检测无向图中的循环
给定一个无向图,如何检查图中是否存在环?
例子,
Input: n = 4, e = 4
Output: Yes
Explanation:
0 1, 1 2, 2 3, 0 2
Diagram:
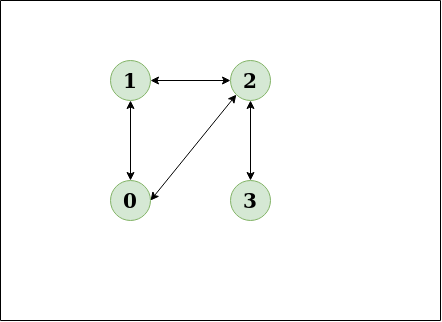
The diagram clearly shows a cycle 0 to 2 to 1 to 0
Input:n = 4, e = 3
0 1, 1 2, 2 3
Output:No
Explanation:
Diagram:
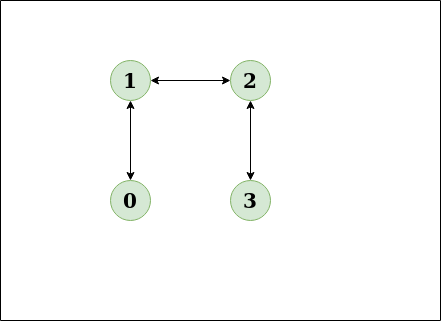
The diagram clearly shows no cycle
关于循环检测的文章:
- 有向图的循环检测。
- 无向图中循环检测的联合查找算法。
方法:从每个未访问的节点运行 DFS。深度优先遍历可用于检测图中的循环。连通图的 DFS 生成一棵树。仅当图中存在后边时,图中才存在循环。后边是将节点连接到自身(自循环)或其在 DFS 生成的树中的祖先之一的边。
要找到其任何祖先的后边缘,请保留一个已访问数组,如果任何已访问节点存在后边缘,则存在一个循环并返回 true。
算法:
- 使用给定数量的边和顶点创建图形。
- 创建一个具有当前索引或顶点、访问数组和父节点的递归函数。
- 将当前节点标记为已访问。
- 找到所有未访问且与当前节点相邻的顶点。递归调用这些顶点的函数,如果递归函数返回true,则返回true。
- 如果相邻节点不是父节点并且已经访问过,则返回 true。
- 创建一个包装类,它为所有顶点调用递归函数,如果任何函数返回 true,则返回 true。
- 否则,如果对于所有顶点,该函数返回 false,则返回 false。
空跑:
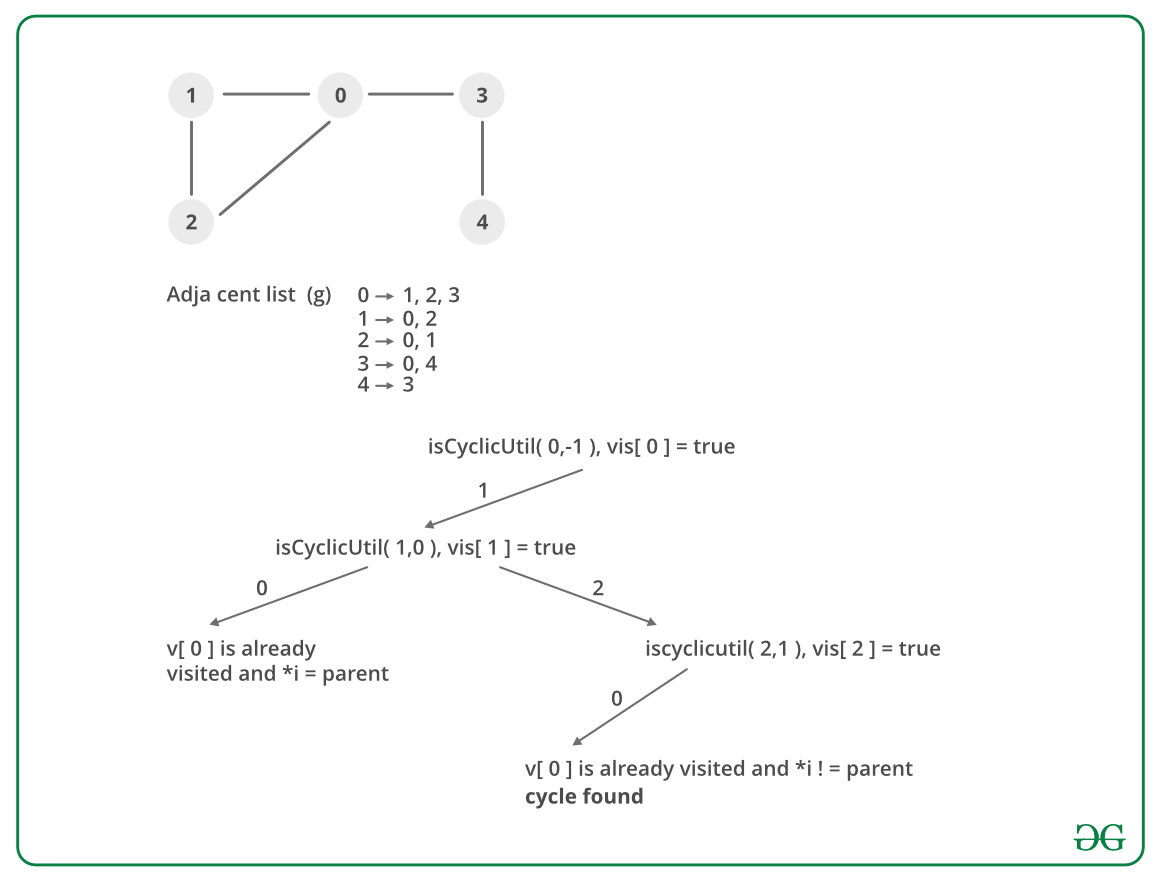
执行:
C++
// A C++ Program to detect
// cycle in an undirected graph
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Class for an undirected graph
class Graph
{
// No. of vertices
int V;
// Pointer to an array
// containing adjacency lists
list *adj;
bool isCyclicUtil(int v, bool visited[],
int parent);
public:
// Constructor
Graph(int V);
// To add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// Returns true if there is a cycle
bool isCyclic();
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
// Add w to v’s list.
adj[v].push_back(w);
// Add v to w’s list.
adj[w].push_back(v);
}
// A recursive function that
// uses visited[] and parent to detect
// cycle in subgraph reachable
// from vertex v.
bool Graph::isCyclicUtil(int v,
bool visited[], int parent)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i !=
adj[v].end(); ++i)
{
// If an adjacent vertex is not visited,
//then recur for that adjacent
if (!visited[*i])
{
if (isCyclicUtil(*i, visited, v))
return true;
}
// If an adjacent vertex is visited and
