鉴于N个顶点和m条边的有向图,任务是找到使给定的图形强连接所需边缘的最小数量。
例子:
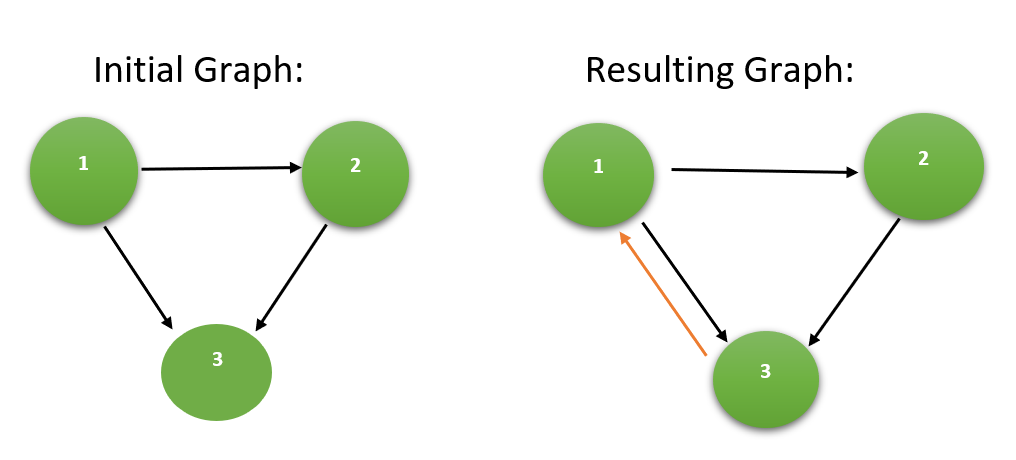
Input: N = 3, M = 3, source[] = {1, 2, 1}, destination[] = {2, 3, 3}
Output: 1
Explanation:
Adding a directed edge joining the pair of vertices {3, 1} makes the graph strongly connected.
Hence, the minimum number of edges required is 1.
Below is the illustration of the above example:
Input: N = 5, M = 5, source[] = {1, 3, 1, 3, 4}, destination[] = {2, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Output: 2
Explanation:
Adding 2 directed edges to join the following pair of vertices makes the graph strongly connected:
- {2, 1}
- {5, 2}
Hence, the minimum number of edges required is 2.
方法:
对于强连通图,每个顶点的入度和出度必须至少为1 。因此,为了使图牢固连接,每个顶点必须具有输入边缘和输出边缘。使图牢固连接所需的传入边缘和传出边缘的数量的最大值是使其牢固连接所需的最小边缘。
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 使用DFS查找图形的每个顶点的度数和度数。
- 如果顶点的入度或出度大于1 ,则将其视为仅1 。
- 计算给定图的总进度和出度。
- 然后,通过max(N-totalIndegree,N-totalOutdegree)给出使图牢固连接所需的最小边数。
- 打印最小边缘数作为结果。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to implement
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Perform DFS to count the in-degree
// and out-degree of the graph
void dfs(int u, vector adj[], int* vis, int* inDeg,
int* outDeg)
{
// Mark the source as visited
vis[u] = 1;
// Traversing adjacent nodes
for (auto v : adj[u])
{
// Mark out-degree as 1
outDeg[u] = 1;
// Mark in-degree as 1
inDeg[v] = 1;
// If not visited
if (vis[v] == 0)
{
// DFS Traversal on
// adjacent vertex
dfs(v, adj, vis, inDeg, outDeg);
}
}
}
// Function to return minimum number
// of edges required to make the graph
// strongly connected
int findMinimumEdges(int source[], int N, int M, int dest[])
{
// For Adjacency List
vector adj[N + 1];
// Create the Adjacency List
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
adj].push_back(dest[i]);
}
// Initialize the in-degree array
int inDeg[N + 1] = { 0 };
// Initialize the out-degree array
int outDeg[N + 1] = { 0 };
// Initialize the visited array
int vis[N + 1] = { 0 };
// Perform DFS to count in-degrees
// and out-degreess
dfs(1, adj, vis, inDeg, outDeg);
// To store the result
int minEdges = 0;
// To store total count of in-degree
// and out-degree
int totalIndegree = 0;
int totalOutdegree = 0;
// Find total in-degree
// and out-degree
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
if (inDeg[i] == 1)
totalIndegree++;
if (outDeg[i] == 1)
totalOutdegree++;
}
// Calculate the minimum
// edges required
minEdges = max(N - totalIndegree, N - totalOutdegree);
// Return the minimum edges
return minEdges;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 5, M = 5;
int source[] = { 1, 3, 1, 3, 4 };
int destination[] = { 2, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// Function call
cout << findMinimumEdges(source, N, M, destination);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Perform DFS to count the
// in-degree and out-degree
// of the graph
static void dfs(int u, Vector adj[],
int[] vis, int[] inDeg,
int[] outDeg)
{
// Mark the source
// as visited
vis[u] = 1;
// Traversing adjacent nodes
for (int v : adj[u])
{
// Mark out-degree as 1
outDeg[u] = 1;
// Mark in-degree as 1
inDeg[v] = 1;
// If not visited
if (vis[v] == 0)
{
// DFS Traversal on
// adjacent vertex
dfs(v, adj, vis,
inDeg, outDeg);
}
}
}
// Function to return minimum
// number of edges required
// to make the graph strongly
// connected
static int findMinimumEdges(int source[],
int N, int M,
int dest[])
{
// For Adjacency List
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector []adj =
new Vector[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = new Vector();
// Create the Adjacency List
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
adj].add(dest[i]);
}
// Initialize the in-degree array
int inDeg[] = new int[N + 1];
// Initialize the out-degree array
int outDeg[] = new int[N + 1];
// Initialize the visited array
int vis[] = new int[N + 1];
// Perform DFS to count
// in-degrees and out-degreess
dfs(1, adj, vis, inDeg, outDeg);
// To store the result
int minEdges = 0;
// To store total count of
// in-degree and out-degree
int totalIndegree = 0;
int totalOutdegree = 0;
