给定一个有向图 G N 个节点和E 个边,由值为[0, N – 1]的节点和一个类型为 { u , v } 的二维数组Edges[][2]组成,它表示顶点u和v之间的有向边。任务是在给定的图G 中找到不属于任何循环的节点。
例子:
Input: N = 4, E = 4, Edges[][2] = { {0, 2}, {0, 1}, {2, 3}, {3, 0} }
Output: 1
Explanation:
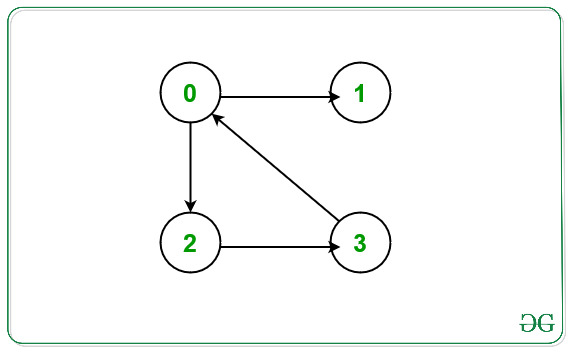
From the given graph above there exists a cycle between the nodes 0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 0.
Node which doesn’t occurs in any cycle is 1.
Hence, print 1.
Input: N = 6, E = 7, Edges[][2] = { {0, 1}, {0, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 1}, {2, 5}, {3, 0}, {4, 5}}
Output: 4 5
Explanation:
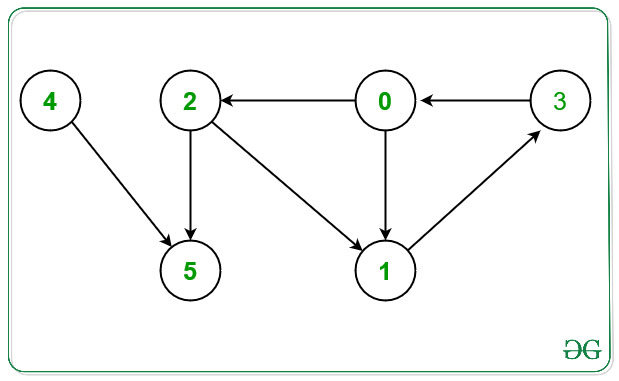
From the given graph above there exists a cycle between the nodes:
1) 0 -> 1 -> 3 -> 0.
2) 0 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3 -> 0.
Nodes which doesn’t occurs in any cycle are 4 and 5.
Hence, print 4 and 5.
朴素方法:最简单的方法是检测给定图中每个节点的有向图中的循环,并仅打印那些不属于给定图中任何循环的节点。
时间复杂度: O(V * (V + E)),其中 V 是顶点数,E 是边数。
辅助空间: O(V)
高效的方法:为了优化上述方法,其思想是在给定图中的任何循环时将中间节点存储为访问循环节点。要实现这一部分,请使用辅助数组cyclePart[] ,该数组将在执行 DFS 遍历时存储中间循环节点。以下是步骤:
- 初始化一个大小为N的辅助数组cyclePart[] ,这样如果cyclePart[i] = 0 ,则第i个节点不存在于任何循环中。
- 初始化一个大小为N的辅助数组recStack[] ,这样它将通过将该节点标记为true将访问过的节点存储在递归堆栈中。
- 对每个未访问节点的给定图执行 DFS 遍历并执行以下操作:
- 现在在给定的图中找到一个循环,每当找到一个循环时,将cyclePart[] 中的节点标记为真,因为该节点是循环的一部分。
- 如果在递归调用中访问了任何节点并且recStack[node]也为真,则该节点是循环的一部分,然后将该节点标记为true 。
- 执行DFS Traversal 后,遍历数组cyclePart[]并打印所有标记为false 的节点,因为这些节点不是任何循环的一部分。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
class Graph {
// No. of vertices
int V;
// Stores the Adjacency List
list* adj;
bool printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
int v, bool visited[], bool* rs,
bool* cyclePart);
public:
// Constructor
Graph(int V);
// Member Functions
void addEdge(int v, int w);
void printNodesNotInCycle();
};
// Function to initialize the graph
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
// Function that adds directed edges
// between node v with node w
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w);
}
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
// and return true if current node v
// formes cycle
bool Graph::printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
int v, bool visited[],
bool* recStack, bool* cyclePart)
{
// If node v is unvisited
if (visited[v] == false) {
// Mark the current node as
// visited and part of
// recursion stack
visited[v] = true;
recStack[v] = true;
// Traverse the Adjacency
// List of current node v
for (auto& child : adj[v]) {
// If child node is unvisited
if (!visited[child]
&& printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
child, visited,
recStack, cyclePart)) {
// If child node is a part
// of cycle node
cyclePart[child] = 1;
return true;
}
// If child node is visited
else if (recStack[child]) {
cyclePart[child] = 1;
return true;
}
}
}
// Remove vertex from recursion stack
recStack[v] = false;
return false;
}
// Function that print the nodes for
// the given directed graph that are
// not present in any cycle
void Graph::printNodesNotInCycle()
{
// Stores the visited node
bool* visited = new bool[V];
// Stores nodes in recursion stack
bool* recStack = new bool[V];
// Stores the nodes that are
// part of any cycle
bool* cyclePart = new bool[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
recStack[i] = false;
cyclePart[i] = false;
}
// Traverse each node
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
// If current node is unvisited
if (!visited[i]) {
// Perform DFS Traversal
if (printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
i, visited, recStack,
cyclePart)) {
// Mark as cycle node
// if it return true
cyclePart[i] = 1;
}
}
}
// Traverse the cyclePart[]
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
// If node i is not a part
// of any cycle
if (cyclePart[i] == 0) {
cout << i << " ";
}
}
}
// Function that print the nodes for
// the given directed graph that are
// not present in any cycle
void solve(int N, int E,
int Edges[][2])
{
// Initialize the graph g
Graph g(N);
// Create a directed Graph
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
g.addEdge(Edges[i][0],
Edges[i][1]);
}
// Function Call
g.printNodesNotInCycle();
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Number of nodes
int N = 6;
// Given Edges
int E = 7;
int Edges[][2] = { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 },
{ 1, 3 }, { 2, 1 },
{ 2, 5 }, { 3, 0 },
{ 4, 5 } };
// Function Call
solve(N, E, Edges);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for above approach
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
class GFG
{
static ArrayList> adj;
static int V;
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
// and return true if current node v
// formes cycle
