问题陈述:设计一个确定的有限自动机,以接受输入{a,b}上三个a和三个b的排列
Input: S = “aaabbb”
Output: Accepted
Explanation:
The input has three a and three b.
Input: S = “abababa”
Output: Accepted
Explanation:
The input has three a and three b.
要设计一个DFA,我们需要通过字符检查输入的字符。这些是设计DFA时应牢记的几个步骤。
- 考虑所有可以接受的所有可能的输入(例如,在本例中为aaabbb,bbbaaa,ababab,abaabb…等)。
- 创建一个初始过渡状态。
- 在每个输入字母上过渡到其他过渡状态。
- 达到最终状态,以便在每个步骤中使用的语言都被接受(例如,在此示例中,a和b的数目相等)。
设计步骤:
步骤1 :创建一个初始状态“ A”,由->表示。
第2步:考虑可能通过转换而出现的字符串aaaabbb或bbbaaa,
- 输入“ a”从状态“ A”到状态“ B”的过渡
- 输入“ a”从状态“ B”到状态“ C”的过渡
- 输入“ a”从状态“ C”到状态“ D”的过渡
- 输入“ a”从状态“ D”到无效状态“ Q2”的过渡
- 输入“ b”从状态“ D”到状态“ E”的过渡
- 输入“ b”从状态“ E”到状态“ F”的过渡
- 输入“ b”从状态“ F”到状态“ G”的过渡
- 输入“ b”从状态“ G”到无效状态“ Q2”的过渡
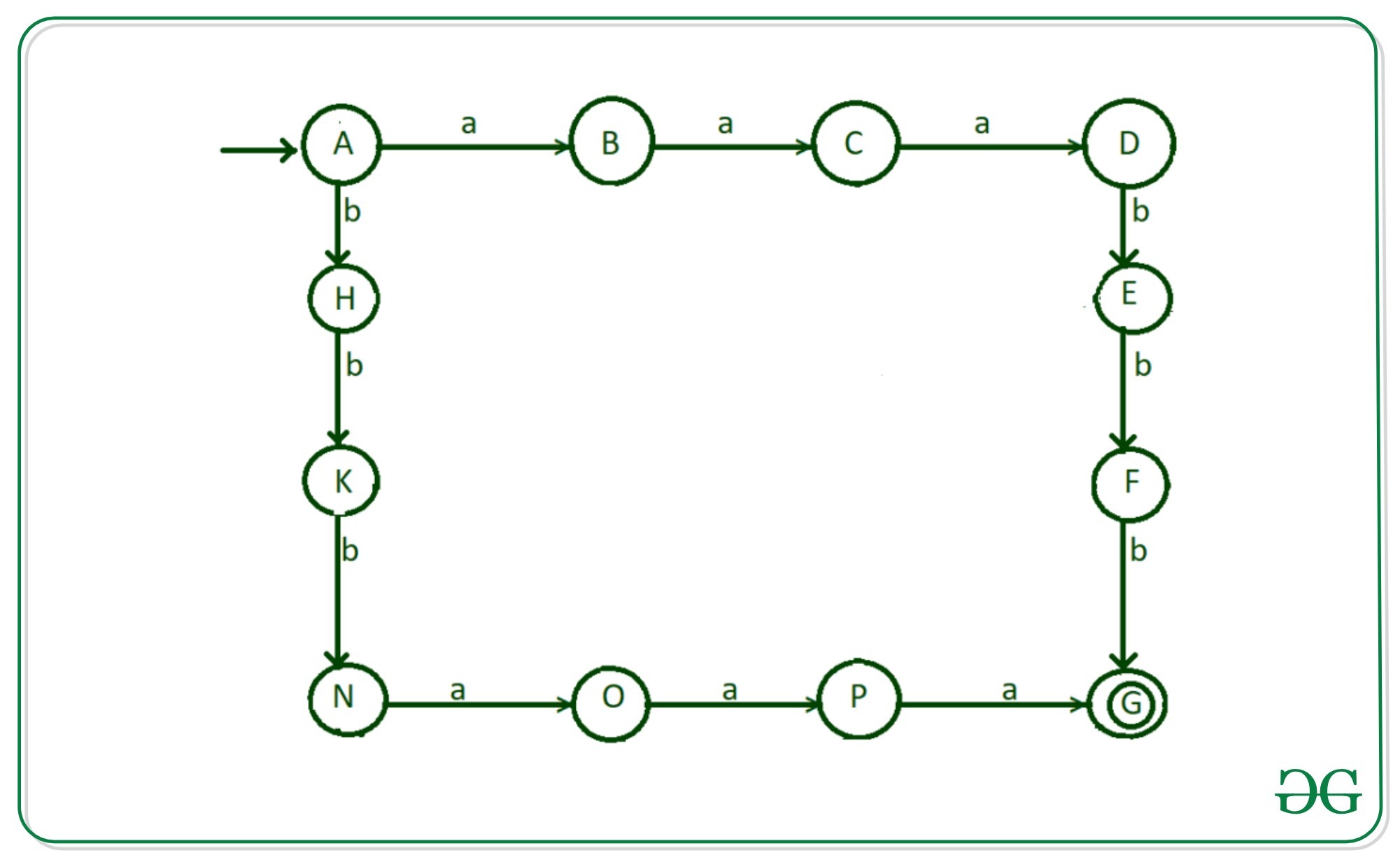
第3步:现在研究b出现在两个a之后的可能性,例如aababb,aabbab。
- “ b”从状态“ C”到状态“ J”的过渡
- “ a”从状态“ J”到状态“ E”的过渡
- “ b”从状态“ J”到状态“ M”的过渡
- “ a”从状态“ M”到状态“ F”的过渡
- “ b”从状态“ M”到状态“ P”的过渡
过渡如图所示。
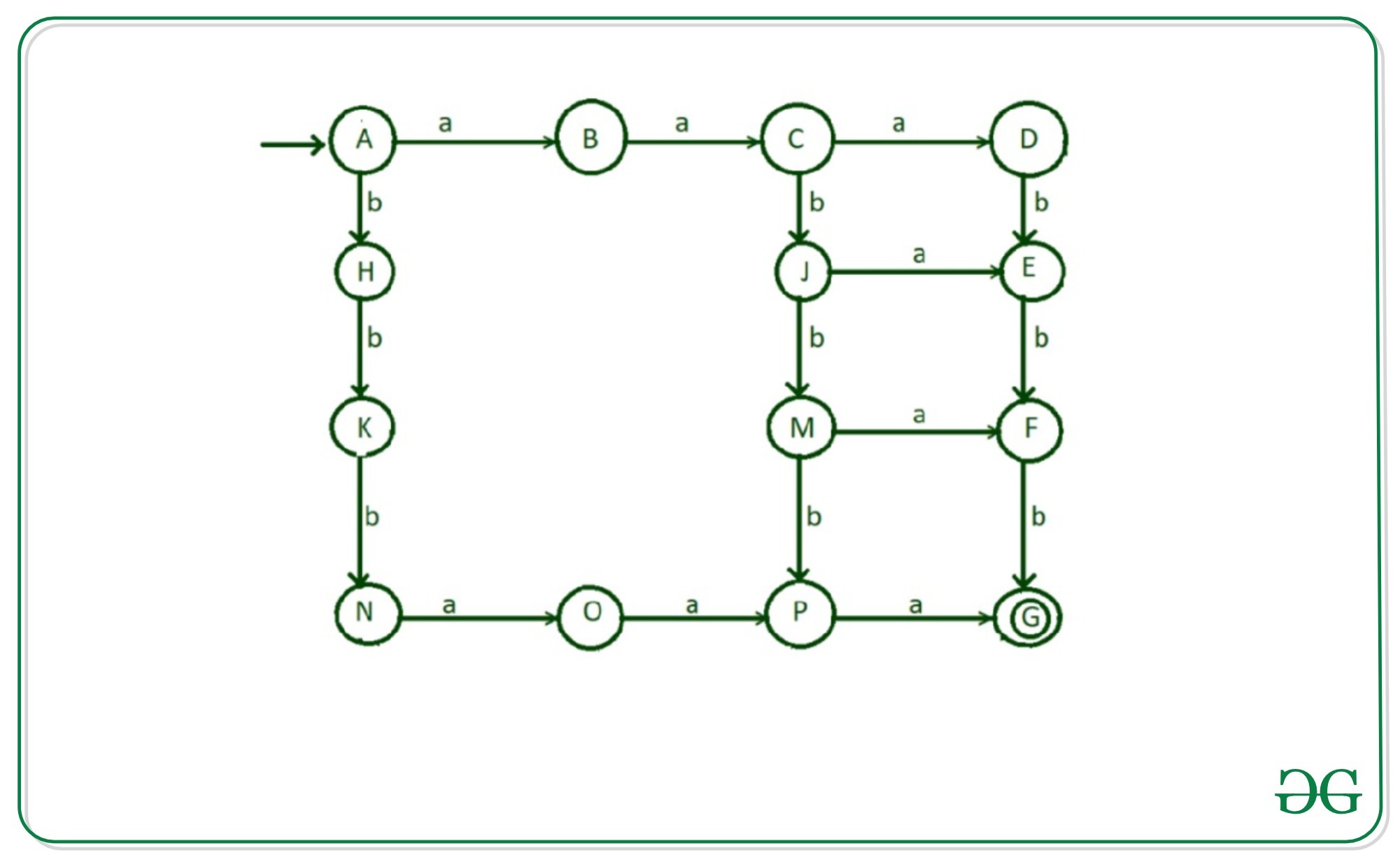
步骤4:现在考虑以“ aba”开始,然后满足给定语言条件的可能性。为此,要进行以下转换:
- “ b”从状态“ B”到状态“ I”的过渡
- “ a”从状态“ I”到状态“ J”的过渡
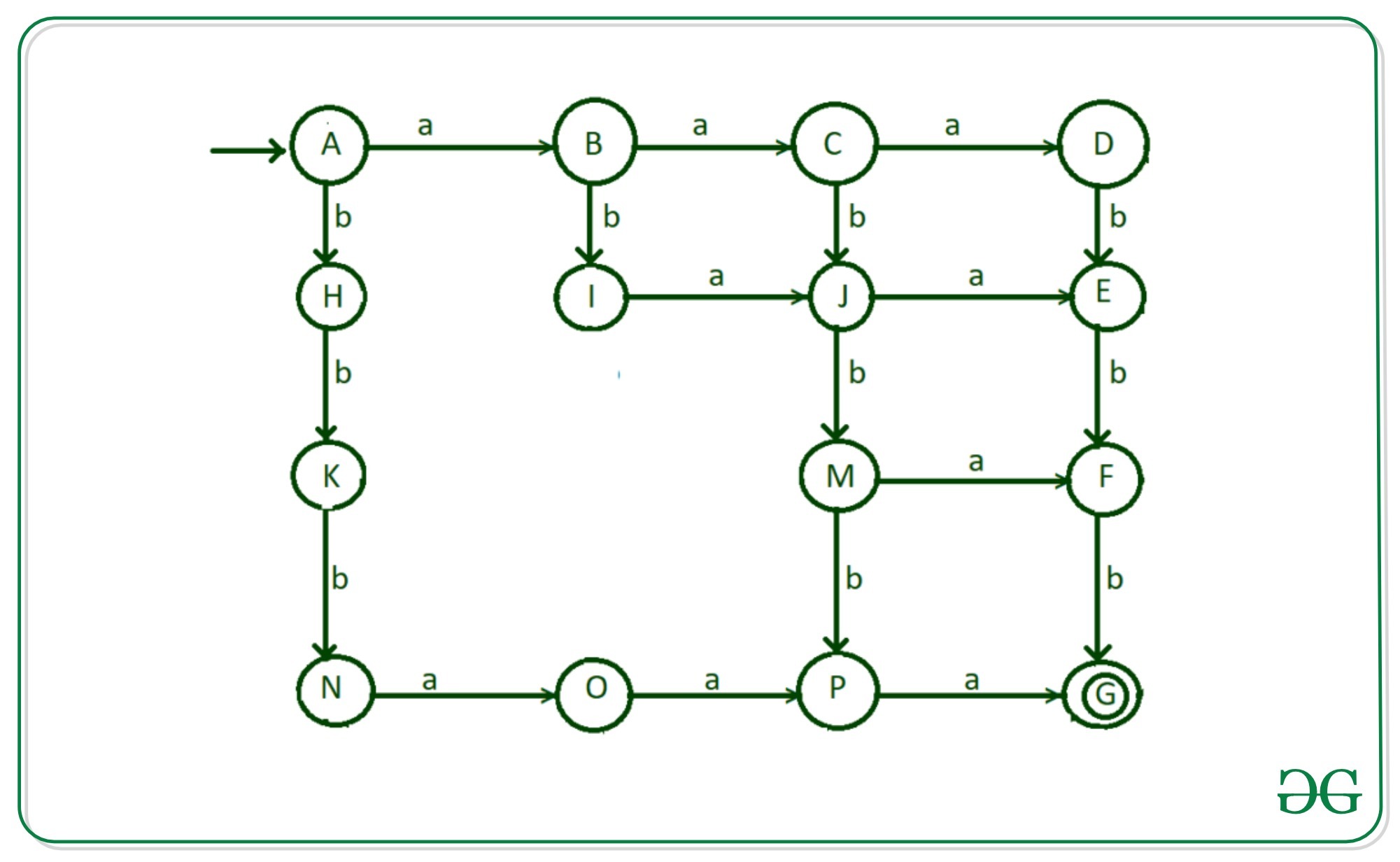
步骤5:现在考虑以“ abb”开头,然后满足给定语言条件的可能性。为此,要进行以下转换:
- “ b”从状态“ I”到状态“ L”的过渡
- “ a”从状态“ L”到状态“ M”的转换
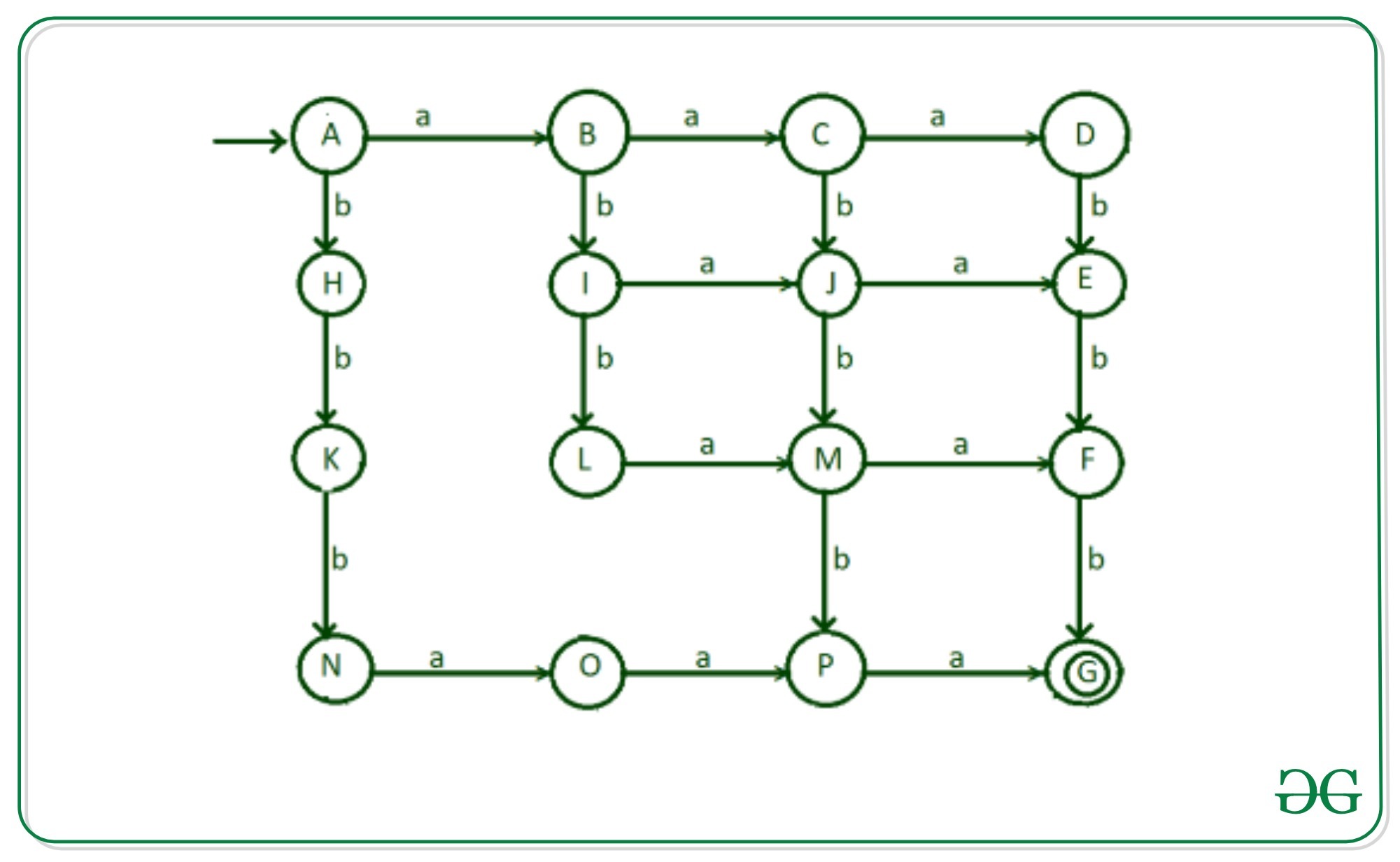
步骤6:现在有一种可能,在读取一个“ a”之后,它会读取所有3个b,然后通过读取剩余的2个a来结束执行。对于“ b”从状态“ L”到“ O”的转换。
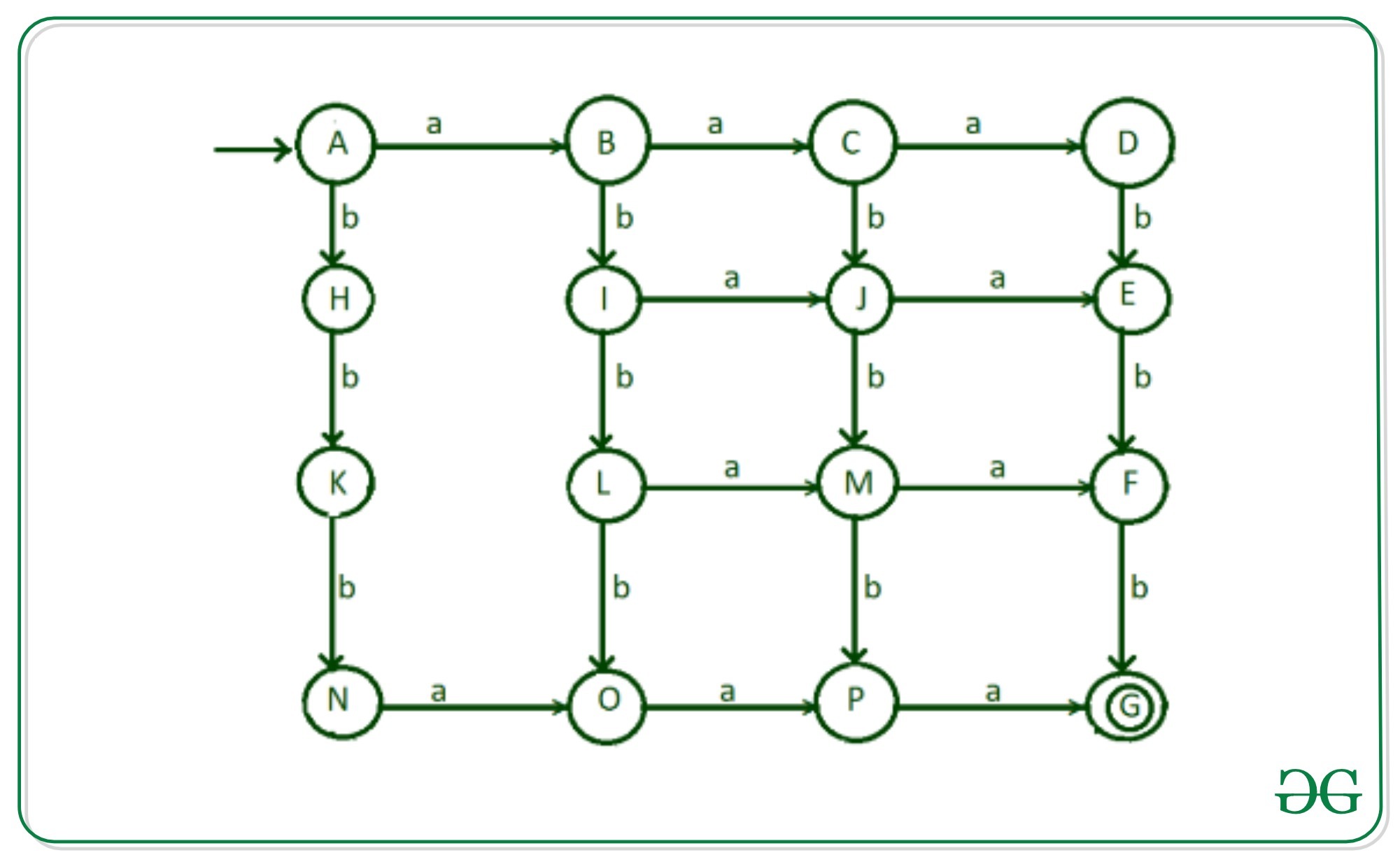
步骤7:有可能在读取一个’b’之后读取了’a’,然后读取了’a’和’b’的任意组合,因此字符串包含3个a和3个b。 ‘从状态“ H”到状态“ I”完成。
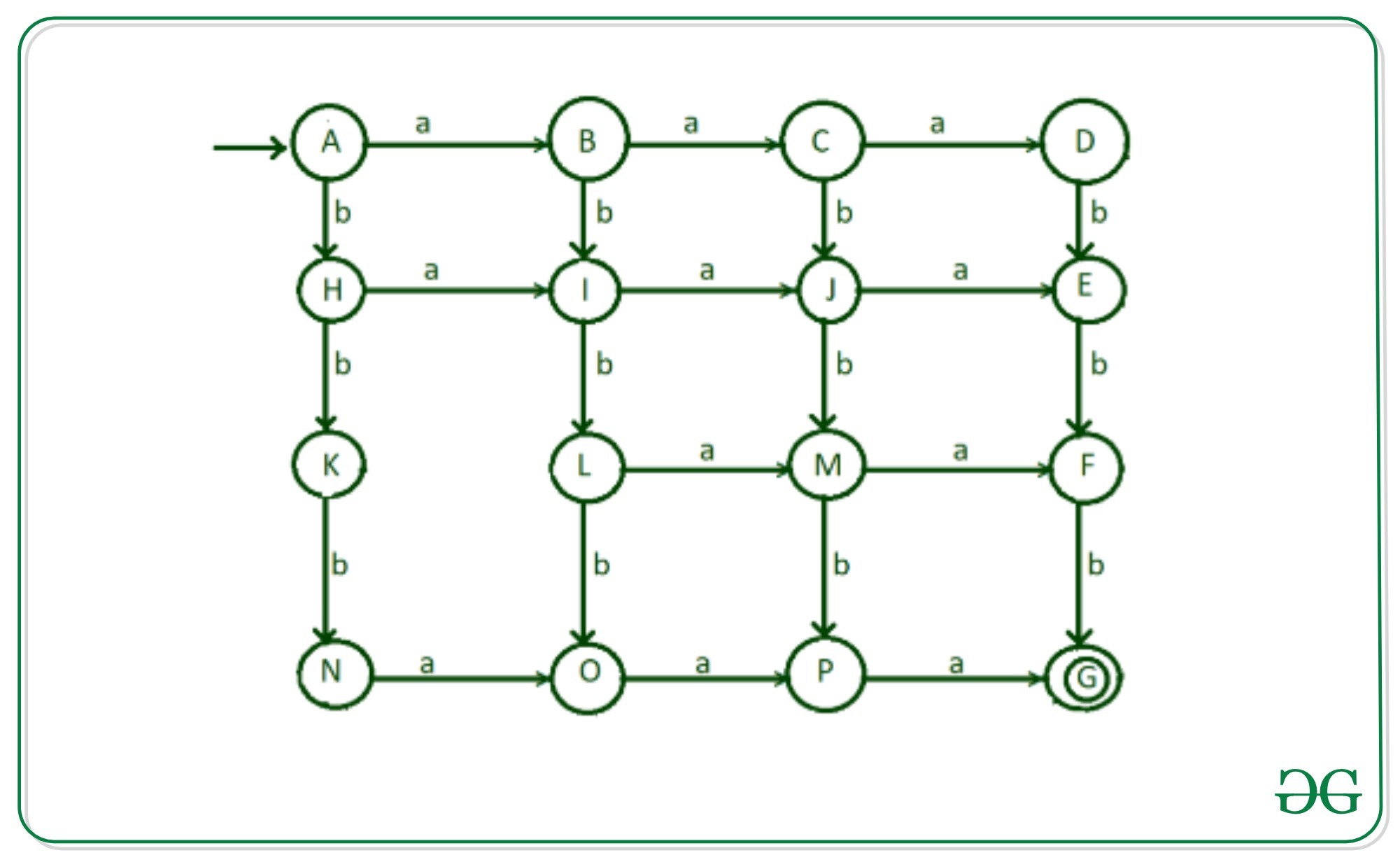
步骤8:现在,考虑字符串以两个b开头,然后对字符串的任何组合进行搜索以获得所需的结果,我们将“ a”从凝视“ K”转换为状态“ L”。
