通过删除任何 K 条边,双向加权图中给定节点之间的最短距离
给定一个正整数K和一个由N个节点和E个边组成的加权无向连通图,作为类型为 {u, v, W} 的数组Edges[] ,表示节点 u和节点 v之间的边具有权重W ,任务是在将最多 K条边的成本减少到0后,找到两个给定节点S和D之间的最短距离。
例子:
Input: N = 5, K = 1, Edges[][] = {{0, 1, 1}, {0, 4, 1}, {1, 2, 2}, {2, 3, 4}, {4, 3, 7}}, s = 0, d = 3
Output: 1
Explanation:
Below is the graph for the given test case:
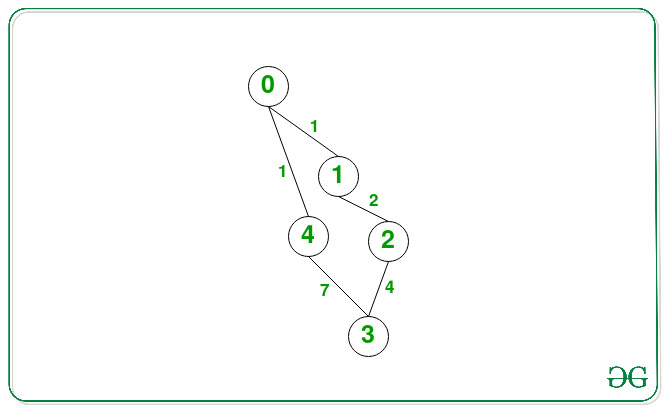
There are 2 possible routes between 0 and 3 viz. {0->1->2->3} and {0->4->3}
after reducing the distance of edge 4->3 to zero, the second route becomes 0->(4, 3) and hence the minimum distance is 1.
Input: N = 5, K = 2, Edges[][] = {{0, 1, 2}, {0, 2, 3}, {2, 1, 2}, {2, 3, 1}, {3, 1, 2}, {3, 4, 3}, {4, 2, 4}}, s = 0, d = 3
Ouput: 2
方法:给定问题可以使用 DFS 遍历并存储两个给定节点之间的所有可能路径来解决。请按照以下步骤解决给定的问题:
- 初始化一个变量,比如minimumCost为INT_MAX ,它存储了得到的最短距离。
- 使用 DFS Traversal 遍历图中从节点S到节点D的所有路径,并将从节点S到D获得的所有边权重存储在向量向量中,例如edgesPath[] 。
- 完成上述步骤后,对存储在edgesPath[]中的每个向量进行降序排序。
- 遍历每个向量的向量edgesPath[]的向量,比如A[] ,执行以下步骤:
- 求A[]中前K个最大边的总和。
- 将minimiumCost的值更新为当前(totalSum – sum)和minimumCost的最小值。
- 完成上述步骤后,打印minimumCost的值作为结果。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program of the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to get all the possible
// paths from the source to destination
void dfs_all(int n, int s, int d,
vector > >& graph,
vector& vis,
vector >& edge_path,
vector& temp_edge)
{
// One possible path, reached node D
if (s == d) {
edge_path.push_back(temp_edge);
return;
}
// Mark node s as visited
vis[s] = true;
// Calculate number of edges with
// node s as connection
int edges_in_a = graph[s].size();
// Traverse all the connections
// of node s
for (int i = 0; i < edges_in_a; i++) {
// If the connected node
// isn't visited
if (!vis[graph[s][i].first]) {
// Push back edge value
// in temp_edge
temp_edge.push_back(
graph[s][i].second);
// Call DFS function recursively
dfs_all(n, graph[s][i].first,
d, graph, vis,
edge_path, temp_edge);
// Pop back last added edge
temp_edge.pop_back();
}
}
// Mark s as unvisited for more
// possible paths
vis[s] = false;
}
// Function to find the minimum sum of
// edges from source to destination
// after reducing at most K cost to 0
int getDistance(
vector >& edge_path, int k)
{
// Store the shortestDistance
int shortestDistance = INT_MAX;
// If edge_path vector is empty,
// means no path exist
if (edge_path.empty())
return -1;
// Traverse all the vector in
// the edge_path
for (auto x : edge_path) {
// Base Case
if (k == x.size())
return 0;
// lets sort the vector in
// decreasing order
sort(x.begin(), x.end(), greater());
// Find the sum of all the nodes
int sum = 0;
// Find the sum of k largest nodes
int ksum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++) {
sum += x[i];
if (i < k)
ksum += x[i];
}
// If the given shortestDistance
// is shortest, then update the
// shortestDistance
shortestDistance
= min(sum - ksum, shortestDistance);
}
// Return the shortestDistance
return shortestDistance;
}
// Function to find the minimum sum of
// weight of edges among all paths from
// source to destination after reducing
// at most K cost to 0
int solve(
vector > > graph,
int n, int k, int src, int dest)
{
// Stores all the vectors of edges for
// every path traversed in DFS call
vector > edge_path;
// Store the edges of particular path
vector temp_edge;
// Boolean visited vector
vector vis(n, false);
// DFS Call
dfs_all(n, src, dest, graph,
vis, edge_path, temp_edge);
