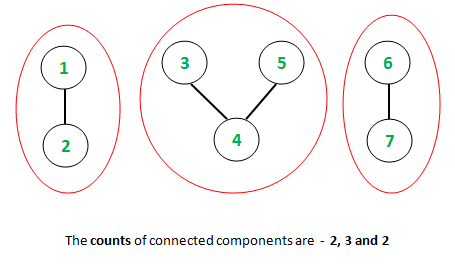
如上所述,与连接的组件关联的计数(连接的组件的大小)为2、3和2。现在,组件的唯一计数为2和3。因此,预期结果为Count = 2
例子:
Input: N = 7
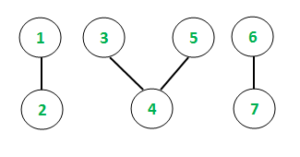
Output: 1 2 Count = 2
3 4 5 Count = 3
6 7 Count = 2
Unique Counts of connected components: 2
Input: N = 10
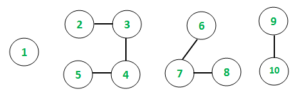
Output: 1 Count = 1
2 3 4 5 Count = 4
6 7 8 Count = 3
9 10 Count = 2
Unique Counts of connected components: 4
先决条件:深度优先搜索
方法:
基本思想是利用“深度优先搜索”遍历方法来跟踪无向图中的连接组件。 STL容器集用于存储所有此类组件的唯一计数,因为已知集合具有以排序方式存储唯一元素的属性。最后,提取Set的大小将为我们提供必要的结果。分步实现如下:
- 初始化一个哈希容器(Set),以存储所连接组件的唯一计数。
- 递归调用深度优先搜索遍历。
- 对于访问的每个顶点,将计数存储在设置的容器中。
- Set的最终大小是必需的结果。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to find unique count of
// connected components
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to add edge in the garph
void add_edge(int u, int v, vector graph[])
{
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
// Function to traverse the undirected graph
// using DFS algorithm and keep a track of
// individual lengths of connected chains
void depthFirst(int v, vector graph[],
vector& visited, int& ans)
{
// Marking the visited vertex as true
visited[v] = true;
cout << v << " ";
// Incrementing the count of
// connected chain length
ans++;
for (auto i : graph[v]) {
if (visited[i] == false) {
// Recursive call to the DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i, graph, visited, ans);
}
}
}
// Function to initialize the graph
// and display the result
void UniqueConnectedComponent(int n,
vector graph[])
{
// Initializing boolean visited array
// to mark visited vertices
vector visited(n + 1, false);
// Initializing a Set container
unordered_set result;
// Following loop invokes DFS algorithm
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (visited[i] == false) {
// ans variable stores the
// individual counts
int ans = 0;
// DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i, graph, visited, ans);
// Inserting the counts of connected
// components in set
result.insert(ans);
cout << "Count = " << ans << "\n";
}
}
cout << "Unique Counts of "
<< "connected components: ";
// The size of the Set container
// gives the desired result
cout << result.size() << "\n";
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Number of nodes
int n = 7;
// Create graph
vector graph[n + 1];
// Constructing the undirected graph
add_edge(1, 2, graph);
add_edge(3, 4, graph);
add_edge(3, 5, graph);
add_edge(6, 7, graph);
// Function call
UniqueConnectedComponent(n, graph);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find
// unique count of
// connected components
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to add edge in the garph
static void add_edge(int u, int v,
Vector graph[])
{
graph[u].add(v);
graph[v].add(u);
}
// Function to traverse the undirected graph
// using DFS algorithm and keep a track of
// individual lengths of connected chains
static int depthFirst(int v,
Vector graph[],
Vector visited,
int ans)
{
// Marking the visited vertex as true
visited.add(v, true);
System.out.print(v + " ");
// Incrementing the count of
// connected chain length
ans++;
for (int i : graph[v])
{
if (visited.get(i) == false)
{
// Recursive call to the DFS algorithm
ans = depthFirst(i, graph, visited, ans);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Function to initialize the graph
// and display the result
static void UniqueConnectedComponent(int n,
Vector graph[])
{
// Initializing boolean visited array
// to mark visited vertices
Vector visited = new Vector<>();
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
visited.add(false);
// Initializing a Set container
HashSet result = new HashSet<>();
// Following loop invokes DFS algorithm
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (visited.get(i) == false)
{
// ans variable stores the
// individual counts
int ans = 0;
// DFS algorithm
ans = depthFirst(i, graph, visited, ans);
// Inserting the counts of connected
// components in set
result.add(ans);
System.out.print("Count = " +
ans + "\n");
}
}
System.out.print("Unique Counts of " +
"connected components: ");
// The size of the Set container
// gives the desired result
System.out.print(result.size() + "\n");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Number of nodes
int n = 7;
// Create graph
