先决条件:遗传算法,旅行商问题
在本文中,提出了一种遗传算法来解决旅行商问题。
遗传算法是启发式搜索算法,其灵感来自支持生命进化的过程。该算法旨在复制自然选择过程以进行世代,即优胜劣汰。标准遗传算法分为五个阶段,分别是:
- 创建初始种群。
- 计算体能。
- 选择最好的基因。
- 越过。
- 变异以引入变体。
可以实施这些算法来找到各种类型优化问题的解决方案。一个这样的问题是旅行商问题。问题是给一个推销员一组城市,他必须找到最短的路线,以访问每个城市一次,然后返回起始城市。
方法:在下面的实现中,将城市作为基因,使用这些字符生成的字符串称为染色体,而适应度得分等于所有提到的城市的路径长度,用于针对人群。
适应度得分定义为基因描述的路径长度。较小的路径长度拟合是基因。基因库中所有基因的适者生存通过群体测试并进入下一次迭代。迭代次数取决于冷却变量的值。冷却变量的值随着每次迭代而不断减小,并在迭代一定次数后达到阈值。
算法:
1. Initialize the population randomly.
2. Determine the fitness of the chromosome.
3. Until done repeat:
1. Select parents.
2. Perform crossover and mutation.
3. Calculate the fitness of the new population.
4. Append it to the gene pool.伪代码
Initialize procedure GA{
Set cooling parameter = 0;
Evaluate population P(t);
While( Not Done ){
Parents(t) = Select_Parents(P(t));
Offspring(t) = Procreate(P(t));
p(t+1) = Select_Survivors(P(t), Offspring(t));
t = t + 1;
}
}突变如何运作?
假设有 5 个城市:0、1、2、3、4。推销员在城市 0,他必须找到穿过所有城市回到城市 0 的最短路线。代表选择的路径的染色体可以是表示为:
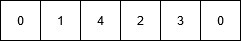
该染色体发生突变。在突变期间,染色体中两个城市的位置交换以形成新的配置,除了第一个和最后一个单元格,因为它们代表起点和终点。

根据下面定义的输入,原始染色体的路径长度等于INT_MAX ,因为城市 1 和城市 4 之间的路径不存在。变异后,形成的新孩子的路径长度等于21 ,这是比原始假设优化得多的答案。这就是遗传算法如何优化难题的解决方案。
下面是上述方法的实现:
CPP
// C++ implementation of the above approach
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Number of cities in TSP
#define V 5
// Names of the cities
#define GENES ABCDE
// Starting Node Value
#define START 0
// Initial population size for the algorithm
#define POP_SIZE 10
// Structure of a GNOME
// string defines the path traversed
// by the salesman while the fitness value
// of the path is stored in an integer
struct individual {
string gnome;
int fitness;
};
// Function to return a random number
// from start and end
int rand_num(int start, int end)
{
int r = end - start;
int rnum = start + rand() % r;
return rnum;
}
// Function to check if the character
// has already occurred in the string
bool repeat(string s, char ch)
{
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (s[i] == ch)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Function to return a mutated GNOME
// Mutated GNOME is a string
// with a random interchange
// of two genes to create variation in species
string mutatedGene(string gnome)
{
while (true) {
int r = rand_num(1, V);
int r1 = rand_num(1, V);
if (r1 != r) {
char temp = gnome[r];
gnome[r] = gnome[r1];
gnome[r1] = temp;
break;
}
}
return gnome;
}
// Function to return a valid GNOME string
// required to create the population
string create_gnome()
{
string gnome = "0";
while (true) {
if (gnome.size() == V) {
gnome += gnome[0];
break;
}
int temp = rand_num(1, V);
if (!repeat(gnome, (char)(temp + 48)))
gnome += (char)(temp + 48);
}
return gnome;
}
// Function to return the fitness value of a gnome.
