给定两条线L1和L2 ,每条线都通过一个点,其位置向量给定为(X, Y, Z)并平行于方向比给定为(a, b, c) 的线,任务是检查线是否L1和L2是否共面。
Coplanar: If two lines are in a same plane then lines can be called as coplanar.
例子:
Input:
L1: (x1, y1, z1) = (-3, 1, 5) and (a1, b1, c1) = (-3, 1, 5)
L2: (x1, y1, z1) = (-1, 2, 5) and (a1, b1, c1) = (-1, 2, 5)
Output: Lines are Coplanar
Input:
L1: (x1, y1, z1) = (1, 2, 3) and (a1, b1, c1) = (2, 4, 6)
L2: (x1, y1, z1) = (-1, -2, -3) and (a1, b1, c1) = (3, 4, 5)
Output: Lines are Non-Coplanar
方法:
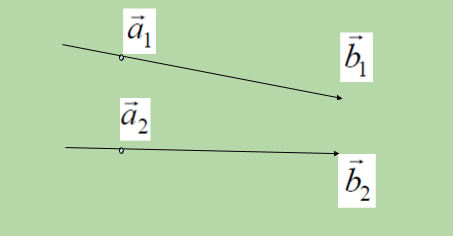
有两种方法可以在 3 维空间中表达一条线:
矢量形式:
以矢量形式确定共面性的两条直线的方程。
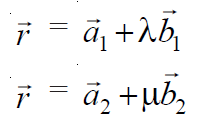
在上面的直线方程中,向量是给定直线穿过的3D 平面中的点,称为位置矢量a , b向量是给定直线平行的 3D 平面中的矢量线。所以可以说,线(1)通过点,假设A ,位置向量a1并平行于向量b1 ,线(2)通过点,假设B ,位置向量a2并平行于向量b2 。所以:
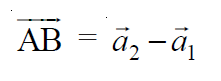
给定的线共面当且仅当AB向量垂直于向量b1和b2的叉积,即,

这里向量b1和b2的叉积将给出另一条向量线,该向量线将垂直于b1和b2向量线。 AB是连接两条给定线的位置向量a1和a2的线向量。现在,通过确定上面的点积是否为零来检查两条线是否共面。
笛卡尔形式:
设(x1, y1, z1)和(x2, y2, z2)分别是点A和B的坐标。
设a1、b1、c1和a2、b2、c2分别为向量b1和b2的方向比。然后
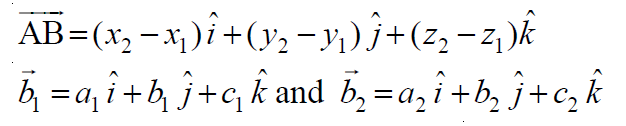
给定的线共面当且仅当:
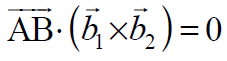
在笛卡尔形式中,它可以表示为:
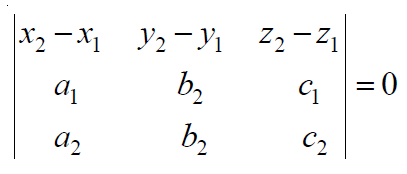
因此,对于这两种形式都需要输入中的位置向量a1和a2 分别为(x1, y1, z1)和(x2, y2, z2)以及向量b1和b2 的方向比为(a1, b1, c1)和(a2, b2, c2)分别。
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 初始化一个 3 X 3 矩阵来存储上面显示的行列式的元素。
- 计算b2和b1的叉积以及(a2 – a1)的点积。
- 如果行列式的值为 0,则这些线共面。否则,它们不共面。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program implement
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to generate determinant
int det(int d[][3])
{
int Sum = d[0][0] * ((d[1][1] * d[2][2]) - (d[2][1] * d[1][2]));
Sum -= d[0][1] * ((d[1][0] * d[2][2]) - (d[1][2] * d[2][0]));
Sum += d[0][2] * ((d[0][1] * d[1][2]) -(d[0][2] * d[1][1]));
// Return the sum
return Sum;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Position vector of first line
int x1 = -3, y1 = 1, z1 = 5;
// Direction ratios of line to
// which first line is parallel
int a1 = -3, b1 = 1, c1 = 5;
// Position vectors of second line
int x2 = -1, y2 = 2, z2 = 5;
// Direction ratios of line to
// which second line is parallel
int a2 = -1, b2 = 2, c2 = 5;
// Determinant to check coplanarity
int det_list[3][3] = { {x2 - x1, y2 - y1, z2 - z1},
{a1, b1, c1}, {a2, b2, c2}};
// If determinant is zero
if(det(det_list) == 0)
{
cout << "Lines are coplanar" << endl;
}
// Otherwise
else
{
cout << "Lines are non coplanar" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 Java
// Java program implement
// the above approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
// Function to generate determinant
static int det(int[][] d)
{
int Sum = d[0][0] * ((d[1][1] * d[2][2]) -
(d[2][1] * d[1][2]));
Sum -= d[0][1] * ((d[1][0] * d[2][2]) -
(d[1][2] * d[2][0]));
Sum += d[0][2] * ((d[0][1] * d[1][2]) -
