给定一个未加权的有向图G作为路径矩阵,任务是找出该图是强连接还是单边连接或弱连接。
Strongly Connected: A graph is said to be strongly connected if every pair of vertices(u, v) in the graph contains a path between each other. In an unweighted directed graph G, every pair of vertices u and v should have a path in each direction between them i.e., bidirectional path. The elements of the path matrix of such a graph will contain all 1’s.
Unilaterally Connected: A graph is said to be unilaterally connected if it contains a directed path from u to v OR a directed path from v to u for every pair of vertices u, v. Hence, at least for any pair of vertices, one vertex should be reachable form the other. Such a path matrix would rather have upper triangle elements containing 1’s OR lower triangle elements containing 1’s.
Weakly Connected: A graph is said to be weakly connected if there doesn’t exist any path between any two pairs of vertices. Hence, if a graph G doesn’t contain a directed path (from u to v or from v to u for every pair of vertices u, v) then it is weakly connected. The elements of such a path matrix of this graph would be random.
例子:
Input: Below is the given graph with path matrix:
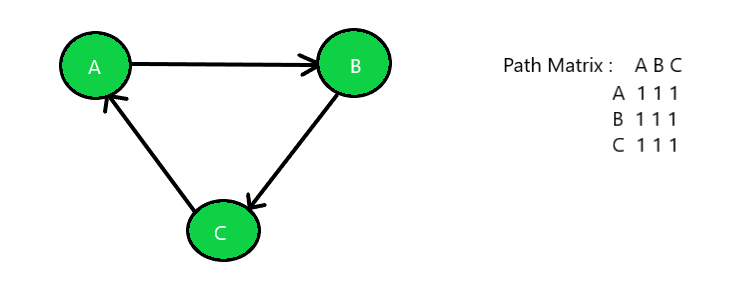
Output: Strongly Connected Graph
Input: Below is the given graph with path matrix:
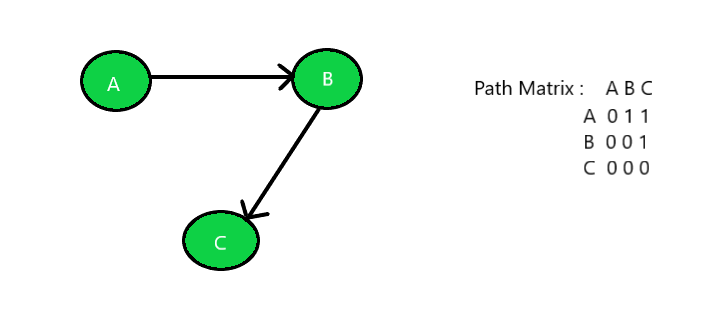
Output: Unilaterally Connected Graph
Input: Below is the given graph with path matrix:
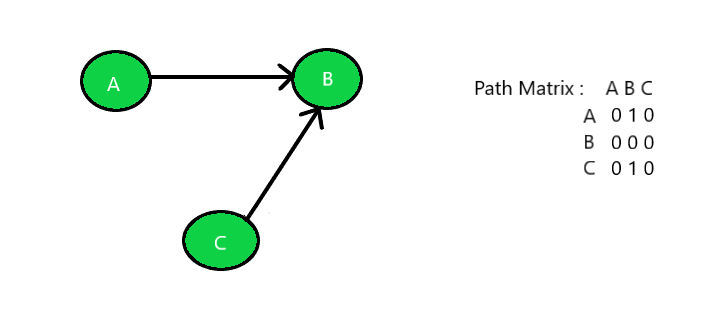
Output: Weakly Connected Graph
方法:
- 对于要强连通的图,使用本文中讨论的方法遍历给定的路径矩阵,检查单元格中的所有值是否为1 。如果是,则打印“Strongly Connected Graph”,否则检查其他两个图。
- 对于要单边连接的图,请使用本文中讨论的方法遍历给定的路径矩阵并检查以下内容:
- 如果主对角线上的所有值都是1s并且除此之外的所有值都是0s 。
- 如果主对角线以下的所有值都是1s ,除此之外的所有值都是0s 。
- 如果满足上述两个条件之一,则给定的图是单边连接的,否则该图是弱连接的图。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
#define V 3
// Function to find the characteristic
// of the given graph
int checkConnected(int graph[][V], int n)
{
// Check whether the graph is
// strongly connected or not
bool strongly = true;
// Traverse the path matrix
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// If all the elements are
// not equal then the graph
// is not strongly connected
if (graph[i][j] != graph[j][i]) {
strongly = false;
break;
}
}
// Break out of the loop if false
if (!strongly) {
break;
}
}
// If true then print strongly
// connected and return
if (strongly) {
cout << "Strongly Connected";
return 0;
}
// Check whether the graph is
// Unilaterally connected by
// checking Upper Triangle element
bool uppertri = true;
// Traverse the path matrix
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// If uppertriangle elements
// are 0 then break out of the
// loop and check the elements
// of lowertriangle matrix
if (i > j && graph[i][j] == 0) {
uppertri = false;
break;
}
}
// Break out of the loop if false
if (!uppertri) {
break;
}
}
// If true then print unilaterally
// connected and return
if (uppertri) {
cout << "Unilaterally Connected";
return 0;
}
// Check lowertraingle elements
bool lowertri = true;
// Traverse the path matrix
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// If lowertraingle elements
// are 0 then break cause
// 1's are expected
if (i < j && graph[i][j] == 0) {
lowertri = false;
break;
}
}
// Break out of the loop if false
if (!lowertri) {
break;
}
}
// If true then print unilaterally
// connected and return
if (lowertri) {
cout << "Unilaterally Connected";
return 0;
}
// If elements are in random order
// unsynchronized then print weakly
// connected and return
else {
cout << "Weakly Connected";
}
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Number of nodes
int n = 3;
// Given Path Matrix
int graph[V][V] = {
{ 0, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 0 },
};
// Function Call
checkConnected(graph, n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static final int V = 3;
// Function to find the characteristic
// of the given graph
static int checkConnected(int graph[][], int n)
{
// Check whether the graph is
// strongly connected or not
boolean strongly = true;
// Traverse the path matrix
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
// If all the elements are
// not equal then the graph
// is not strongly connected
if (graph[i][j] != graph[j][i])
{
strongly = false;
break;
}
}
// Break out of the loop if false
if (!strongly)
{
break;
}
}
// If true then print strongly
// connected and return
if (strongly)
{
System.out.print("Strongly Connected");
return 0;
}
// Check whether the graph is
// Unilaterally connected by
// checking Upper Triangle element
boolean uppertri = true;
// Traverse the path matrix
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
// If uppertriangle elements
// are 0 then break out of the
// loop and check the elements
// of lowertriangle matrix
if (i > j && graph[i][j] == 0)
{
uppertri = false;
break;
}
}
// Break out of the loop if false
if (!uppertri)
{
break;
}
}
// If true then print unilaterally
// connected and return
if (uppertri)
{
System.out.print("Unilaterally Connected");
return 0;
}
// Check lowertraingle elements
