先决条件:有限自动机介绍,设计有限自动机
问题 1:
构造 DFA,它接受 {0, 1} 上所有字符串的集合,这些字符串解释为可以被 2 整除的二进制数。
解释:
考虑以下输入,
{0, 01, 10, 11, 100, 101, 110........}语言的状态转换图如下:
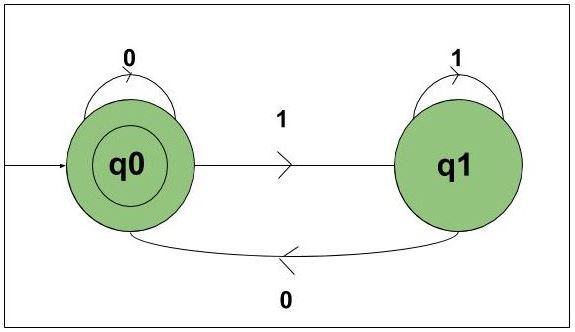
在这个 DFA 中有两个状态 q0 和 q1,输入是 {0, 1} 的字符串,它被解释为二进制数。
状态 q0 是最终状态,q1 是非最终状态。状态 q0 将表示所有可被 2 整除的数字,即 {0, 10, 100, 110 …..}。
状态 q1 将代表所有不能被 2 整除的数字,即 {01, 11, 101, ……}。
def stateq0(n):
#if length found 0
#print not accepted
if (len(n)==0):
print("string accepted")
else:
#if at index 0
#'0' found call
#function stateq0
if(n[0]=='0'):
stateq0(n[1:])
#else if '1' found
#call function q1.
elif (n[0]=='1'):
stateq1(n[1:])
def stateq1(n):
#if length found 0
#print not accepted
if (len(n)==0):
print("string not accepted")
else:
#if at index 0
#'0' found call
#function stateq0
if(n[0]=='0'):
stateq0(n[1:])
#else if '1' found
#call function q1.
elif (n[0]=='1'):
stateq1(n[1:])
#take number from user
n=int(input())
#converting number to binary
n = bin(n).replace("0b", "")
#call stateA
#to check the input
stateq0(n)
INPUT: 5
OUTPUT: String Not Accepted
上面的自动机将接受 {0, 1} 上所有字符串的集合,当解释为二进制数时,它可以被 2 整除。
每当数字不能被 2 整除时,它就会从状态 q0 转到 q1。当该数字可被 2 整除时,它将从状态 q1 转到 q0,或者如果它最初在 q0 中,则它将接受它。
问题 2:
构造 DFA,它接受 {0, 1} 上所有字符串的集合,这些字符串解释为可以被 3 整除的二进制数。
解释:
请参阅解决方案:使用 DFA 的 3 的二进制字符串倍数。
问题 3:
构造 DFA,它接受 {0, 1} 上所有字符串的集合,这些字符串解释为可以被 4 整除的二进制数。
解释:
考虑以下输入,
{0, 01, 10, 11, 100, 101, 110........}语言的状态转换图如下:
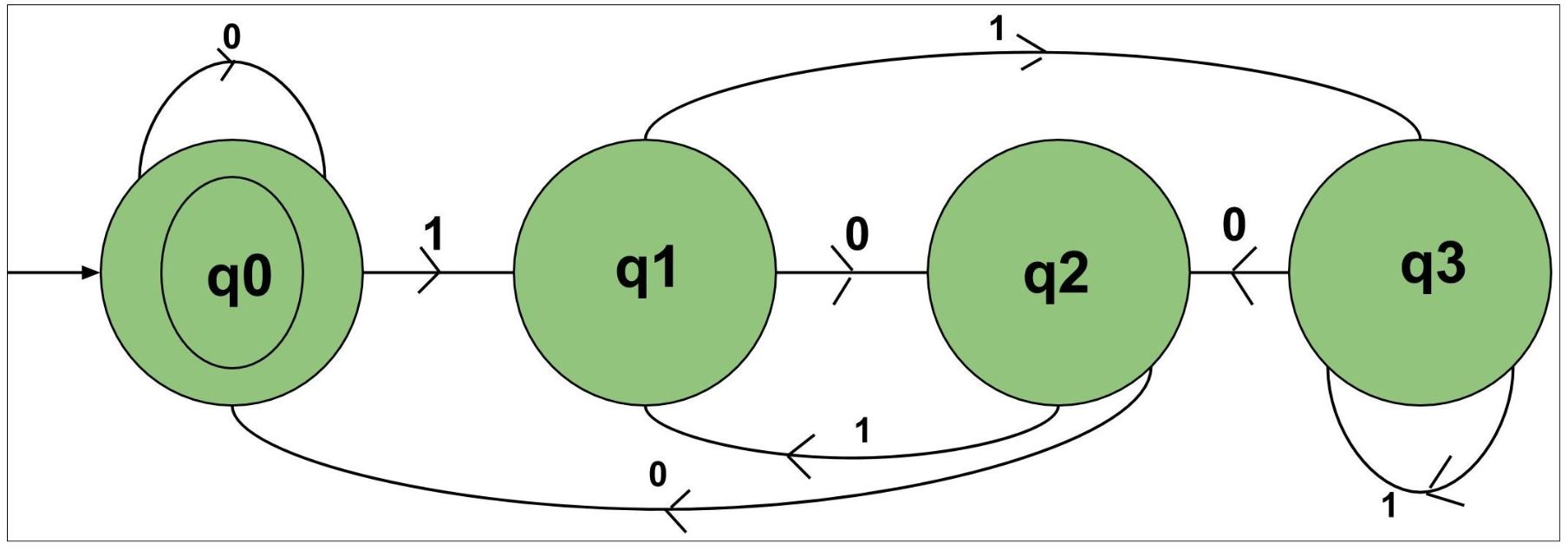
解释:
在这个 DFA 中有三个状态 q0、q1、q2、q3,输入是 {0, 1} 的字符串,它被解释为二进制数。状态 q0 是最终状态,q1、q2、q3 是非最终状态。
- 状态 q0 将代表所有可以被 4 整除的数字,即 {0, 100, 1000 …..}。