Vector []graph = new Vector[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++)
graph[i] = new Vector();
// Constructing the undirected graph
add_edge(1, 2, graph);
add_edge(3, 4, graph);
add_edge(3, 5, graph);
add_edge(6, 7, graph);
// Function call
UniqueConnectedComponent(n, graph);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh Python3
# Python3 program to find unique count of
# connected components
graph = [[] for i in range(100 + 1)]
visited = [False] * (100 + 1)
ans = 0
# Function to add edge in the garph
def add_edge(u, v):
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
# Function to traverse the undirected graph
# using DFS algorithm and keep a track of
# individual lengths of connected chains
def depthFirst(v):
global ans
# Marking the visited vertex as true
visited[v] = True
print(v, end = " ")
#print(ans,end="-")
# Incrementing the count of
# connected chain length
ans += 1
for i in graph[v]:
if (visited[i] == False):
# Recursive call to the
# DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i)
# Function to initialize the graph
# and display the result
def UniqueConnectedComponent(n):
global ans
# Initializing boolean visited array
# to mark visited vertices
# Initializing a Set container
result = {}
# Following loop invokes DFS algorithm
for i in range(1, n + 1):
if (visited[i] == False):
# ans variable stores the
# individual counts
# ans = 0
# DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i)
# Inserting the counts of connected
# components in set
result[ans] = 1
print("Count = ", ans)
ans = 0
print("Unique Counts of connected "
"components: ", end = "")
# The size of the Set container
# gives the desired result
print(len(result))
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Number of nodes
n = 7
# Create graph
# Constructing the undirected graph
add_edge(1, 2)
add_edge(3, 4)
add_edge(3, 5)
add_edge(6, 7)
# Function call
UniqueConnectedComponent(n)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# program to find
// unique count of
// connected components
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Function to add edge in the garph
static void add_edge(int u, int v,
List []graph)
{
graph[u].Add(v);
graph[v].Add(u);
}
// Function to traverse the undirected graph
// using DFS algorithm and keep a track of
// individual lengths of connected chains
static int depthFirst(int v,
List []graph,
List visited,
int ans)
{
// Marking the visited
// vertex as true
visited.Insert(v, true);
Console.Write(v + " ");
// Incrementing the count of
// connected chain length
ans++;
foreach (int i in graph[v])
{
if (visited[i] == false)
{
// Recursive call to
// the DFS algorithm
ans = depthFirst(i, graph,
visited, ans);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Function to initialize the graph
// and display the result
static void UniqueConnectedComponent(int n,
List []graph)
{
// Initializing bool visited array
// to mark visited vertices
List visited = new List();
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
visited.Add(false);
// Initializing a Set container
HashSet result = new HashSet();
// Following loop invokes DFS algorithm
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (visited[i] == false)
{
// ans variable stores the
// individual counts
int ans = 0;
// DFS algorithm
ans = depthFirst(i, graph, visited, ans);
// Inserting the counts of connected
// components in set
result.Add(ans);
Console.Write("Count = " +
ans + "\n");
}
}
Console.Write("Unique Counts of " +
"connected components: ");
// The size of the Set container
// gives the desired result
Console.Write(result.Count + "\n");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Number of nodes
int n = 7;
// Create graph
List []graph = new List[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < graph.Length; i++)
graph[i] = new List();
// Constructing the undirected graph
add_edge(1, 2, graph);
add_edge(3, 4, graph);
add_edge(3, 5, graph);
add_edge(6, 7, graph);
// Function call
UniqueConnectedComponent(n, graph);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput 输出:
1 2 Count = 2
3 4 5 Count = 3
6 7 Count = 2
Unique Counts of connected components: 2
时间复杂度:
从以上实现中可以明显看出,使用深度优先搜索算法遍历了该图。使用Set容器存储单个计数,其中插入操作花费O(1)时间。总体复杂度仅基于DFS算法递归运行所花费的时间。因此,程序的时间复杂度为O(E + V) ,其中E是边的数量,V是图形的顶点数量。
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。