给定平面中二维数组arr[][]形式的 N条线,每行由 2 个整数组成(比如m & c ),其中m是线的斜率, c是该线的 y 截距.给你Q 个查询,每个查询由x-coordinates 组成。任务是为每个查询找到对应于每一行的最小可能y 坐标。
例子:
Input: arr[][] = { { 4, 0 }, { -3, 0 }, { 5, 1 }, { 3, -1 },{ 2, 3 }, { 1, 4 } } and Q[] = {-6, 3, 100}
Output:
-29
-9
-300
Explanation:
The minimum value for x = -6 from the given set of lines is -29.
The minimum value for x = 3 from the given set of lines is -9.
The minimum value for x = -100 from the given set of lines is -300.
朴素的方法:朴素的方法是找到每条线的 y 坐标,所有 y 坐标中的最小值将给出最小的 y 坐标值。对所有查询重复上述操作给出O(N*Q)的时间复杂度。
有效的方法:
观察
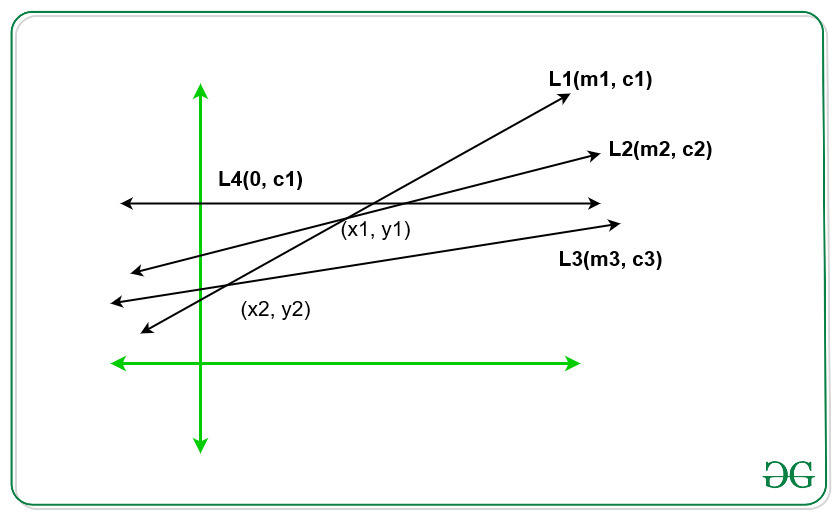
- L1的L2是两行,它们相交于(X1,Y1),如果L1比前X = X1下然后L2将在x = X1比L1更低。这意味着对于某些连续范围,这些线给出了较低的值。
- L4是平行于 x 轴的直线,它是常数,因为y = c4并且从不给出对应于所有直线的最小值。
- 因此,斜率较高的线在较低的 x 坐标处给出最小值,在较高的 x 坐标处给出最大值。例如,如果斜率(L1) > 斜率(L2)并且它们在(x1, y1)处相交,那么对于x < x1,线L1给出最小值,对于x > x1,线L2给出最小值。
- 对于线L1、L2 和 L3,如果斜率(L1) > 斜率(L2) > 斜率(L3)并且如果L1 和 L3 的交点低于L1 和 L2 ,那么我们可以忽略线L2,因为它不能给出最小值任何 x 坐标的值。
基于以上观察,以下是步骤:
- 按斜率降序对斜率进行排序。
- 从一组具有相同斜率的线中,保留具有最小y 截距值的线并丢弃所有剩余的具有相同斜率的线。
- 将前两行添加到一组有效行中并找到交点(例如(a, b) )。
- 对于下一组剩余的行,请执行以下操作:
- 找到倒数第二行和当前行的交点(比如(c, d) )。
- 如果(c, d)小于(a, b) ,则从有效行中删除插入的最后一行,因为它由于当前行而不再有效。
- 重复以上步骤,生成所有有效行集。
- 现在我们设置了有效行,并且有效行集中的每一行都以递增的顺序在连续范围内形成最小值,即L1在范围 [a, b] 中是最小值,而 L2 在范围[b, c] 中是最小值。
- 对 range[] 执行二分搜索以查找x-coordinates的每个查询的最小 y 坐标。
下面是上述方法的实现:
CPP
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// To store the valid lines
vector > lines;
// To store the distinct lines
vector > distinct;
// To store the ranges of intersection
// points
vector > ranges;
// Function that returns the intersection
// points
pair intersection(pair a,
pair b)
{
int x = a.second - b.second;
int y = b.first - a.first;
return { x, y };
}
// Function to see if a line is eligible
// or not.
