给定一个有V个顶点和E 条边的有向无环图,其中每条边{U, V}代表作业U和V,这样作业V只能在作业U完成后开始。任务是确定每个作业完成所需的最短时间,其中每个作业需要单位时间才能完成。
例子:
Input: N = 10, E = 13, Below is the given graph:
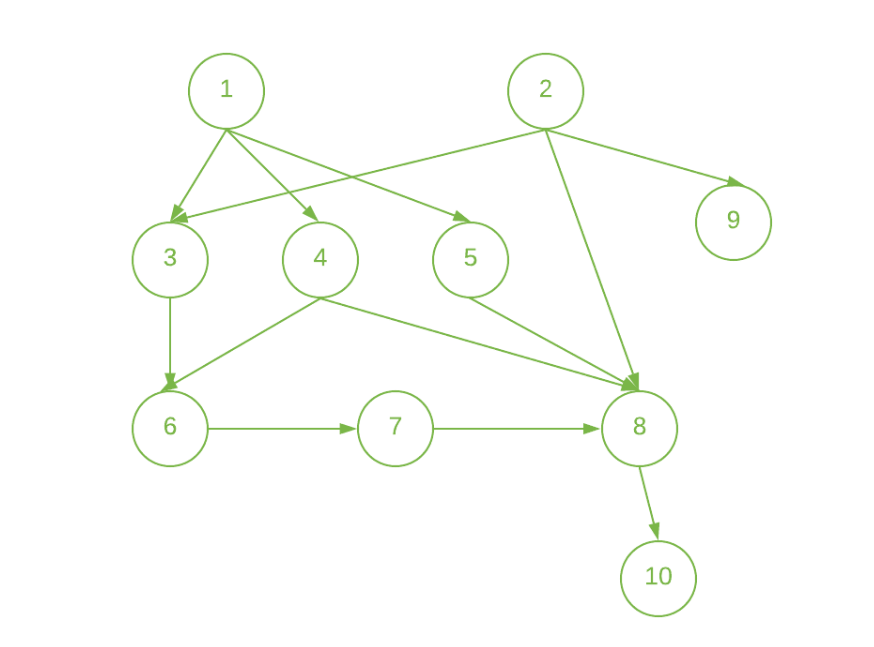
Output: 1 1 2 2 2 3 4 5 2 6
Explanation:
Start the jobs 1 and 2 at the beginning and complete them at 1 unit of time.
Since, jobs 3, 4, 5, and 9 have the only dependency on one job (i.e 1st job for jobs 3, 4, and 5 and 2nd job for job 9). So, we can start these jobs at 1st unit of time and complete these at 2nd unit of time after the completion of the dependent Job.
Similarly,
Job 6 can only be done after 3rd and 4th jobs are done. So, start it at 2nd unit of time and complete it at 3rd unit of time.
Job 7 can only be done after job 6 is done. So, you can start it at 3rd unit of time and complete it at 4th unit of time.
Job 8 can only be done after 4th, 5th, and 7th jobs are done. So, start it at 4th unit of time and complete it at 5th unit of time.
Job 10 can only be done after the 8th job is done. So, start it at 5th unit of time and complete it at 6th unit of time.
Input: N = 7, E = 7, Below is the given graph:
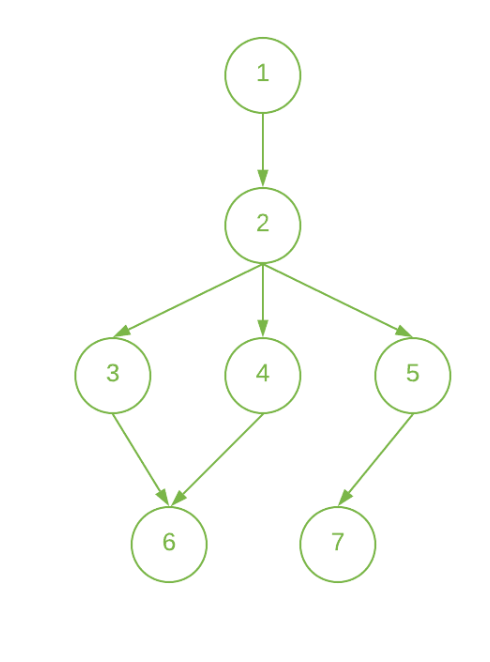
Output: 1 2 3 3 3 4 4
Explanation:
Start the Job 1 at the beginning and complete it at 1st unit of time.
The job 2 can only be done after 1st Job is done. So, start it at 1st unit of time and complete it at 2nd unit of time.
