给定有向图的邻接表表示,任务是检查通过所有可能的路径从任何顶点到任何其他顶点的成本是否相等。如果从顶点A到顶点B的成本为c ,那么从顶点B到顶点A的成本将为-c 。
例子:
Input: arr[][] = {{0, 2, 0, 1}, {-2, 0, 1, 0}, {0, -1, 0, -2}, {-1, 0, 2, 0}}
Output: Yes
Explanation:

Here the cost of going from any node to any other node is equal for all possible paths. For example, if we go from 1 to 4 via (1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4) whose cost is (2 + 1 + (-2)) i.e. 1 and via ( 1 -> 4 ) which is a reverse edge whose cost is 1. Similarly, the cost for all other paths is equal.
Input: arr[][] = {{0, 1, 0, 3, 0}, {-1, 0, 3, 0, 4}, {0, -3, 0, 1, 1}, {-3, 0, -1, 0, 0}, {0, -4, -1, 0, 0}}
Output: No
Explanation:
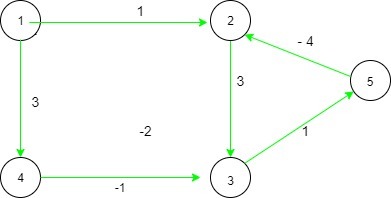
For the following two paths from edge 1 to 4, (1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4), Cost = (1 + 3 + 1) = 5 and (1 -> 4), Cost = 3. Since the costs are difference, the answer is No
方法:这个想法是维护两个数组dis[] ,它维护行进路径的距离和visited[] ,它维护访问过的顶点。该图使用成对的二维向量存储。该对的第一个值是目标节点,第二个值是与之相关的成本。现在,DFS 在图上运行。每个顶点都会出现以下两种情况:
- 如果没有访问到达下一个节点,则该DIS数组与值DIS [CURRENT_NODE]新边缘的+成本从2D发现矢量即当前节点到下一个节点以达到和相同的函数被调用与更新的未访问的同一个节点。
- 如果访问了该节点,则将下一个要到达的节点的距离与 dis[curr] + 到达下一个节点的边的成本进行比较。如果它们相等,则布尔变量标志被更新为真并且循环继续到下一个顶点。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
vector > adj[100005];
// Initialize distance and visited array
int vis[100005] = { 0 },
dist[100005] = { 0 },
flg;
// Function to perform dfs and check
// For a given vertex If the distance
// for all the paths is equal or not
void dfs(int curr)
{
vis[curr] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < adj[curr].size(); i++) {
// Checking the next node to reach
// is visited or not
if (vis[adj[curr][i].first]) {
// Case 2: comparing the distance
if (dist[adj[curr][i].first]
!= dist[curr] + adj[curr][i].second)
flg = 1;
}
else {
// Case 1: Adding the distance
// and updating the array
dist[adj[curr][i].first] = dist[curr]
+ adj[curr][i].second;
// Calling the function again with the
// same node
dfs(adj[curr][i].first);
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 4, m = 4;
flg = 0;
// Creating the graph as mentioned
// in example 1
adj[0].push_back({ 1, 2 });
adj[1].push_back({ 0, -2 });
adj[1].push_back({ 2, 1 });
adj[2].push_back({ 1, -1 });
adj[2].push_back({ 3, -2 });
adj[3].push_back({ 2, 2 });
adj[3].push_back({ 0, -1 });
adj[0].push_back({ 3, 1 });
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (flg)
// If for any vertex, flg is true,
// then the distance is not equal
break;
if (!vis[i])
// Calling the DFS function if
// the vertex is not visited
dfs(i);
}
if (flg)
cout << "No" << endl;
else
cout << "Yes" << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static class pair {
int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second) {
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
static Vector[] adj = new Vector[100005];
// Initialize distance and visited array
static int[] vis = new int[100005];
static int[] dist = new int[100005];
static int flg;
// Function to perform dfs and check
// For a given vertex If the distance
// for all the paths is equal or not
static void dfs(int curr) {
vis[curr] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < adj[curr].size(); i++) {
// Checking the next node to reach
// is visited or not
if (vis[adj[curr].get(i).first] > 0) {
// Case 2: comparing the distance
if (dist[adj[curr].get(i).first] !=
dist[curr] + adj[curr].get(i).second)
flg = 1;
} else {
// Case 1: Adding the distance
// and updating the array
dist[adj[curr].get(i).first] =
dist[curr] + adj[curr].get(i).second;
// Calling the function again with the
// same node
dfs(adj[curr].get(i).first);
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 4, m = 4;
flg = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++) {
adj[i] = new Vector();
}