return getDistance(edge_path, k);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 5, e = 5, k = 1;
vector > > graph(n);
// Given Adjacency List
graph[0].push_back(make_pair(1, 1));
graph[1].push_back(make_pair(0, 1));
graph[0].push_back(make_pair(4, 1));
graph[4].push_back(make_pair(0, 1));
graph[1].push_back(make_pair(2, 2));
graph[2].push_back(make_pair(1, 2));
graph[2].push_back(make_pair(3, 4));
graph[3].push_back(make_pair(2, 4));
graph[4].push_back(make_pair(3, 7));
graph[3].push_back(make_pair(4, 7));
int a = 0, b = 3;
cout << solve(graph, n, k, a, b);
return 0;
} C++
// C++ program of the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to get all the possible
// paths from the source to destination
void dfs_all(int n, int s, int d,
vector > >& graph,
vector& vis,
vector >& edge_path,
vector& temp_edge)
{
// One possible path, reached node D
if (s == d) {
edge_path.push_back(temp_edge);
return;
}
// Mark node s as visited
vis[s] = true;
// Calculate number of edges with
// node s as connection
int edges_in_a = graph[s].size();
// Traverse all the connections
// of node s
for (int i = 0; i < edges_in_a; i++) {
// If the connected node
// isn't visited
if (!vis[graph[s][i].first]) {
// Push back edge value
// in temp_edge
temp_edge.push_back(
graph[s][i].second);
// Call DFS function recursively
dfs_all(n, graph[s][i].first,
d, graph, vis,
edge_path, temp_edge);
// Pop back last added edge
temp_edge.pop_back();
}
}
// Mark s as unvisited for more
// possible paths
vis[s] = false;
}
// Function to find the minimum sum of
// edges from source to destination
// after reducing at most K cost to 0
int getDistance(
vector >& edge_path, int k)
{
int shortestDistance = INT_MAX;
// If edge_path vector is empty,
// means no path exist
if (edge_path.empty())
return -1;
// Traverse all the vector in
// the edge_path
for (auto x : edge_path) {
if (k == x.size())
return 0;
// Use heap to store the array
priority_queue,
greater >
minHeap;
// Find the sum of all the nodes
int sum = 0;
// Find the sum of k largest nodes
int ksum = 0;
// Find the largest K edges using
// minHeap
for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++) {
sum += x[i];
ksum += x[i];
// Pushing edge in MinHeap
minHeap.push(x[i]);
// If heap size is K
if (minHeap.size() > k) {
ksum -= minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
}
}
// If the shortestDistance is
// smallest, then update the
// shortestDistance
shortestDistance
= min(sum - ksum, shortestDistance);
}
// Return the shortestDistance
return shortestDistance;
}
// Function to find the minimum sum of
// weight of edges among all paths from
// source to destination after reducing
// at most K cost to 0
int solve(
vector > > graph,
int n, int k, int src, int dest)
{
// Stores all the vectors of edges for
// every path traversed in DFS call
vector > edge_path;
// Store the edges of particular path
vector temp_edge;
// Boolean visited vector
vector vis(n, false);
// DFS Call
dfs_all(n, src, dest, graph,
vis, edge_path, temp_edge);
return getDistance(edge_path, k);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 5, e = 5, k = 1;
vector > > graph(n);
// Given Adjacency List
graph[0].push_back(make_pair(1, 1));
graph[1].push_back(make_pair(0, 1));
graph[0].push_back(make_pair(4, 1));
graph[4].push_back(make_pair(0, 1));
graph[1].push_back(make_pair(2, 2));
graph[2].push_back(make_pair(1, 2));
graph[2].push_back(make_pair(3, 4));