boolean lowertri = true;
// Traverse the path matrix
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
// If lowertraingle elements
// are 0 then break cause
// 1's are expected
if (i < j && graph[i][j] == 0)
{
lowertri = false;
break;
}
}
// Break out of the loop if false
if (!lowertri)
{
break;
}
}
// If true then print unilaterally
// connected and return
if (lowertri)
{
System.out.print("Unilaterally Connected");
return 0;
}
// If elements are in random order
// unsynchronized then print weakly
// connected and return
else
{
System.out.print("Weakly Connected");
}
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Number of nodes
int n = 3;
// Given Path Matrix
int graph[][] = { { 0, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 0 } };
// Function call
checkConnected(graph, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# Python3 implementation of
# the above approach
V = 3
# Function to find the
# characteristic of the
# given graph
def checkConnected(graph, n):
# Check whether the graph is
# strongly connected or not
strongly = True;
# Traverse the path
# matrix
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
# If all the elements are
# not equal then the graph
# is not strongly connected
if (graph[i][j] != graph[j][i]):
strongly = False;
break
# Break out of the
# loop if false
if not strongly:
break;
# If true then print
# strongly connected and return
if (strongly):
print("Strongly Connected");
exit()
# Check whether the graph is
# Unilaterally connected by
# checking Upper Triangle element
uppertri = True;
# Traverse the path matrix
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
# If uppertriangle elements
# are 0 then break out of the
# loop and check the elements
# of lowertriangle matrix
if (i > j and graph[i][j] == 0):
uppertri = False;
break;
# Break out of the
# loop if false
if not uppertri:
break;
# If true then print
# unilaterally connected
# and return
if uppertri:
print("Unilaterally Connected");
exit()
# Check lowertraingle elements
lowertri = True;
# Traverse the path matrix
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
# If lowertraingle elements
# are 0 then break cause
# 1's are expected
if (i < j and graph[i][j] == 0):
lowertri = False;
break;
# Break out of the
# loop if false
if not lowertri:
break;
# If true then print
# unilaterally connected
# and return
if lowertri:
print("Unilaterally Connected")
exit()
# If elements are in random order
# unsynchronized then print weakly
# connected and return
else:
print("Weakly Connected")
exit()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Number of nodes
n = 3;
# Given Path Matrix
graph = [[0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0]];
# Function Call
checkConnected(graph, n);
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# implementation of the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
//static readonly int V = 3;
// Function to find the characteristic
// of the given graph
static int checkConnected(int [,]graph, int n)
{
// Check whether the graph is
// strongly connected or not
bool strongly = true;
// Traverse the path matrix
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
// If all the elements are
// not equal then the graph
// is not strongly connected
if (graph[i, j] != graph[j, i])
{
strongly = false;
break;
}
}
// Break out of the loop if false
if (!strongly)
{
break;
}
}
// If true then print strongly
// connected and return
if (strongly)
{
Console.Write("Strongly Connected");
return 0;
}
// Check whether the graph is
// Unilaterally connected by
// checking Upper Triangle element
bool uppertri = true;
// Traverse the path matrix
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
// If uppertriangle elements
// are 0 then break out of the
// loop and check the elements
// of lowertriangle matrix
if (i > j && graph[i, j] == 0)
{
uppertri = false;
break;
}
}
// Break out of the loop if false
if (!uppertri)
{
break;
}
}
// If true then print unilaterally
// connected and return
if (uppertri)
{
Console.Write("Unilaterally Connected");
return 0;
}
// Check lowertraingle elements
bool lowertri = true;
// Traverse the path matrix
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
// If lowertraingle elements
// are 0 then break cause
// 1's are expected
if (i < j && graph[i, j] == 0)
{
lowertri = false;
break;
}
}
// Break out of the loop if false
if (!lowertri)
{
break;
}
}
// If true then print unilaterally
// connected and return
if (lowertri)
{
Console.Write("Unilaterally Connected");
return 0;
}
// If elements are in random order
// unsynchronized then print weakly
// connected and return
else
{
Console.Write("Weakly Connected");
}
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Number of nodes
int n = 3;
// Given Path Matrix
int [,]graph = { { 0, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 0 } };
// Function call
checkConnected(graph, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarJavascript
Unilaterally Connected时间复杂度: O(N 2 )
辅助空间: O(1)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。