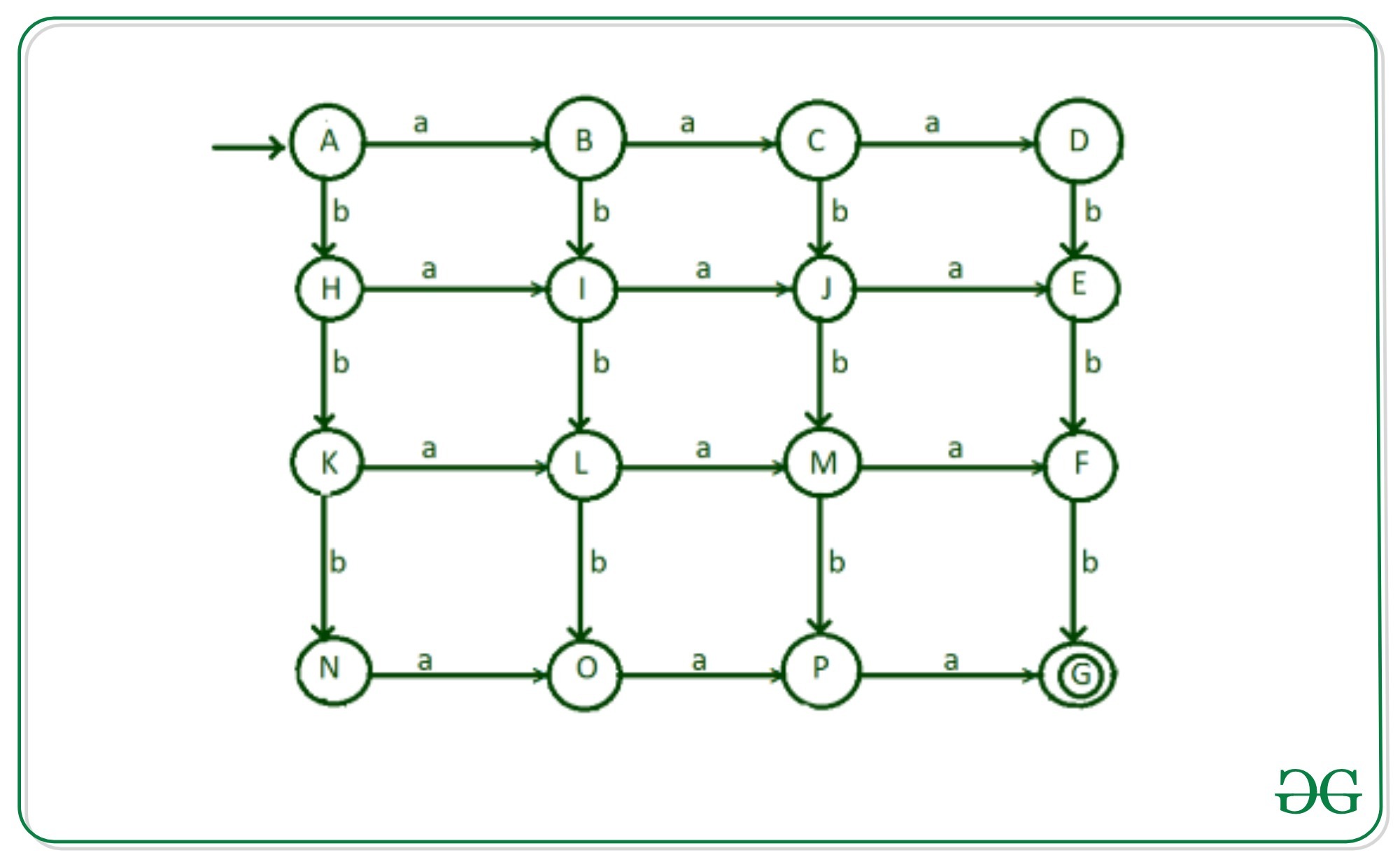
步骤9:现在输入状态D,E,F,G的字母’a’和状态G,N,O,P的’b’进行转换。剩余的过渡将变为无效状态“ Q1”和“ Q2”。
- 输入“ a”从状态“ D”到无效状态“ Q1”的过渡
- 输入“ a”从状态“ E”到无效状态“ Q1”的过渡
- 输入“ a”从状态“ F”到无效状态“ Q1”的过渡
- 输入“ a”从状态“ G”到无效状态“ Q1”的过渡
- 输入“ b”从状态“ G”到无效状态“ Q2”的过渡
- 输入“ b”从状态“ N”到无效状态“ Q2”的过渡
- 输入“ b”从状态“ O”到无效状态“ Q2”的过渡
- 输入“ b”从状态“ P”到无效状态“ Q2”的过渡

以上DFA的转换表
| STATES | INPUT (a) | INPUT (b) |
|---|---|---|
| —> A (initial state) | B | H |
| B | C | I |
| C | D | J |
| D | Q2 (dead state) | E |
| E | Q2 (dead state) | F |
| F | Q2 (dead state) | G*(final state) |
| G* (final state) | Q2 (dead state) | Q1 (dead state) |
| H | I | K |
| I | J | L |
| J | E | M |
| K | L | N |
| L | M | O |
| M | F | P |
| N | O | Q1 (dead state) |
| O | P | Q1 (dead state) |
| P | G* (final state) | Q1 (dead state) |
以下是DFA的实施:
Java
// Java implementation of the
// DFA of permutation of three
// a's and three b's
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// State A
static void stateA(String n)
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateB(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
{
stateH(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State B
static void stateB(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateC(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateI(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State C
static void stateC(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateD(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateJ(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State D