graph[3].push_back(make_pair(2, 4));
graph[4].push_back(make_pair(3, 7));
graph[3].push_back(make_pair(4, 7));
int a = 0, b = 3;
cout << solve(graph, n, k, a, b);
return 0;
} 1
时间复杂度: O((N*log N)N N )
辅助空间: O(N 2 )
高效方法:上述方法也可以在找到所有可能路径后进行排序的步骤进行优化。这个想法不是排序,而是使用 MinHeap 计算图中K个最大权重的总和,以将这些步骤的时间复杂度降低到O(N*log K) 。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program of the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to get all the possible
// paths from the source to destination
void dfs_all(int n, int s, int d,
vector > >& graph,
vector& vis,
vector >& edge_path,
vector& temp_edge)
{
// One possible path, reached node D
if (s == d) {
edge_path.push_back(temp_edge);
return;
}
// Mark node s as visited
vis[s] = true;
// Calculate number of edges with
// node s as connection
int edges_in_a = graph[s].size();
// Traverse all the connections
// of node s
for (int i = 0; i < edges_in_a; i++) {
// If the connected node
// isn't visited
if (!vis[graph[s][i].first]) {
// Push back edge value
// in temp_edge
temp_edge.push_back(
graph[s][i].second);
// Call DFS function recursively
dfs_all(n, graph[s][i].first,
d, graph, vis,
edge_path, temp_edge);
// Pop back last added edge
temp_edge.pop_back();
}
}
// Mark s as unvisited for more
// possible paths
vis[s] = false;
}
// Function to find the minimum sum of
// edges from source to destination
// after reducing at most K cost to 0
int getDistance(
vector >& edge_path, int k)
{
int shortestDistance = INT_MAX;
// If edge_path vector is empty,
// means no path exist
if (edge_path.empty())
return -1;
// Traverse all the vector in
// the edge_path
for (auto x : edge_path) {
if (k == x.size())
return 0;
// Use heap to store the array
priority_queue,
greater >
minHeap;
// Find the sum of all the nodes
int sum = 0;
// Find the sum of k largest nodes
int ksum = 0;
// Find the largest K edges using
// minHeap
for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++) {
sum += x[i];
ksum += x[i];
// Pushing edge in MinHeap
minHeap.push(x[i]);
// If heap size is K
if (minHeap.size() > k) {
ksum -= minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
}
}
// If the shortestDistance is
// smallest, then update the
// shortestDistance
shortestDistance
= min(sum - ksum, shortestDistance);
}
// Return the shortestDistance
return shortestDistance;
}
// Function to find the minimum sum of
// weight of edges among all paths from
// source to destination after reducing
// at most K cost to 0
int solve(
vector > > graph,
int n, int k, int src, int dest)
{
// Stores all the vectors of edges for
// every path traversed in DFS call
vector > edge_path;
// Store the edges of particular path
vector temp_edge;
// Boolean visited vector
vector vis(n, false);
// DFS Call
dfs_all(n, src, dest, graph,
vis, edge_path, temp_edge);
return getDistance(edge_path, k);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 5, e = 5, k = 1;
vector > > graph(n);
// Given Adjacency List
graph[0].push_back(make_pair(1, 1));
graph[1].push_back(make_pair(0, 1));
graph[0].push_back(make_pair(4, 1));
graph[4].push_back(make_pair(0, 1));
graph[1].push_back(make_pair(2, 2));
graph[2].push_back(make_pair(1, 2));
graph[2].push_back(make_pair(3, 4));
graph[3].push_back(make_pair(2, 4));
graph[4].push_back(make_pair(3, 7));
graph[3].push_back(make_pair(4, 7));
int a = 0, b = 3;
cout << solve(graph, n, k, a, b);
return 0;
}
1
时间复杂度: O((N*log K)N N )
辅助空间: O(N 2 )