// Find total in-degree
// and out-degree
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
if (inDeg[i] == 1)
totalIndegree++;
if (outDeg[i] == 1)
totalOutdegree++;
}
// Calculate the minimum
// edges required
minEdges = Math.max(N - totalIndegree,
N - totalOutdegree);
// Return the minimum edges
return minEdges;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 5, M = 5;
int source[] = {1, 3, 1, 3, 4};
int destination[] = {2, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// Function call
System.out.print(findMinimumEdges(source,
N, M,
destination));
}
} Python3
# Python3 program to implement
# the above approach
# Perform DFS to count the in-degree
# and out-degree of the graph
def dfs(u, adj, vis,inDeg, outDeg):
# Mark the source as visited
vis[u] = 1;
# Traversing adjacent nodes
for v in adj[u]:
# Mark out-degree as 1
outDeg[u] = 1;
# Mark in-degree as 1
inDeg[u] = 1;
# If not visited
if (vis[v] == 0):
# DFS Traversal on
# adjacent vertex
dfs(v, adj, vis,
inDeg, outDeg)
# Function to return minimum
# number of edges required
# to make the graph strongly
# connected
def findMinimumEdges(source, N,
M, dest):
# For Adjacency List
adj = [[] for i in range(N + 1)]
# Create the Adjacency List
for i in range(M):
adj].append(dest[i]);
# Initialize the in-degree array
inDeg = [0 for i in range(N + 1)]
# Initialize the out-degree array
outDeg = [0 for i in range(N + 1)]
# Initialize the visited array
vis = [0 for i in range(N + 1)]
# Perform DFS to count in-degrees
# and out-degreess
dfs(1, adj, vis, inDeg, outDeg);
# To store the result
minEdges = 0;
# To store total count of
# in-degree and out-degree
totalIndegree = 0;
totalOutdegree = 0;
# Find total in-degree
# and out-degree
for i in range(1, N):
if (inDeg[i] == 1):
totalIndegree += 1;
if (outDeg[i] == 1):
totalOutdegree += 1;
# Calculate the minimum
# edges required
minEdges = max(N - totalIndegree,
N - totalOutdegree);
# Return the minimum edges
return minEdges;
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 5
M = 5
source = [1, 3, 1, 3, 4]
destination = [2, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# Function call
print(findMinimumEdges(source, N,
M, destination))
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Perform DFS to count the
// in-degree and out-degree
// of the graph
static void dfs(int u, List []adj,
int[] vis, int[] inDeg,
int[] outDeg)
{
// Mark the source
// as visited
vis[u] = 1;
// Traversing adjacent nodes
foreach (int v in adj[u])
{
// Mark out-degree as 1
outDeg[u] = 1;
// Mark in-degree as 1
inDeg[v] = 1;
// If not visited
if (vis[v] == 0)
{
// DFS Traversal on
// adjacent vertex
dfs(v, adj, vis,
inDeg, outDeg);
}
}
}
// Function to return minimum
// number of edges required
// to make the graph strongly
// connected
static int findMinimumEdges(int []source,
int N, int M,
int []dest)
{
// For Adjacency List
List []adj = new List[N + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < adj.Length; i++)
adj[i] = new List();
// Create the Adjacency List
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
adj].Add(dest[i]);
}
// Initialize the in-degree array
int []inDeg = new int[N + 1];
// Initialize the out-degree array
int []outDeg = new int[N + 1];
// Initialize the visited array
int []vis = new int[N + 1];
// Perform DFS to count
// in-degrees and out-degreess
dfs(1, adj, vis, inDeg, outDeg);
// To store the result
int minEdges = 0;
// To store total count of
// in-degree and out-degree
int totalIndegree = 0;
int totalOutdegree = 0;
// Find total in-degree
// and out-degree
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
if (inDeg[i] == 1)
totalIndegree++;
if (outDeg[i] == 1)
totalOutdegree++;
}
// Calculate the minimum
// edges required
minEdges = Math.Max(N - totalIndegree,
N - totalOutdegree);
// Return the minimum edges
return minEdges;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 5, M = 5;
int []source = { 1, 3, 1, 3, 4 };
int []destination = { 2, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// Function call
Console.Write(findMinimumEdges(source,
N, M,
destination));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar 2时间复杂度: O(N + M)
辅助空间: O(N)