使用匈牙利方法的旅行商问题
一个旅行推销员计划访问N个城市,每个城市只访问一次,然后返回他开始的城市。城市 i和城市 j之间的距离为C ij 。找到他能做的最短的旅行。
注意:从城市 i 到城市 i 的旅行是不可能的,并且 C ij可能不等于 C ji 。
例子:
Input: See the routes in the image.

Output: 80
Explanation: The shortest route can be achieved following the path C1 -> C2 -> C4 -> C3 -> C1.
So the route length is 10 + 25 + 30 + 15 = 80.
Input: See the routes in the image.
Output: 15
Explanation: The shortest route is C1 -> C2 -> C3 -> C4 -> C5 -> C1. So the path length is 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 1 = 15.
直觉:假设有 3 个城市,即城市 1 、城市 2 和城市 3。访问城市的所有可能组合是
1->2->3->1 (1->2, 2->3, 3->1)
1->3->2->1 (1->3, 3->2, 2->1)
2->1->3->2 (2->1, 1->3, 3->2)
2->3->1->2 (2->3, 3->1, 1->2)
3->1->2->3 (3->1, 1->2, 2->3)
3->2->1->3 (3->2, 2->1,1->3)
因此,可以通过6 种不同的方式游览城市,但如果仔细观察,可以看出第 1、第 4 和第 5 次旅行是等效的,第 2、第 3 和第 6 次旅行是等效的。因此,可能的不同组合实际上是2 ,而那些是
1->2->3->1
1->3->2->1
因此,如果有N 个城市可以访问,那么可以有(N-1) 个!前往每个城市一次并返回起始城市的方法。这类问题可以通过匈牙利法、分支定界法、惩罚法和最近邻法来解决。我们将看到如何使用匈牙利方法解决此类问题。
方法:下面提到的是使用匈牙利方法解决问题的步骤。
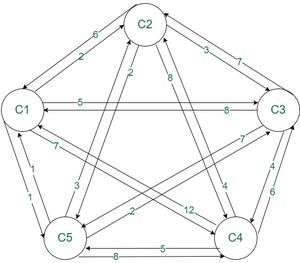
考虑图像中显示的示例:
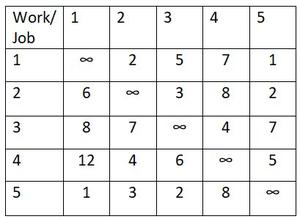
请按照上述示例的解决方案说明更好地理解。
步骤 1:在成本矩阵的每一行中找到最小的成本元素。从相应行的每个其他元素中减去该元素。因此,降低成本矩阵的每一行中至少有一个零
Illustration:
- Subtracting 1st row with the minimum value 1.
- Subtracting 2nd row with the minimum value 2.
- Subtracting 3rd row with the minimum value 4.
- Subtracting 4th row with the minimum value 4.
- Subtracting 5th row with the minimum value 1.
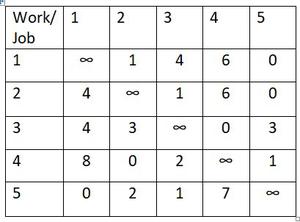
步骤2:类似地,在得到的降低成本矩阵中找到每一列的最小元素,并从对应列的每个元素中减去该最小元素。因此,在第二个降低成本矩阵的每一行和每一列中应该至少有一个零。
Illustration:
- Subtracting 1st column with the minimum value 0.
- Subtracting 2nd column with the minimum value 0.
- Subtracting 3rd column with the minimum value 1.
- Subtracting 4th column with the minimum value 0.
- Subtracting 5th column with the minimum value 0.

第 3 步:在矩阵中进行赋值,如下所示。
- 逐行移动,直到找到带有单个零的行。
- 分配包含零的单元格并划掉其列中的所有其他零。
- 继续此过程,直到分配了所有带有单个零的行。
- 对每一列重复该过程。
- 如果一行和(或)一列有两个或多个零,并且无法通过检查选择一个,则分配这些零中的任意一个,并划掉该行/列的所有其他零。
Illustration:
Row wise cell (1,5) is assigned. So, column wise cell (2,5) is crossed off.
Row wise cell (2,3) is assigned. So, column wise cell (5,3) is crossed off.
Row wise cell (3,4) is assigned.
Row wise cell (4,2) is assigned.
Row wise cell (5,1) is assigned.
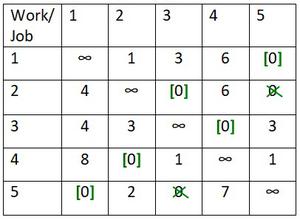
Here, the number of assignment is equal to the number of cities and the tour is 1->5->1 and 2->3->4->2 which means salesman will travel from city 1 to city 5 and return to city 1 and then again start from city , travel to city 3, city 4 and return to city 2. Therefore, we are getting two cycle and hence it is not the solution.
步骤4:通过引入最小的非零元素并重复步骤2和步骤3,可以获得下一个最佳解决方案
Illustration: In this case, minimum non-zero element is 1.
Row wise cell (3,4) is assigned.
Row wise cell (1,2) is assigned. So, column wise cell (4,2) is crossed off and row wise cell (1,5) is crossed off.
Row wise cell (2,5) is assigned. So, row wise cell (2,3) is crossed off and column wise cell (4,5) is crossed off.
Row wise cell (4,3) is assigned. So, column wise cell (5,3) is crossed off.
Row wise cell (5,1) is assigned.

Now, the sequence is 1->2->5->1 and 3->4->3. Again, we are getting two cycle therefore this is also not the solution.
第 5 步:进行不同的可能分配
Illustration:
Row wise cell (3,4) is assigned.
Row wise cell (1,2) is assigned. So, column wise cell (4,2) is crossed off and row wise cell (1,5) is crossed off.
Row wise cell (2,3) is assigned. So, column wise cell (4,3) and (5,3) is crossed off and row wise cell (2,5) is crossed off.
Row wise cell (4,5) is assigned.
Row wise cell (5,1) is assigned.
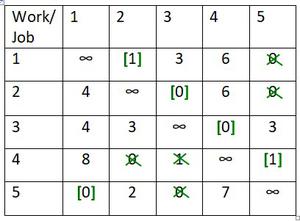
The sequence is 1->2->3->4->5->1. So, this solution is optimal and total distance of this tour is
Cell12 + Cell23 + Cell34 + Cell45 + Cell51 = (2+3+4+5+1) =15.