// The fitness value is the path length
// of the path represented by the GNOME.
int cal_fitness(string gnome)
{
int map[V][V] = { { 0, 2, INT_MAX, 12, 5 },
{ 2, 0, 4, 8, INT_MAX },
{ INT_MAX, 4, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 12, 8, 3, 0, 10 },
{ 5, INT_MAX, 3, 10, 0 } };
int f = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < gnome.size() - 1; i++) {
if (map[gnome[i] - 48][gnome[i + 1] - 48] == INT_MAX)
return INT_MAX;
f += map[gnome[i] - 48][gnome[i + 1] - 48];
}
return f;
}
// Function to return the updated value
// of the cooling element.
int cooldown(int temp)
{
return (90 * temp) / 100;
}
// Comparator for GNOME struct.
bool lessthan(struct individual t1,
struct individual t2)
{
return t1.fitness < t2.fitness;
}
// Utility function for TSP problem.
void TSPUtil(int map[V][V])
{
// Generation Number
int gen = 1;
// Number of Gene Iterations
int gen_thres = 5;
vector population;
struct individual temp;
// Populating the GNOME pool.
for (int i = 0; i < POP_SIZE; i++) {
temp.gnome = create_gnome();
temp.fitness = cal_fitness(temp.gnome);
population.push_back(temp);
}
cout << "\nInitial population: " << endl
<< "GNOME FITNESS VALUE\n";
for (int i = 0; i < POP_SIZE; i++)
cout << population[i].gnome << " "
<< population[i].fitness << endl;
cout << "\n";
bool found = false;
int temperature = 10000;
// Iteration to perform
// population crossing and gene mutation.
while (temperature > 1000 && gen <= gen_thres) {
sort(population.begin(), population.end(), lessthan);
cout << "\nCurrent temp: " << temperature << "\n";
vector new_population;
for (int i = 0; i < POP_SIZE; i++) {
struct individual p1 = population[i];
while (true) {
string new_g = mutatedGene(p1.gnome);
struct individual new_gnome;
new_gnome.gnome = new_g;
new_gnome.fitness = cal_fitness(new_gnome.gnome);
if (new_gnome.fitness <= population[i].fitness) {
new_population.push_back(new_gnome);
break;
}
else {
// Accepting the rejected children at
// a possible probability above threshold.
float prob = pow(2.7,
-1 * ((float)(new_gnome.fitness
- population[i].fitness)
/ temperature));
if (prob > 0.5) {
new_population.push_back(new_gnome);
break;
}
}
}
}
temperature = cooldown(temperature);
population = new_population;
cout << "Generation " << gen << " \n";
cout << "GNOME FITNESS VALUE\n";
for (int i = 0; i < POP_SIZE; i++)
cout << population[i].gnome << " "
<< population[i].fitness << endl;
gen++;
}
}
int main()
{
int map[V][V] = { { 0, 2, INT_MAX, 12, 5 },
{ 2, 0, 4, 8, INT_MAX },
{ INT_MAX, 4, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 12, 8, 3, 0, 10 },
{ 5, INT_MAX, 3, 10, 0 } };
TSPUtil(map);
} 输出:
Initial population:
GNOME FITNESS VALUE
043210 24
023410 2147483647
031420 2147483647
034210 31
043210 24
023140 2147483647
032410 2147483647
012340 24
012340 24
032410 2147483647
Current temp: 10000
Generation 1
GNOME FITNESS VALUE
013240 21
013240 21
012430 31
012430 31
031240 32
024310 2147483647
013420 2147483647
032140 2147483647
034210 31
012430 31
Current temp: 9000
Generation 2
GNOME FITNESS VALUE
031240 32
043210 24
012340 24
042130 32
043210 24
012340 24
034210 31
014320 2147483647
014320 2147483647
023140 2147483647
Current temp: 8100
Generation 3
GNOME FITNESS VALUE
013240 21
042310 21
013240 21
013240 21
031240 32
013240 21
012430 31
034120 2147483647
041320 2147483647
043120 2147483647
Current temp: 7290
Generation 4
GNOME FITNESS VALUE
031240 32
043210 24
043210 24
043210 24
012340 24
042130 32
013240 21
014320 2147483647
021340 2147483647
043210 24
Current temp: 6561
Generation 5
GNOME FITNESS VALUE
043210 24
042310 21
042310 21
013240 21
042310 21
034210 31
013240 21
042310 21
024310 2147483647
024310 2147483647如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。