static void stateD(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateE(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State E
static void stateE(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateF(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State F
static void stateF(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateQ2(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateG(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State G
static void stateG(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateQ2(n);
}
}
// State H
static void stateH(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateI(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateK(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State I
static void stateI(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateJ(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateL(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State J
static void stateJ(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateE(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateM(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State K
static void stateK(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateL(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateN(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State L
static void stateL(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateM(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateO(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State M
static void stateM(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateF(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateP(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State N
static void stateN(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
if (n.charAt(0) =='a')
stateO(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateQ1(n);
}
// State Q
static void stateO(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateP(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateQ1(n);
}
}
// State P
static void stateP(String n)
{
if (n.length() == 0)
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if (n.charAt(0) == 'a')
stateG(n.substring(1));
else if (n.charAt(0) == 'b')
stateQ1(n.substring(1));
}
}
// State Q1
static void stateQ1(String n)
{
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
}
// State Q2
static void stateQ2(String n)
{
System.out.print("String Not Accepted");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Take String input
String n = "abaabb";
// Call stateA
// to check the input
stateA(n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76Python3
# Python3 implementation of the
# DFA of permutation of three
# a's and three b's
# State A
def stateA(n):
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateB(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateH(n[1:])
