给定一个图,任务是使用图中节点的度数检测图中的循环,并打印任何循环中涉及的所有节点。如果图中没有循环,则打印-1 。
例子:
Input:
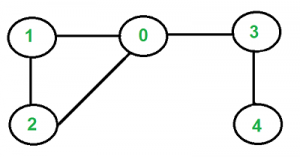
Output: 0 1 2
方法:递归地移除所有度数为 1 的顶点。这可以通过存储顶点到它们度数的映射来有效地完成。
最初,遍历地图并将度数 = 1 的所有顶点存储在队列中。只要队列不为空,就遍历队列。对于队列中的每个节点,将其标记为已访问,并遍历所有连接到它的节点(使用邻接表),并在映射中将每个节点的度数减 1。将所有度数等于 1 的节点添加到队列中。在这个算法结束时,所有未被访问的节点都是循环的一部分。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++14
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Graph class
class Graph
{
public:
// No. of vertices of graph
int v;
// Adjacency List
vector *l;
Graph(int v)
{
this->v = v;
this->l = new vector[v];
}
void addedge(int i, int j)
{
l[i].push_back(j);
l[j].push_back(i);
}
};
// Function to find a cycle in the given graph if exists
void findCycle(int n, int r, Graph g)
{
// HashMap to store the degree of each node
unordered_map degree;
for (int i = 0; i < g.v; i++)
degree[i] = g.l[i].size();
// Array to track visited nodes
int visited[g.v] = {0};
// Queue to store the nodes of degree 1
queue q;
// Continuously adding those nodes whose
// degree is 1 to the queue
while (true)
{
// Adding nodes to queue whose degree is 1
// and is not visited
for (int i = 0; i < degree.size(); i++)
if (degree.at(i) == 1 and !visited[i])
q.push(i);
// If queue becomes empty then get out
// of the continuous loop
if (q.empty())
break;
while (!q.empty())
{
// Remove the front element from the queue
int temp = q.front();
q.pop();
// Mark the removed element visited
visited[temp] = 1;
// Decrement the degree of all those nodes
// adjacent to removed node
for (int i = 0; i < g.l[temp].size(); i++)
{
int value = degree[g.l[temp][i]];
degree[g.l[temp][i]] = --value;
}
}
}
int flag = 0;
// Checking all the nodes which are not visited
// i.e. they are part of the cycle
for (int i = 0; i < g.v; i++)
if (visited[i] == 0)
flag = 1;
if (flag == 0)
cout << "-1";
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < g.v; i++)
if (visited[i] == 0)
cout << i << " ";
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// No of nodes
int n = 5;
// No of edges
int e = 5;
Graph g(n);
g.addedge(0, 1);
g.addedge(0, 2);
g.addedge(0, 3);
g.addedge(1, 2);
g.addedge(3, 4);
findCycle(n, e, g);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552 Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
// Graph class
class Graph {
// No. of vertices of graph
int v;
// Adjacency List
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ArrayList> l;
Graph(int v)
{
this.v = v;
this.l = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
l.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
}
void addedge(int i, int j)
{
l.get(i).add(j);
l.get(j).add(i);
}
}
class GFG {
// Function to find a cycle in the given graph if exists
static void findCycle(int n, int e, Graph g)
{
// HashMap to store the degree of each node
HashMap degree = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
degree.put(i, g.l.get(i).size());
// Array to track visited nodes
int visited[] = new int[g.v];
// Initially all nodes are not visited
for (int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++)
visited[i] = 0;
// Queue to store the nodes of degree 1
Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
// Continuously adding those nodes whose
// degree is 1 to the queue
while (true) {
// Adding nodes to queue whose degree is 1
// and is not visited
for (int i = 0; i < degree.size(); i++){
if ((int)degree.get(i) == 1 && visited[i] == 0)
q.add(i);
}
// If queue becomes empty then get out
// of the continuous loop
if (q.isEmpty())
break;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// Remove the front element from the queue
int temp = (int)q.poll();
// Mark the removed element visited
visited[temp] = 1;
// Decrement the degree of all those nodes
// adjacent to removed node
for (int i = 0; i < g.l.get(temp).size(); i++) {
int value = (int)degree.get((int)g.l.get(temp).get(i));
degree.replace(g.l.get(temp).get(i), --value);
}
}
}
int flag = 0;
// Checking all the nodes which are not visited
// i.e. they are part of the cycle
for (int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++)
if (visited[i] == 0)
flag = 1;
if (flag == 0)
System.out.print("-1");
else {
for (int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++)
