通过将 N-ary Tree 转换为以 K 为根节点的邻接表表示的级别顺序遍历
给定 N 叉树的根节点和整数K ,任务是将给定树转换为邻接表表示,并打印考虑顶点K作为根节点的级别顺序遍历。
例子:
Input: Tree in the image below, K = 5
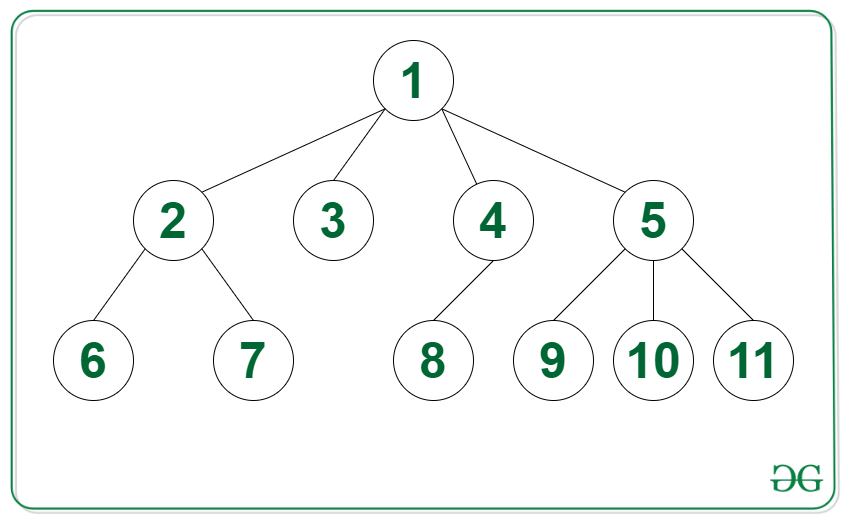
Output:
5
1 9 10 11
2 3 4
6 7 8
Input: Tree in the image below, K = 5
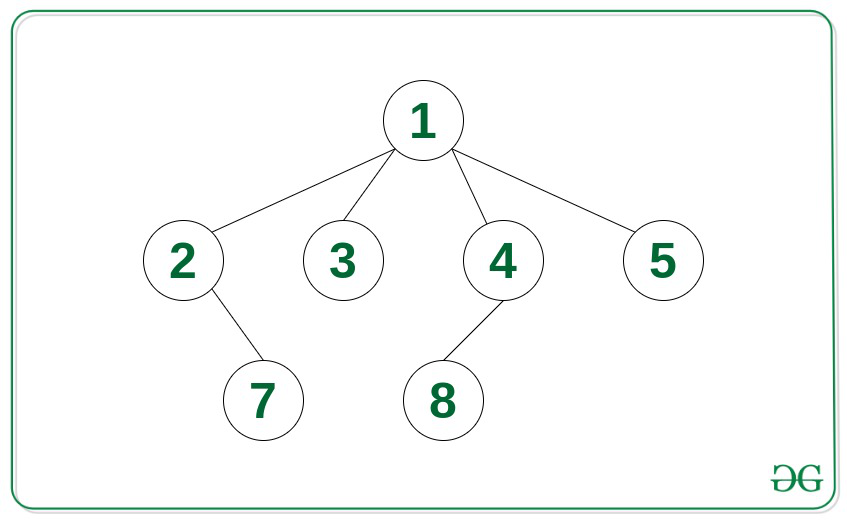
Output:
5
1
2 3 4
7 8
方法:给定的问题可以通过在N-ary树上使用DFS Traversal并根据邻接表表示将所有边的关系存储到邻接表中来解决。创建的邻接表可用于打印以K为根节点的 Level Order Traversal。这可以使用本文中讨论的 BFS 遍历来完成。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// A binary tree node
struct Node {
int data;
vector child;
};
// Function to create a new tree node
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = key;
return temp;
}
// Adjacency list to store the Tree
vector > adj;
// Function to perform the DFS traversal
// of the N-ary tree using the given
// pointer to the root node of the tree
void DFS(struct Node* node)
{
// Traverse all child of node
for (auto x : node->child) {
if (x != NULL) {
// Insert the pair of vertices
// into the adjacency list
adj[node->data].push_back(x->data);
adj[x->data].push_back(node->data);
// Recursive call for DFS on x
DFS(x);
}
}
}
// Function to print the level order
// traversal of the given tree with
// s as root node
void levelOrderTrav(int s, int N)
{
// Create a queue for Level
// Order Traversal
queue q;
// Stores if the current
// node is visited
vector visited(N);
q.push(s);
// -1 marks the end of level
q.push(-1);
visited[s] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
int v = q.front();
q.pop();
// If v marks the end of level
if (v == -1) {
if (!q.empty())
q.push(-1);
// Print a newline character
cout << endl;
continue;
}
// Print current vertex
cout << v << " ";
// Add the child vertices of
// the current node in queue
for (int u : adj[v]) {
if (!visited[u]) {
visited[u] = true;
q.push(u);
}
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(1);
(root->child).push_back(newNode(2));
(root->child).push_back(newNode(3));
(root->child).push_back(newNode(4));
(root->child).push_back(newNode(5));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode(6));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode(7));
(root->child[2]->child).push_back(newNode(8));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode(9));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode(10));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode(11));
int N = 11;
int K = 5;
adj.resize(N + 1, vector());
DFS(root);
levelOrderTrav(5, 11);
return 0;
} 输出:
5
1 9 10 11
2 3 4
6 7 8
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)