Since, Job 3, 4, and 5 have the only dependency on 2nd Job. So, start these jobs at 2nd unit of time and complete these at 3rd unit of time.
The Job 6 can only be done after the 3rd and 4th Job is done. So, start it at 3rd unit of time and complete it at 4th unit of time.
The Job 7 can only be done after the 5th Job is done. So, start it at 3rd hour and complete it at 4th unit of time.
方法:只有作为作业先决条件的所有作业都完成后,才能开始作业。因此,想法是对给定的网络使用拓扑排序。以下是步骤:
- 完成不依赖任何其他作业的作业。
- 创建一个数组inDegree[]来存储给定网络中每个节点的依赖节点的计数。
- 初始化一个队列并推送所有inDegree[]为 0 的顶点。
- 将计时器初始化为 1 并存储当前队列大小(比如size )并执行以下操作:
- 从队列中弹出节点,直到大小为0并将该节点的完成时间更新到计时器。
- 当从队列中弹出节点(比如节点U )时,减少连接到它的每个节点的inDegree 。
- 如果上述步骤中任何节点的inDegree为0 ,则将该节点插入队列。
- 在所有上述步骤之后增加计时器。
- 上一步遍历每个节点后,打印所有节点的完成时间。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
#define maxN 100000
// Adjacency List to store the graph
vector graph[maxN];
// Array to store the in-degree of node
int indegree[maxN];
// Array to store the time in which
// the job i can be done
int job[maxN];
// Function to add directed edge
// between two vertices
void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
// Insert edge from u to v
graph[u].push_back(v);
// Increasing the indegree
// of vertex v
indegree[v]++;
}
// Function to find the minimum time
// needed by each node to get the task
void printOrder(int n, int m)
{
// Find the topo sort order
// using the indegree approach
// Queue to store the
// nodes while processing
queue q;
// Pushing all the vertex in the
// queue whose in-degree is 0
// Update the time of the jobs
// who don't require any job to
// be completed before this job
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) {
q.push(i);
job[i] = 1;
}
}
// Iterate until queue is empty
while (!q.empty()) {
// Get front element of queue
int cur = q.front();
// Pop the front element
q.pop();
for (int adj : graph[cur]) {
// Decrease in-degree of
// the current node
indegree[adj]--;
// Push its adjacent elements
if (indegree[adj] == 0) {
job[adj] = job[cur] + 1;
q.push(adj);
}
}
}
// Print the time to complete
// the job
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << job[i] << " ";
cout << "\n";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Nodes N and edges M
int n, m;
n = 10;
m = 13;
// Given Directed Edges of graph
addEdge(1, 3);
addEdge(1, 4);
addEdge(1, 5);
addEdge(2, 3);
addEdge(2, 8);
addEdge(2, 9);
addEdge(3, 6);
addEdge(4, 6);
addEdge(4, 8);
addEdge(5, 8);
addEdge(6, 7);
addEdge(7, 8);
addEdge(8, 10);
// Function Call
printOrder(n, m);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static final int maxN = 100000;
// Adjacency List to store the graph
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector []graph = new Vector[maxN];
// Array to store the in-degree of node
static int []indegree = new int[maxN];
// Array to store the time in which
// the job i can be done
static int []job = new int[maxN];
// Function to add directed edge
// between two vertices
static void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
// Insert edge from u to v
graph[u].add(v);
// Increasing the indegree
// of vertex v
indegree[v]++;
}
// Function to find the minimum time
// needed by each node to get the task
static void printOrder(int n, int m)
{
// Find the topo sort order
// using the indegree approach
// Queue to store the
// nodes while processing
Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
// Pushing all the vertex in the
// queue whose in-degree is 0
// Update the time of the jobs
// who don't require any job to
// be completed before this job
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (indegree[i] == 0)
{
q.add(i);
job[i] = 1;
}
}
// Iterate until queue is empty
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
// Get front element of queue
int cur = q.peek();
// Pop the front element
q.remove();
for(int adj : graph[cur])
{
// Decrease in-degree of
// the current node
indegree[adj]--;
// Push its adjacent elements
if (indegree[adj] == 0){
job[adj] = 1 + job[cur];
q.add(adj);
}
}
}
// Print the time to complete
// the job
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
System.out.print(job[i] + " ");
System.out.print("\n");
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given Nodes N and edges M
int n, m;
n = 10;
m = 13;
for(int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++)
graph[i] = new Vector();
// Given directed edges of graph
addEdge(1, 3);
addEdge(1, 4);
addEdge(1, 5);
addEdge(2, 3);
addEdge(2, 8);
addEdge(2, 9);
addEdge(3, 6);
addEdge(4, 6);
addEdge(4, 8);
addEdge(5, 8);
addEdge(6, 7);
addEdge(7, 8);
addEdge(8, 10);
// Function call
printOrder(n, m);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
from collections import defaultdict
# Class to represent a graph
class Graph:
def __init__(self, vertices, edges):
# Dictionary containing adjacency List
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
# No. of vertices
self.n = vertices
# No. of edges
self.m = edges
# Function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
# Function to find the minimum time
# needed by each node to get the task
def printOrder(self, n, m):