static boolean printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
int v, boolean visited[],
boolean[] recStack, boolean[] cyclePart)
{
// If node v is unvisited
if (visited[v] == false)
{
// Mark the current node as
// visited and part of
// recursion stack
visited[v] = true;
recStack[v] = true;
// Traverse the Adjacency
// List of current node v
for (Integer child : adj.get(v))
{
// If child node is unvisited
if (!visited[child]
&& printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
child, visited,
recStack, cyclePart))
{
// If child node is a part
// of cycle node
cyclePart[child] = true;
return true;
}
// If child node is visited
else if (recStack[child])
{
cyclePart[child] = true;
return true;
}
}
}
// Remove vertex from recursion stack
recStack[v] = false;
return false;
}
static void printNodesNotInCycle()
{
// Stores the visited node
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
// Stores nodes in recursion stack
boolean[] recStack = new boolean[V];
// Stores the nodes that are
// part of any cycle
boolean[] cyclePart = new boolean[V];
// Traverse each node
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// If current node is unvisited
if (!visited[i])
{
// Perform DFS Traversal
if (printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
i, visited, recStack,
cyclePart)) {
// Mark as cycle node
// if it return true
cyclePart[i] = true;
}
}
}
// Traverse the cyclePart[]
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// If node i is not a part
// of any cycle
if (!cyclePart[i])
{
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
}
// Function that print the nodes for
// the given directed graph that are
// not present in any cycle
static void solve(int N, int E,
int Edges[][])
{
adj = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
// Create a directed Graph
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
adj.get(Edges[i][0]).add(Edges[i][1]);
}
// Function Call
printNodesNotInCycle();
}
// Driver function
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// Given Number of nodes
V = 6;
// Given Edges
int E = 7;
int Edges[][] = { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 },
{ 1, 3 }, { 2, 1 },
{ 2, 5 }, { 3, 0 },
{ 4, 5 } };
// Function Call
solve(V, E, Edges);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
class Graph:
# Function to initialize the graph
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.adj = [[] for i in range(self.V)]
# Function that adds directed edges
# between node v with node w
def addEdge(self, v, w):
self.adj[v].append(w);
# Function to perform DFS Traversal
# and return True if current node v
# formes cycle
def printNodesNotInCycleUtil(self, v, visited,recStack, cyclePart):
# If node v is unvisited
if (visited[v] == False):
# Mark the current node as
# visited and part of
# recursion stack
visited[v] = True;
recStack[v] = True;
# Traverse the Adjacency
# List of current node v
for child in self.adj[v]:
# If child node is unvisited
if (not visited[child] and self.printNodesNotInCycleUtil(child, visited,recStack, cyclePart)):
# If child node is a part
# of cycle node
cyclePart[child] = 1;
return True;
# If child node is visited
elif (recStack[child]):
cyclePart[child] = 1;
return True;
# Remove vertex from recursion stack
recStack[v] = False;
return False;
# Function that print the nodes for
# the given directed graph that are
# not present in any cycle
def printNodesNotInCycle(self):
# Stores the visited node
visited = [False for i in range(self.V)];
# Stores nodes in recursion stack
recStack = [False for i in range(self.V)];
# Stores the nodes that are
# part of any cycle
cyclePart = [False for i in range(self.V)]
# Traverse each node
for i in range(self.V):
# If current node is unvisited
if (not visited[i]):
# Perform DFS Traversal
if(self.printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
i, visited, recStack,
cyclePart)):
# Mark as cycle node
# if it return True
cyclePart[i] = 1;
# Traverse the cyclePart[]
for i in range(self.V):
# If node i is not a part
# of any cycle
if (cyclePart[i] == 0) :
print(i,end=' ')
# Function that print the nodes for
# the given directed graph that are
# not present in any cycle
def solve( N, E, Edges):
# Initialize the graph g
g = Graph(N);
# Create a directed Graph
for i in range(E):
g.addEdge(Edges[i][0],
Edges[i][1]);
# Function Call
g.printNodesNotInCycle();
# Driver Code
if __name__=='__main__':
# Given Number of nodes
N = 6;
# Given Edges
E = 7;
Edges = [ [ 0, 1 ], [ 0, 2 ],
[ 1, 3 ], [ 2, 1 ],
[ 2, 5 ], [ 3, 0 ],
[ 4, 5 ] ];
# Function Call
solve(N, E, Edges);
# This code is contributed by rutvik_564 5时间复杂度: O(V + E)
空间复杂度: O(V)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live