打印无向图中的所有循环
给定一个无向图,打印其中形成循环的所有顶点。
先决条件:使用颜色检测有向图中的循环
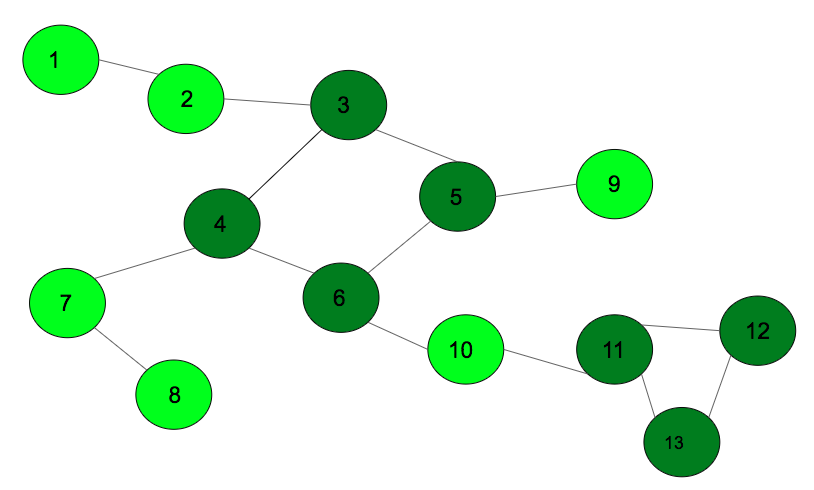
在上图中,循环已用深绿色标记。以上的输出将是
1st cycle: 3 5 4 6
2nd cycle: 11 12 13
方法:使用图形着色方法,用唯一的数字标记不同循环的所有顶点。一旦图遍历完成,将所有相似的标记数字推送到邻接表并相应地打印邻接表。下面给出算法:
- 将边缘插入邻接列表。
- 调用使用着色方法标记顶点的 DFS函数。
- 每当有一个部分访问的顶点时,回溯直到到达当前顶点并用循环数标记所有顶点。标记完所有顶点后,增加循环数。
- 一旦 Dfs 完成,迭代边缘并将相同的标记数字边缘推送到另一个邻接列表。
- 迭代另一个邻接列表并打印顶点循环数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to print all the cycles
// in an undirected graph
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 100000;
// variables to be used
// in both functions
vector graph[N];
vector cycles[N];
// Function to mark the vertex with
// different colors for different cycles
void dfs_cycle(int u, int p, int color[],
int mark[], int par[], int& cyclenumber)
{
// already (completely) visited vertex.
if (color[u] == 2) {
return;
}
// seen vertex, but was not completely visited -> cycle detected.
// backtrack based on parents to find the complete cycle.
if (color[u] == 1) {
cyclenumber++;
int cur = p;
mark[cur] = cyclenumber;
// backtrack the vertex which are
// in the current cycle thats found
while (cur != u) {
cur = par[cur];
mark[cur] = cyclenumber;
}
return;
}
par[u] = p;
// partially visited.
color[u] = 1;
// simple dfs on graph
for (int v : graph[u]) {
// if it has not been visited previously
if (v == par[u]) {
continue;
}
dfs_cycle(v, u, color, mark, par, cyclenumber);
}
// completely visited.