# Create a vector to store indegrees of all
# vertices. Initialize all indegrees as 0.
indegree = [0] * (self.n + 1)
# Traverse adjacency lists to fill indegrees
# of vertices. This step takes O(V + E) time
for i in self.graph:
for j in self.graph[i]:
indegree[j] += 1
# Array to store the time in which
# the job i can be done
job = [0] * (self.n + 1)
# Create an queue and enqueue all
# vertices with indegree 0
q = []
# Update the time of the jobs
# who don't require any job to
# be completed before this job
for i in range(1, self.n + 1):
if indegree[i] == 0:
q.append(i)
job[i] = 1
# Iterate until queue is empty
while q:
# Get front element of queue
cur = q.pop(0)
for adj in self.graph[cur]:
# Decrease in-degree of
# the current node
indegree[adj] -= 1
# Push its adjacent elements
if (indegree[adj] == 0):
job[adj] = 1 + job[cur]
q.append(adj)
# Print the time to complete
# the job
for i in range(1, n + 1):
print(job[i], end = " ")
print()
# Driver Code
# Given Nodes N and edges M
n = 10
m = 13
g = Graph(n, m)
# Given Directed Edges of graph
g.addEdge(1, 3)
g.addEdge(1, 4)
g.addEdge(1, 5)
g.addEdge(2, 3)
g.addEdge(2, 8)
g.addEdge(2, 9)
g.addEdge(3, 6)
g.addEdge(4, 6)
g.addEdge(4, 8)
g.addEdge(5, 8)
g.addEdge(6, 7)
g.addEdge(7, 8)
g.addEdge(8, 10)
# Function Call
g.printOrder(n, m)
# This code is contributed by Aanchal TiwariC#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static readonly int maxN = 100000;
// Adjacency List to store the graph
static List []graph = new List[maxN];
// Array to store the in-degree of node
static int []indegree = new int[maxN];
// Array to store the time in which
// the job i can be done
static int []job = new int[maxN];
// Function to add directed edge
// between two vertices
static void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
// Insert edge from u to v
graph[u].Add(v);
// Increasing the indegree
// of vertex v
indegree[v]++;
}
// Function to find the minimum time
// needed by each node to get the task
static void printOrder(int n, int m)
{
// Find the topo sort order
// using the indegree approach
// Queue to store the
// nodes while processing
Queue q = new Queue();
// Pushing all the vertex in the
// queue whose in-degree is 0
// Update the time of the jobs
// who don't require any job to
// be completed before this job
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (indegree[i] == 0)
{
q.Enqueue(i);
job[i] = 1;
}
}
// Iterate until queue is empty
while (q.Count != 0)
{
// Get front element of queue
int cur = q.Peek();
// Pop the front element
q.Dequeue();
foreach(int adj in graph[cur])
{
// Decrease in-degree of
// the current node
indegree[adj]--;
// Push its adjacent elements
if (indegree[adj] == 0){
job[adj] = 1 + job[cur];
q.Enqueue(adj);
}
}
}
// Print the time to complete
// the job
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
Console.Write(job[i] + " ");
Console.Write("\n");
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Given Nodes N and edges M
int n, m;
n = 10;
m = 13;
for(int i = 0; i < graph.Length; i++)
graph[i] = new List();
// Given directed edges of graph
addEdge(1, 3);
addEdge(1, 4);
addEdge(1, 5);
addEdge(2, 3);
addEdge(2, 8);
addEdge(2, 9);
addEdge(3, 6);
addEdge(4, 6);
addEdge(4, 8);
addEdge(5, 8);
addEdge(6, 7);
addEdge(7, 8);
addEdge(8, 10);
// Function call
printOrder(n, m);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar 1 1 2 2 2 3 4 5 2 6时间复杂度: O(V+E),其中 V 是节点数,E 是边数。
辅助空间: O(V)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。