(d[0][2] * d[1][1]));
// Return the sum
return Sum;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// Position vector of first line
int x1 = -3, y1 = 1, z1 = 5;
// Direction ratios of line to
// which first line is parallel
int a1 = -3, b1 = 1, c1 = 5;
// Position vectors of second line
int x2 = -1, y2 = 2, z2 = 5;
// Direction ratios of line to
// which second line is parallel
int a2 = -1, b2 = 2, c2 = 5;
// Determinant to check coplanarity
int[][] det_list = { {x2 - x1, y2 - y1, z2 - z1},
{a1, b1, c1}, {a2, b2, c2}};
// If determinant is zero
if(det(det_list) == 0)
System.out.print("Lines are coplanar");
// Otherwise
else
System.out.print("Lines are non coplanar");
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeatPython3
# Python Program implement
# the above approach
# Function to generate determinant
def det(d):
Sum = d[0][0] * ((d[1][1] * d[2][2])
- (d[2][1] * d[1][2]))
Sum -= d[0][1] * ((d[1][0] * d[2][2])
- (d[1][2] * d[2][0]))
Sum += d[0][2] * ((d[0][1] * d[1][2])
- (d[0][2] * d[1][1]))
# Return the sum
return Sum
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Position vector of first line
x1, y1, z1 = -3, 1, 5
# Direction ratios of line to
# which first line is parallel
a1, b1, c1 = -3, 1, 5
# Position vectors of second line
x2, y2, z2 = -1, 2, 5
# Direction ratios of line to
# which second line is parallel
a2, b2, c2 = -1, 2, 5
# Determinant to check coplanarity
det_list = [[x2-x1, y2-y1, z2-z1],
[a1, b1, c1], [a2, b2, c2]]
# If determinant is zero
if(det(det_list) == 0):
print("Lines are coplanar")
# Otherwise
else:
print("Lines are non coplanar")C#
// C# program implement
// the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to generate determinant
static int det(int[,] d)
{
int Sum = d[0, 0] * ((d[1, 1] * d[2, 2]) -
(d[2, 1] * d[1, 2]));
Sum -= d[0, 1] * ((d[1, 0] * d[2, 2]) -
(d[1, 2] * d[2, 0]));
Sum += d[0, 2] * ((d[0, 1] * d[1, 2]) -
(d[0, 2] * d[1, 1]));
// Return the sum
return Sum;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Position vector of first line
int x1 = -3, y1 = 1, z1 = 5;
// Direction ratios of line to
// which first line is parallel
int a1 = -3, b1 = 1, c1 = 5;
// Position vectors of second line
int x2 = -1, y2 = 2, z2 = 5;
// Direction ratios of line to
// which second line is parallel
int a2 = -1, b2 = 2, c2 = 5;
// Determinant to check coplanarity
int[,] det_list = { {x2 - x1, y2 - y1, z2 - z1},
{a1, b1, c1}, {a2, b2, c2}};
// If determinant is zero
if (det(det_list) == 0)
Console.Write("Lines are coplanar");
// Otherwise
else
Console.Write("Lines are non coplanar");
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjoy_62Javascript
Lines are coplanar时间复杂度: O(1)
辅助空间: O(1)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live