# State B
def stateB(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateC(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateI(n[1:])
# State C
def stateC(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateD(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateJ(n[1:])
# State D
def stateD(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateQ2(n)
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateE(n[1:])
# State E
def stateE(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateQ2(n)
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateF(n[1:])
# State F
def stateF(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateQ2(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateG(n[1:])
# State G
def stateG(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateQ2(n)
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateQ2(n)
# State H
def stateH(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateI(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateK(n[1:])
# State I
def stateI(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateJ(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateL(n[1:])
# State J
def stateJ(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateE(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateM(n[1:])
# State K
def stateK(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateL(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateN(n[1:])
# State L
def stateL(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateM(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateO(n[1:])
# State M
def stateM(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateF(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateP(n[1:])
# State N
def stateN(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateO(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateQ1(n)
# State Q
def stateO(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateP(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateQ1(n)
# State P
def stateP(n):
if(len(n)== 0):
print("String Not Accepted")
else:
if(n[0]=='a'):
stateG(n[1:])
elif (n[0]=='b'):
stateQ1(n[1:])
# State Q1
def stateQ1(n):
print("String Not Accepted")
# State Q2
def stateQ2(n):
print("String Not Accepted")
# take string input
n = "abaabb"
# call stateA
# to check the input
stateA(n)C#
// C# implementation of the
// DFA of permutation of three
// a's and three b's
using System;
using System.Collections;
class GFG{
// State A
static void stateA(string n)
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateB(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
{
stateH(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State B
static void stateB(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateC(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateI(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State C
