给定一个无向的未加权图。任务是找到给定图中最短周期的长度。如果不存在循环,则打印 -1。
例子:
Input:

Output: 4
Cycle 6 -> 1 -> 5 -> 0 -> 6
Input:
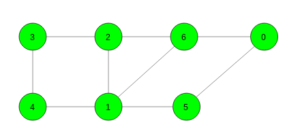
Output: 3
Cycle 6 -> 1 -> 2 -> 6
先决条件: Dijkstra
方法:对于每个顶点,我们检查是否有可能获得涉及该顶点的最短周期。对于每个顶点,首先将当前顶点推入队列,然后是它的邻居,如果已经访问过的顶点再次出现,则循环存在。
对每个顶点应用上述过程,得到最短周期的长度。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
#define N 100200
vector gr[N];
// Function to add edge
void Add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].push_back(y);
gr[y].push_back(x);
}
// Function to find the length of
// the shortest cycle in the graph
int shortest_cycle(int n)
{
// To store length of the shortest cycle
int ans = INT_MAX;
// For all vertices
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Make distance maximum
vector dist(n, (int)(1e9));
// Take a imaginary parent
vector par(n, -1);
// Distance of source to source is 0
dist[i] = 0;
queue q;
// Push the source element
q.push(i);
// Continue until queue is not empty
while (!q.empty()) {
// Take the first element
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
// Traverse for all it's childs
for (int child : gr[x]) {
// If it is not visited yet
if (dist[child] == (int)(1e9)) {
// Increase distance by 1
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
// Change parent
par[child] = x;
// Push into the queue
q.push(child);
}
// If it is already visited
else if (par[x] != child and par[child] != x)
ans = min(ans, dist[x] + dist[child] + 1);
}
}
}
// If graph contains no cycle
if (ans == INT_MAX)
return -1;
// If graph contains cycle
else
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Number of vertices
int n = 7;
// Add edges
Add_edge(0, 6);
Add_edge(0, 5);
Add_edge(5, 1);
Add_edge(1, 6);
Add_edge(2, 6);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
Add_edge(4, 1);
// Function call
cout << shortest_cycle(n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static final int N = 100200;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector[] gr = new Vector[N];
// Function to add edge
static void Add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].add(y);
gr[y].add(x);
}
// Function to find the length of
// the shortest cycle in the graph
static int shortest_cycle(int n)
{
// To store length of the shortest cycle
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// For all vertices
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Make distance maximum
int[] dist = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, (int) 1e9);
// Take a imaginary parent
int[] par = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(par, -1);
// Distance of source to source is 0
dist[i] = 0;
Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
// Push the source element
q.add(i);
// Continue until queue is not empty
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
// Take the first element
int x = q.poll();
// Traverse for all it's childs
for (int child : gr[x])
{
// If it is not visited yet
if (dist[child] == (int) (1e9))
{
// Increase distance by 1
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
// Change parent
par[child] = x;
// Push into the queue
q.add(child);
} else if (par[x] != child && par[child] != x)
ans = Math.min(ans, dist[x] + dist[child] + 1);
}
}
}
// If graph contains no cycle
if (ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE)
return -1;
// If graph contains cycle
else
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
gr[i] = new Vector<>();
// Number of vertices
int n = 7;
// Add edges
Add_edge(0, 6);
Add_edge(0, 5);
Add_edge(5, 1);
Add_edge(1, 6);
Add_edge(2, 6);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
Add_edge(4, 1);
// Function call
System.out.println(shortest_cycle(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552 Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
from sys import maxsize as INT_MAX
from collections import deque
N = 100200
gr = [0] * N
for i in range(N):
gr[i] = []
# Function to add edge
def add_edge(x: int, y: int) -> None:
global gr
gr[x].append(y)
gr[y].append(x)
# Function to find the length of
# the shortest cycle in the graph
def shortest_cycle(n: int) -> int:
# To store length of the shortest cycle
ans = INT_MAX
# For all vertices
for i in range(n):
# Make distance maximum
dist = [int(1e9)] * n
# Take a imaginary parent
par = [-1] * n
# Distance of source to source is 0
dist[i] = 0
q = deque()
# Push the source element
q.append(i)
# Continue until queue is not empty
while q:
# Take the first element
x = q[0]
q.popleft()
# Traverse for all it's childs
for child in gr[x]:
# If it is not visited yet
if dist[child] == int(1e9):
# Increase distance by 1
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x]
# Change parent
par[child] = x
# Push into the queue
q.append(child)
# If it is already visited
elif par[x] != child and par[child] != x:
ans = min(ans, dist[x] +
dist[child] + 1)
# If graph contains no cycle
if ans == INT_MAX:
return -1
# If graph contains cycle
else:
return ans
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Number of vertices
n = 7
# Add edges
add_edge(0, 6)
add_edge(0, 5)
add_edge(5, 1)
add_edge(1, 6)
add_edge(2, 6)
add_edge(2, 3)
add_edge(3, 4)
add_edge(4, 1)
# Function call
print(shortest_cycle(n))
# This code is contributed by
# sanjeev2552C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static readonly int N = 100200;
static List[] gr = new List[N];
// Function to add edge
static void Add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].Add(y);
gr[y].Add(x);
}
// Function to find the length of
// the shortest cycle in the graph
static int shortest_cycle(int n)
{
// To store length of the shortest cycle
int ans = int.MaxValue;
// For all vertices
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Make distance maximum
int[] dist = new int[n];
fill(dist, (int) 1e9);
// Take a imaginary parent
int[] par = new int[n];
fill(par, -1);
// Distance of source to source is 0
dist[i] = 0;
List q = new List();
// Push the source element
q.Add(i);
// Continue until queue is not empty
while (q.Count!=0)
{
// Take the first element
int x = q[0];
q.RemoveAt(0);
// Traverse for all it's childs
foreach (int child in gr[x])
{
// If it is not visited yet
if (dist[child] == (int) (1e9))
{
// Increase distance by 1
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
// Change parent
par[child] = x;
// Push into the queue
q.Add(child);
} else if (par[x] != child && par[child] != x)
ans = Math.Min(ans, dist[x] + dist[child] + 1);
}
}
}
// If graph contains no cycle
if (ans == int.MaxValue)
return -1;
// If graph contains cycle
else
return ans;
}
static int[] fill(int []arr, int val)
{
for(int i = 0;i();
// Number of vertices
int n = 7;
// Add edges
Add_edge(0, 6);
Add_edge(0, 5);
Add_edge(5, 1);
Add_edge(1, 6);
Add_edge(2, 6);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
Add_edge(4, 1);
// Function call
Console.WriteLine(shortest_cycle(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Javascript
输出:
4如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。