// is not parent of current vertex,
// then there exists a cycle in the graph.
else if (*i != parent)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Returns true if the graph contains
// a cycle, else false.
bool Graph::isCyclic()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not
// visited and not part of recursion
// stack
bool *visited = new bool[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Call the recursive helper
// function to detect cycle in different
// DFS trees
for (int u = 0; u < V; u++)
{
// Don't recur for u if
// it is already visited
if (!visited[u])
if (isCyclicUtil(u, visited, -1))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
Graph g1(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(2, 1);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
g1.isCyclic()?
cout << "Graph contains cycle\n":
cout << "Graph doesn't contain cycle\n";
Graph g2(3);
g2.addEdge(0, 1);
g2.addEdge(1, 2);
g2.isCyclic()?
cout << "Graph contains cycle\n":
cout << "Graph doesn't contain cycle\n";
return 0;
}
Java
// A Java Program to detect cycle in an undirected graph
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// This class represents a
// directed graph using adjacency list
// representation
class Graph
{
// No. of vertices
private int V;
// Adjacency List Representation
private LinkedList adj[];
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for(int i=0; i it =
adj[v].iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
{
i = it.next();
// If an adjacent is not
// visited, then recur for that
// adjacent
if (!visited[i])
{
if (isCyclicUtil(i, visited, v))
return true;
}
// If an adjacent is visited
// and not parent of current
// vertex, then there is a cycle.
else if (i != parent)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Returns true if the graph
// contains a cycle, else false.