if (visited[i] == 0)
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// No of nodes
int n = 5;
// No of edges
int e = 5;
Graph g = new Graph(n);
g.addedge(0, 1);
g.addedge(0, 2);
g.addedge(0, 3);
g.addedge(1, 2);
g.addedge(3, 4);
findCycle(n, e, g);
}
}
// This Code has been contributed by Mukul Sharma Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# Graph class
class Graph:
def __init__(self, v):
# No. of vertices of graph
self.v = v
# Adjacency List
self.l = [0] * v
for i in range(self.v):
self.l[i] = []
def addedge(self, i: int, j: int):
self.l[i].append(j)
self.l[j].append(i)
# Function to find a cycle in the given graph if exists
def findCycle(n: int, e: int, g: Graph) -> None:
# HashMap to store the degree of each node
degree = dict()
for i in range(len(g.l)):
degree[i] = len(g.l[i])
# Array to track visited nodes
visited = [0] * g.v
# Initially all nodes are not visited
for i in range(len(visited)):
visited[i] = 0
# Queue to store the nodes of degree 1
q = list()
# Continuously adding those nodes whose
# degree is 1 to the queue
while True:
# Adding nodes to queue whose degree is 1
# and is not visited
for i in range(len(degree)):
if degree[i] == 1 and visited[i] == 0:
q.append(i)
# If queue becomes empty then get out
# of the continuous loop
if len(q) == 0:
break
while q:
# Remove the front element from the queue
temp = q.pop()
# Mark the removed element visited
visited[temp] = 1
# Decrement the degree of all those nodes
# adjacent to removed node
for i in range(len(g.l[temp])):
value = degree[g.l[temp][i]]
degree[g.l[temp][i]] = value - 1
flag = 0
# Checking all the nodes which are not visited
# i.e. they are part of the cycle
for i in range(len(visited)):
if visited[i] == 0:
flag = 1
if flag == 0:
print("-1")
else:
for i in range(len(visited)):
if visited[i] == 0:
print(i, end = " ")
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# No of nodes
n = 5
# No of edges
e = 5
g = Graph(n)
g.addedge(0, 1)
g.addedge(0, 2)
g.addedge(0, 3)
g.addedge(1, 2)
g.addedge(3, 4)
findCycle(n, e, g)
# This code is contributed by
# sanjeev2552C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// Graph class
public class Graph
{
// No. of vertices of graph
public int v;
// Adjacency List
public List []l;
public Graph(int v)
{
this.v = v;
this.l = new List[v];
for(int i = 0; i < v; i++)
{
l[i] = new List();
}
}
public void addedge(int i, int j)
{
l[i].Add(j);
l[j].Add(i);
}
}
class GFG{
// Function to find a cycle in the
// given graph if exists
static void findCycle(int n, int e, Graph g)
{
// Dictionary to store the degree of each node
Dictionary degree = new Dictionary();
for(int i = 0; i < g.l.Length; i++)
degree.Add(i, g.l[i].Count);
// Array to track visited nodes
int []visited = new int[g.v];
// Initially all nodes are not visited
for(int i = 0; i < visited.Length; i++)
visited[i] = 0;
// Queue to store the nodes of degree 1
List q = new List();
// Continuously adding those nodes whose
// degree is 1 to the queue
while (true)
{
// Adding nodes to queue whose degree is 1
// and is not visited
for(int i = 0; i < degree.Count; i++)
if ((int)degree[i] == 1 && visited[i] == 0)
q.Add(i);
// If queue becomes empty then get out
// of the continuous loop
if (q.Count!=0)
break;
while (q.Count != 0)
{
// Remove the front element from the queue
int temp = q[0];
q.RemoveAt(0);
// Mark the removed element visited
visited[temp] = 1;
// Decrement the degree of all those nodes
// adjacent to removed node
for(int i = 0; i < g.l[temp].Count; i++)
{
int value = (int)degree[(int)g.l[temp][i]];
degree[g.l[temp][i]] = value -= 1;
}
}
}
int flag = 0;
// Checking all the nodes which are not visited
// i.e. they are part of the cycle
for(int i = 0; i < visited.Length; i++)
if (visited[i] == 0)
flag = 1;
if (flag == 0)
Console.Write("-1");
else
{
for(int i = 0; i < visited.Length-2; i++)
if (visited[i] == 0)
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// No of nodes
int n = 5;
// No of edges
int e = 5;
Graph g = new Graph(n);
g.addedge(0, 1);
g.addedge(0, 2);
g.addedge(0, 3);
g.addedge(1, 2);
g.addedge(3, 4);
findCycle(n, e, g);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh Javascript
输出:
0 1 2如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。