- 状态 q1 将表示所有不能被 4 整除且被 4 除时余数为 1 的数字,即 {01, 101,,……}。
- 状态 q2 将表示所有不能被 4 整除的数,除以 4 的余数为 2,即 {10, 110, ……}。
- 状态 q4 将代表所有不能被 4 整除的数,除以 4 的余数为 3,即 {11, 111, ……}。
上面的自动机将接受 {0, 1} 上所有字符串的集合,当解释为二进制数时,它可以被 4 整除。
- 状态 每当数字不能被 4 整除并给出 1 的余数时,它将进入状态 q1。
- 状态 每当数字不能被 4 整除并给出 2 的余数时,它将进入状态 q2。
- 状态 每当数字不能被 4 整除并给出 3 的余数时,它将进入状态 q3。
- 状态 每当数字可以被 4 整除时,它就会进入状态 q0,或者如果它最初在 q0 中,那么它将接受它。
def stateq0(n):
#if length found 0
#print not accepted
if (len(n)==0):
print("string accepted")
else:
#if at index 0
#'0' found call
#function stateq0
if(n[0]=='0'):
stateq0(n[1:])
#else if '1' found
#call function q1.
elif (n[0]=='1'):
stateq1(n[1:])
def stateq1(n):
#if length found 0
#print not accepted
if (len(n)==0):
print("string not accepted")
else:
#if at index 0
#'0' found call
#function stateq2
if(n[0]=='0'):
stateq2(n[1:])
#else if '1' found
#call function q3.
elif (n[0]=='1'):
stateq3(n[1:])
def stateq2(n):
#if length found 0
#print not accepted
if (len(n)==0):
print("string not accepted")
else:
#if at index 0
#'0' found call
#function stateq0
if(n[0]=='0'):
stateq0(n[1:])
#else if '1' found
#call function q1.
elif (n[0]=='1'):
stateq1(n[1:])
def stateq3(n):
#if length found 0
#print not accepted
if (len(n)==0):
print("string not accepted")
else:
#if at index 0
#'0' found call
#function stateq2
if(n[0]=='0'):
stateq2(n[1:])
#else if '1' found
#call function q3.
elif (n[0]=='1'):
stateq3(n[1:])
#take number from user
n=int(input())
#converting number to binary
n = bin(n).replace("0b", "")
#call stateA
#to check the input
stateq0(n)