color[u] = 2;
}
// add the edges to the graph
void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
// Function to print the cycles
void printCycles(int edges, int mark[], int& cyclenumber)
{
// push the edges that into the
// cycle adjacency list
for (int i = 1; i <= edges; i++) {
if (mark[i] != 0)
cycles[mark[i]].push_back(i);
}
// print all the vertex with same cycle
for (int i = 1; i <= cyclenumber; i++) {
// Print the i-th cycle
cout << "Cycle Number " << i << ": ";
for (int x : cycles[i])
cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// add edges
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(2, 3);
addEdge(3, 4);
addEdge(4, 6);
addEdge(4, 7);
addEdge(5, 6);
addEdge(3, 5);
addEdge(7, 8);
addEdge(6, 10);
addEdge(5, 9);
addEdge(10, 11);
addEdge(11, 12);
addEdge(11, 13);
addEdge(12, 13);
// arrays required to color the
// graph, store the parent of node
int color[N];
int par[N];
// mark with unique numbers
int mark[N];
// store the numbers of cycle
int cyclenumber = 0;
int edges = 13;
// call DFS to mark the cycles
dfs_cycle(1, 0, color, mark, par, cyclenumber);
// function to print the cycles
printCycles(edges, mark, cyclenumber);
} Java
// Java program to print all the cycles
// in an undirected graph
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static final int N = 100000;
// variables to be used
// in both functions
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector[] graph = new Vector[N];
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector[] cycles = new Vector[N];
static int cyclenumber;
// Function to mark the vertex with
// different colors for different cycles
static void dfs_cycle(int u, int p, int[] color,
int[] mark, int[] par)
{
// already (completely) visited vertex.
if (color[u] == 2)
{
return;
}
// seen vertex, but was not completely visited -> cycle detected.
// backtrack based on parents to find the complete cycle.
if (color[u] == 1)
{
cyclenumber++;
int cur = p;
mark[cur] = cyclenumber;
// backtrack the vertex which are
// in the current cycle thats found
while (cur != u)
{
cur = par[cur];
mark[cur] = cyclenumber;
}
return;
}
par[u] = p;
// partially visited.
color[u] = 1;
// simple dfs on graph
for (int v : graph[u])
{
// if it has not been visited previously
if (v == par[u])
{
continue;
}
dfs_cycle(v, u, color, mark, par);
}
// completely visited.
color[u] = 2;
}
// add the edges to the graph
static void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
graph[u].add(v);
graph[v].add(u);
}
// Function to print the cycles
static void printCycles(int edges, int mark[])
{
// push the edges that into the
// cycle adjacency list
for (int i = 1; i <= edges; i++)
{
if (mark[i] != 0)
cycles[mark[i]].add(i);
}
// print all the vertex with same cycle
for (int i = 1; i <= cyclenumber; i++)
{
// Print the i-th cycle
System.out.printf("Cycle Number %d: ", i);
for (int x : cycles[i])
System.out.printf("%d ", x);
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
graph[i] = new Vector<>();
cycles[i] = new Vector<>();
}
// add edges
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(2, 3);
addEdge(3, 4);
addEdge(4, 6);
addEdge(4, 7);
addEdge(5, 6);
addEdge(3, 5);
addEdge(7, 8);
addEdge(6, 10);
addEdge(5, 9);
addEdge(10, 11);
addEdge(11, 12);
addEdge(11, 13);
addEdge(12, 13);
// arrays required to color the
// graph, store the parent of node
int[] color = new int[N];
int[] par = new int[N];
// mark with unique numbers
int[] mark = new int[N];
// store the numbers of cycle
cyclenumber = 0;
int edges = 13;
// call DFS to mark the cycles
dfs_cycle(1, 0, color, mark, par);
// function to print the cycles
printCycles(edges, mark);
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552 Python3
# Python3 program to print all the cycles
# in an undirected graph
N = 100000
# variables to be used
# in both functions
graph = [[] for i in range(N)]
cycles = [[] for i in range(N)]
# Function to mark the vertex with
# different colors for different cycles
def dfs_cycle(u, p, color: list,
mark: list, par: list):
global cyclenumber
# already (completely) visited vertex.
if color[u] == 2:
return
# seen vertex, but was not
# completely visited -> cycle detected.
# backtrack based on parents to
# find the complete cycle.
if color[u] == 1:
cyclenumber += 1
cur = p
mark[cur] = cyclenumber
# backtrack the vertex which are
# in the current cycle thats found
while cur != u:
cur = par[cur]
mark[cur] = cyclenumber
return
par[u] = p
# partially visited.
color[u] = 1
# simple dfs on graph
for v in graph[u]:
# if it has not been visited previously
if v == par[u]:
continue
dfs_cycle(v, u, color, mark, par)
# completely visited.
color[u] = 2
# add the edges to the graph
def addEdge(u, v):
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
# Function to print the cycles
def printCycles(edges, mark: list):
# push the edges that into the
# cycle adjacency list
for i in range(1, edges + 1):
if mark[i] != 0:
cycles[mark[i]].append(i)
# print all the vertex with same cycle
for i in range(1, cyclenumber + 1):
# Print the i-th cycle
print("Cycle Number %d:" % i, end = " ")
for x in cycles[i]:
print(x, end = " ")
print()
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# add edges
addEdge(1, 2)
addEdge(2, 3)
addEdge(3, 4)
addEdge(4, 6)
addEdge(4, 7)
addEdge(5, 6)
addEdge(3, 5)
addEdge(7, 8)
addEdge(6, 10)
addEdge(5, 9)
addEdge(10, 11)
addEdge(11, 12)
addEdge(11, 13)
addEdge(12, 13)
# arrays required to color the
# graph, store the parent of node
color = [0] * N
par = [0] * N
# mark with unique numbers
mark = [0] * N
# store the numbers of cycle
cyclenumber = 0
edges = 13
# call DFS to mark the cycles
dfs_cycle(1, 0, color, mark, par)
# function to print the cycles
printCycles(edges, mark)
# This code is contributed by
# sanjeev2552C#
// C# program to print all
// the cycles in an undirected
// graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static readonly int N = 100000;
// variables to be used
// in both functions
static List[] graph =
new List[N];
static List[] cycles =
new List[N];
static int cyclenumber;
// Function to mark the vertex with
// different colors for different cycles
static void dfs_cycle(int u, int p,
int[] color,
int[] mark,
int[] par)
{
// already (completely)
// visited vertex.
if (color[u] == 2)
{
return;
}
// seen vertex, but was not
// completely visited -> cycle
// detected. backtrack based on
// parents to find the complete
// cycle.
if (color[u] == 1)
{
cyclenumber++;
int cur = p;
mark[cur] = cyclenumber;
// backtrack the vertex which
// are in the current cycle
// thats found
while (cur != u)
{
cur = par[cur];
mark[cur] = cyclenumber;
}
return;
}
par[u] = p;
// partially visited.
color[u] = 1;
// simple dfs on graph
foreach (int v in graph[u])
{
// if it has not been
// visited previously
if (v == par[u])
{
continue;
}
dfs_cycle(v, u, color,
mark, par);
}
// completely visited.
color[u] = 2;
}
// add the edges to the
// graph
static void addEdge(int u,
int v)
{
graph[u].Add(v);
graph[v].Add(u);
}
// Function to print the cycles
static void printCycles(int edges,
int []mark)
{
// push the edges that into the
// cycle adjacency list
for (int i = 1; i <= edges; i++)
{
if (mark[i] != 0)
cycles[mark[i]].Add(i);
}
// print all the vertex with
// same cycle
for (int i = 1;
i <= cyclenumber; i++)
{
// Print the i-th cycle
Console.Write("Cycle Number " + i + ":");
foreach (int x in cycles[i])
Console.Write(" " + x);
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
graph[i] = new List();
cycles[i] = new List();
}
// add edges
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(2, 3);
addEdge(3, 4);
addEdge(4, 6);
addEdge(4, 7);
addEdge(5, 6);
addEdge(3, 5);
addEdge(7, 8);
addEdge(6, 10);
addEdge(5, 9);
addEdge(10, 11);
addEdge(11, 12);
addEdge(11, 13);
addEdge(12, 13);
// arrays required to color
// the graph, store the parent
// of node
int[] color = new int[N];
int[] par = new int[N];
// mark with unique numbers
int[] mark = new int[N];
// store the numbers of cycle
cyclenumber = 0;
int edges = 13;
// call DFS to mark
// the cycles
dfs_cycle(1, 0, color,
mark, par);
// function to print the cycles
printCycles(edges, mark);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar Javascript
输出:
Cycle Number 1: 3 4 5 6
Cycle Number 2: 11 12 13 时间复杂度: O(N + M),其中 N 是顶点数,M 是边数。
辅助空间: O(N + M)