// L3 is the current line being added and
// we check eligibility of L2
bool isleft(pair l1,
pair l2,
pair l3)
{
pair x1, x2;
// Find intersections
x1 = intersection(l1, l3);
x2 = intersection(l1, l2);
// Returns true if x1 is left of x2
return (x1.first * x2.second
< x2.first * x1.second);
}
// Comparator function to sort the line[]
bool cmp(pair a, pair b)
{
if (a.first != b.first)
return a.first > b.first;
else
return a.second < b.second;
}
// Find x-coordinate of intersection
// of 2 lines
int xintersect(pair a,
pair b)
{
int A = a.second - b.second;
int B = b.first - a.first;
// Find the x coordinate
int x = A / B;
if (A * B < 0)
x -= 1;
return x;
}
// Function to returns the minimum
// possible value for y
int findy(vector >& ranges,
int pt)
{
int lo = 0, hi = ranges.size() - 1;
int mid = 0;
// Binary search to find the minimum
// value
while (lo <= hi) {
// Find middle element
mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
if (ranges[mid].first <= pt
&& ranges[mid].second >= pt) {
break;
}
else if (ranges[mid].first > pt) {
hi = mid - 1;
}
else {
lo = mid + 1;
}
}
// Returns the minimum value
return lines[mid].first * pt + lines[mid].second;
}
// Function to add a valid line and
// remove the invalid lines
void add(pair x)
{
// Add the current line
lines.push_back(x);
// While Loop
while (lines.size() >= 3
&& isleft(lines[lines.size() - 3],
lines[lines.size() - 2],
lines[lines.size() - 1])) {
// Erase invalid lines
lines.erase(lines.end() - 2);
}
}
// Function to updateLines on the
// basis of distinct slopes
void updateLines(pair line[],
int n)
{
// Sort the line according to
// decreasing order of slope
sort(line, line + n, cmp);
// To track for last slope
int lastslope = INT_MIN;
// Traverse the line[] and find
// set of distinct lines
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (line[i].first == lastslope)
continue;
// Push the current line in
// array distinct[]
distinct.push_back(line[i]);
// Update the last slope
lastslope = line[i].first;
}
// Traverse the distinct[] and
// update the valid lines to lines[]
for (int i = 0; i < distinct.size(); i++)
add(distinct[i]);
int left = INT_MIN;
int i, right = 0;
// Traverse the valid lines array
for (i = 0; i < lines.size() - 1; i++) {
// Find the intersection point
int right = xintersect(lines[i],
lines[i + 1]);
// Insert the current intersection
// points in ranges[]
ranges.push_back({ left, right });
left = right + 1;
}
ranges.push_back({ left, INT_MAX });
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 6;
// Set of lines of slopes and y intercept
pair line[] = { { 4, 0 }, { -3, 0 },
{ 5, 1 }, { 3, -1 },
{ 2, 3 }, { 1, 4 } };
// Function Call
updateLines(line, n);
// Queries for x-coordinates
int Q[] = { -6, 3, 100 };
// Traverse Queries to find minimum
// y-coordinates
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// Use Binary Search in ranges
// to find the minimum y-coordinates
cout << findy(ranges, Q[i])
<< endl;
}
return 0;
} 输出:
-29
-9
-300时间复杂度: O(N + Q*log N) ,其中 N 是行数,Q 是查询数。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。