Boolean isCyclic()
{
// Mark all the vertices as
// not visited and not part of
// recursion stack
Boolean visited[] = new Boolean[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Call the recursive helper
// function to detect cycle in
// different DFS trees
for (int u = 0; u < V; u++)
{
// Don't recur for u if already visited
if (!visited[u])
if (isCyclicUtil(u, visited, -1))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Driver method to test above methods
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Create a graph given
// in the above diagram
Graph g1 = new Graph(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(2, 1);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
if (g1.isCyclic())
System.out.println("Graph
contains cycle");
else
System.out.println("Graph
doesn't contains cycle");
Graph g2 = new Graph(3);
g2.addEdge(0, 1);
g2.addEdge(1, 2);
if (g2.isCyclic())
System.out.println("Graph
contains cycle");
else
System.out.println("Graph
doesn't contains cycle");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija Python3
# Python Program to detect cycle in an undirected graph
from collections import defaultdict
# This class represents a undirected
# graph using adjacency list representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self,vertices):
# No. of vertices
self.V= vertices #No. of vertices
# Default dictionary to store graph
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
# Function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self,v,w):
#Add w to v_s list
self.graph[v].append(w)
#Add v to w_s list
self.graph[w].append(v)
# A recursive function that uses
# visited[] and parent to detect
# cycle in subgraph reachable from vertex v.
def isCyclicUtil(self,v,visited,parent):
# Mark the current node as visited
visited[v]= True
# Recur for all the vertices
# adjacent to this vertex
for i in self.graph[v]:
# If the node is not
# visited then recurse on it
if visited[i]==False :
if(self.isCyclicUtil(i,visited,v)):
return True
# If an adjacent vertex is
# visited and not parent
# of current vertex,
# then there is a cycle
elif parent!=i:
return True
return False
# Returns true if the graph
# contains a cycle, else false.
def isCyclic(self):
# Mark all the vertices
# as not visited
visited =[False]*(self.V)
# Call the recursive helper
# function to detect cycle in different
# DFS trees
for i in range(self.V):
# Don't recur for u if it
# is already visited
if visited[i] ==False:
if(self.isCyclicUtil
(i,visited,-1)) == True:
return True
return False
# Create a graph given in the above diagram
g = Graph(5)
g.addEdge(1, 0)
g.addEdge(1, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 0)
g.addEdge(0, 3)
g.addEdge(3, 4)
if g.isCyclic():
print ("Graph contains cycle")
else :
print ("Graph does not contain cycle ")
g1 = Graph(3)
g1.addEdge(0,1)
g1.addEdge(1,2)
if g1.isCyclic():
print ("Graph contains cycle")
else :
print ("Graph does not contain cycle ")
#This code is contributed by Neelam YadavC#
// C# Program to detect cycle in an undirected graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// This class represents a directed graph
// using adjacency list representation
class Graph
{
private int V; // No. of vertices
// Adjacency List Representation
private List []adj;
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new List[v];
for(int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new List();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].Add(w);
adj[w].Add(v);
}
// A recursive function that uses visited[]
// and parent to detect cycle in subgraph
// reachable from vertex v.
Boolean isCyclicUtil(int v, Boolean []visited,
int parent)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
foreach(int i in adj[v])
{
// If an adjacent is not visited,
// then recur for that adjacent
if (!visited[i])
{
if (isCyclicUtil(i, visited, v))
return true;
}
// If an adjacent is visited and
// not parent of current vertex,
// then there is a cycle.
else if (i != parent)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Returns true if the graph contains
// a cycle, else false.
Boolean isCyclic()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
// and not part of recursion stack
Boolean []visited = new Boolean[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Call the recursive helper function
// to detect cycle in different DFS trees
for (int u = 0; u < V; u++)
// Don't recur for u if already visited
if (!visited[u])
if (isCyclicUtil(u, visited, -1))
return true;
return false;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g1 = new Graph(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(2, 1);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
if (g1.isCyclic())
Console.WriteLine("Graph contains cycle");
else
Console.WriteLine("Graph doesn't contains cycle");
Graph g2 = new Graph(3);
g2.addEdge(0, 1);
g2.addEdge(1, 2);
if (g2.isCyclic())
Console.WriteLine("Graph contains cycle");
else
Console.WriteLine("Graph doesn't contains cycle");
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 输出:
Graph contains cycle
Graph doesn't contain cycle复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(V+E)。
该程序对使用邻接表表示的图进行简单的 DFS 遍历。所以时间复杂度是O(V+E)。 - 空间复杂度: O(V)。
存储访问过的数组需要 O(V) 空间。