// Creating the graph as mentioned
// in example 1
adj[0].add(new pair(1, 2));
adj[1].add(new pair(0, -2));
adj[1].add(new pair(2, 1));
adj[2].add(new pair(1, -1));
adj[2].add(new pair(3, -2));
adj[3].add(new pair(2, 2));
adj[3].add(new pair(0, -1));
adj[0].add(new pair(3, 1));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (flg == 1)
// If for any vertex, flg is true,
// then the distance is not equal
break;
if (vis[i] != 1)
// Calling the DFS function if
// the vertex is not visited
dfs(i);
}
if (flg == 1)
System.out.print("No" + "\n");
else
System.out.print("Yes" + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 Python3
# Python3 implementation of the above approach
adj = [[] for i in range(100005)]
# Initialize distance and visited array
vis = [0]*100005
dist = [0]*100005
flg = 0
# Function to perform dfs and check
# For a given vertex If the distance
# for all the paths is equal or not
def dfs(curr):
vis[curr] = 1
for i in range(len(adj[curr])):
# Checking the next node to reach
# is visited or not
if (vis[adj[curr][i][0]]):
# Case 2: comparing the distance
if (dist[adj[curr][i][0]]
!= dist[curr] + adj[curr][i][1]):
flg = 1
else:
# Case 1: Adding the distance
# and updating the array
dist[adj[curr][i][0]] = dist[curr]+ adj[curr][i][1]
# Calling the function again with the
# same node
dfs(adj[curr][i][0])
# Driver code
n = 4
m = 4
flg = 0
# Creating the graph as mentioned
# in example 1
adj[0].append([1, 2])
adj[1].append([0, -2])
adj[1].append([2, 1])
adj[2].append([1, -1])
adj[2].append([3, -2])
adj[3].append([2, 2])
adj[3].append([0, -1])
adj[0].append([3, 1])
for i in range(n):
if (flg):
# If for any vertex, flg is true,
# then the distance is not equal
break
if (vis[i] == 0):
# Calling the DFS function if
# the vertex is not visited
dfs(i)
if (flg):
print("No")
else:
print("Yes")
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# implementation of the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
class pair {
public int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second) {
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
static List[] adj = new List[100005];
// Initialize distance and visited array
static int[] vis = new int[100005];
static int[] dist = new int[100005];
static int flg;
// Function to perform dfs and check
// For a given vertex If the distance
// for all the paths is equal or not
static void dfs(int curr) {
vis[curr] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < adj[curr].Count; i++) {
// Checking the next node to reach
// is visited or not
if (vis[adj[curr][i].first] > 0) {
// Case 2: comparing the distance
if (dist[adj[curr][i].first] !=
dist[curr] + adj[curr][i].second)
flg = 1;
} else {
// Case 1: Adding the distance
// and updating the array
dist[adj[curr][i].first] =
dist[curr] + adj[curr][i].second;
// Calling the function again with the
// same node
dfs(adj[curr][i].first);
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args) {
int n = 4;
flg = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < adj.Length; i++) {
adj[i] = new List();
}
// Creating the graph as mentioned
// in example 1
adj[0].Add(new pair(1, 2));
adj[1].Add(new pair(0, -2));
adj[1].Add(new pair(2, 1));
adj[2].Add(new pair(1, -1));
adj[2].Add(new pair(3, -2));
adj[3].Add(new pair(2, 2));
adj[3].Add(new pair(0, -1));
adj[0].Add(new pair(3, 1));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (flg == 1)
// If for any vertex, flg is true,
// then the distance is not equal
break;
if (vis[i] != 1)
// Calling the DFS function if
// the vertex is not visited
dfs(i);
}
if (flg == 1)
Console.Write("No" + "\n");
else
Console.Write("Yes" + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Javascript
Yes时间复杂度: O(V + E) 其中 V 是顶点数,E 是边数
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。