static void stateC(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateD(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateJ(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State D
static void stateD(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateE(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State E
static void stateE(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateF(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State F
static void stateF(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateQ2(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateG(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State G
static void stateG(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateQ2(n);
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateQ2(n);
}
}
// State H
static void stateH(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateI(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateK(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State I
static void stateI(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateJ(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateL(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State J
static void stateJ(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateE(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateM(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State K
static void stateK(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateL(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateN(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State L
static void stateL(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateM(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateO(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State M
static void stateM(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateF(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateP(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State N
static void stateN(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
if(n[0] =='a')
stateO(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateQ1(n);
}
// State Q
static void stateO(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateP(n.Substring(1));
else if(n[0] == 'b')
stateQ1(n);
}
}
// State P
static void stateP(string n)
{
if(n.Length == 0)
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
else
{
if(n[0] == 'a')
stateG(n.Substring(1));
else if (n[0] == 'b')
stateQ1(n.Substring(1));
}
}
// State Q1
static void stateQ1(string n)
{
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
}
// State Q2
static void stateQ2(string n)
{
Console.Write("String Not Accepted");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main (string[] args)
{
// Take string input
string n = "abaabb";
// Call stateA
// to check the input
stateA(n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56String Accepted如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。