给定一个数组arr[]表示一个 Generic(N-ary) 树。任务是用节点的深度(级别)替换节点数据。假设根的级别为 0。
Array Representation: The N-ary tree is serialized in the array arr[] using level order traversal as described below:
- The input is given as a level order traversal of N-ary Tree.
- The first element of the array arr[] is the root node.
- Then, followed by a number N, which denotes the number of children of the previous node. Value zero denotes Null Node.
例子:
Input: arr[] = { 10, 3, 20, 30, 40, 2, 40, 50, 0, 0, 0, 0 }
Below is the N-ary Tree of the above array level order traversal: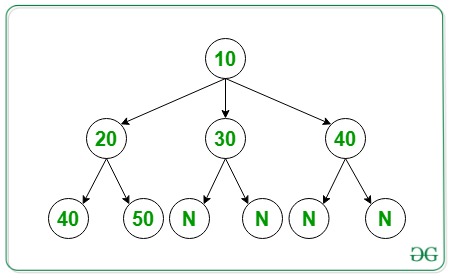
Output:
Below is the representation of the above output: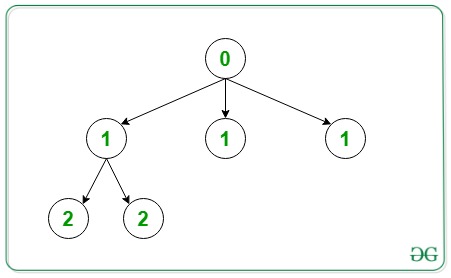
Input: arr[] = {1, 3, 2, 3, 4, 2, 5, 6, 0, 0, 2, 8, 9}
Below is the N-ary Tree of the above array level order traversal: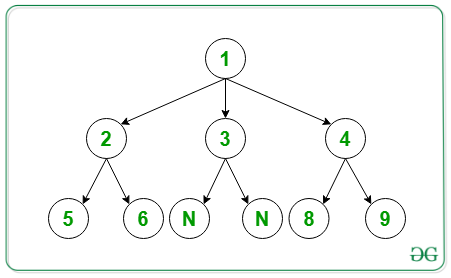
Output:
Below is the representation of the above output: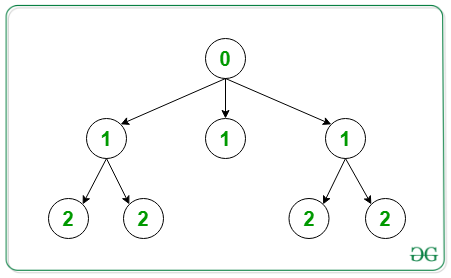
方法:
- 从根开始遍历树。
- 在遍历节点的传递深度作为参数时。
- 通过将其作为 0 传递给 root 和 (1 + 当前级别) 传递给孩子来跟踪深度。
下面是上述方法的实现:
// C++ program to implement node with
// it's depth value
#include
using namespace std;
// Treenode class using template
template
class TreeNode {
public:
// To store node value
T data;
// Pointer to TreeNode to store
// the child node
vector*> children;
// Constructor to assign data
// to node
TreeNode(T data)
{
this->data = data;
}
// Destructors to delete a node
~TreeNode()
{
for (int i = 0;
i < children.size(); i++) {
delete children[i];
}
}
};
// Function to take input level wise
// i.e., in level order traversal
TreeNode* takeInputLevelWise(int arr[])
{
int idx = 1;
// Input root
int rootData = arr[0];
// Initialize tree with a root node
TreeNode* root
= new TreeNode(rootData);
// Intialise queue for appending
// node as a child of parent in
// N-ary tree
queue*> pendingNodes;
// Push the root node in queue
pendingNodes.push(root);
// While queue is not empty append
// child to the root
while (pendingNodes.size() != 0) {
// Take the first node
TreeNode* front
= pendingNodes.front();
pendingNodes.pop();
// Input number of child
int numChild = arr[idx];
idx++;
for (int i = 0; i < numChild; i++) {
int childData = arr[idx];
idx++;
// Make child Node
TreeNode* child
= new TreeNode(childData);
// Append child node to
// it's parent
front->children.push_back(child);
pendingNodes.push(child);
}
}
return root;
}
// Function to print each node data
// in level order
void printLevelATNewLine(TreeNode* root)
{
queue*> q;
q.push(root);
q.push(NULL);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* first = q.front();
q.pop();
if (first == NULL) {
if (q.empty()) {
break;
}
cout << endl;
q.push(NULL);
continue;
}
cout << first->data << " ";
for (int i = 0;
i < first->children.size(); i++) {
q.push(first->children[i]);
}
}
}
// Helper function to replace the
// node data with their level value
void helper(TreeNode* root,
int depth)
{
// Replace the node data with
// it's depth
root->data = depth;
for (int i = 0;
i < root->children.size(); i++) {
helper(root->children[i], depth + 1);
}
}
// Function to replace with depth
void replaceWithDepthValue(TreeNode* root)
{
helper(root, 0);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given level order traversal in
// the array arr[]
int arr[] = { 10, 3, 20, 30, 40, 2,
40, 50, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
// Intialise Tree
TreeNode* root;
root = takeInputLevelWise(arr);
// Function call to replace with
// depth value
replaceWithDepthValue(root);
// Function call to print
// in level order
printLevelATNewLine(root);
return 0;
}
输出:
0
1 1 1
2 2
时间复杂度: O(N),其中 N 是 Tree 中的节点数。
辅助空间: O(N),其中 N 是 Tree 中的节点数。
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live