给定 N 个节点和M 条边的有向加权图,任务是计算节点1到N 之间最短路径的数量。
例子:
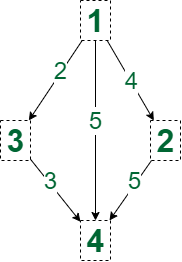
Input: N = 4, M = 5, edges = {{1, 4, 5}, {1, 2, 4}, {2, 4, 5}, {1, 3, 2}, {3, 4, 3}}
Output: 2
Explanation: The number of shortest path from node 1 to node 4 is 2, having cost 5.
Input: N = 3, M = 2, edges = {{1, 2, 4}, {1, 3, 5}}
Output: 1
方法:该问题可以通过 Dijkstra 算法解决。使用两个数组,比如dist[]来存储到源顶点的最短距离和大小为N 的路径 [] ,来存储从源顶点到顶点N的不同最短路径的数量。请按照以下步骤操作。
- 初始化一个优先级队列,比如pq,来存储顶点数和它的距离值。
- 初始化一个零向量,比如大小为N 的路径 [] ,并使路径 [1]等于1 。
- 初始化一个大数向量 (1e9),比如大小为N 的dist[] ,并使dist[1]等于0 。
- 在pq不为空时迭代。
- 从pq 中弹出并将顶点值存储在一个变量中,比如u ,并将距离值存储在变量d 中。
- 如果d大于u ,则继续。
- 对于每个顶点u 的每个 v ,如果dist[v] > dist[u]+(u 和 v 的边成本),则将dist[v] 减少到 dist[u] +(u 和 v 的边成本)和将顶点 u的路径数分配给顶点 v的路径数。
- 对于每个顶点u 的每个 v ,如果dist[v] = dist[u] + (u 和 v 的边成本) ,则将顶点u的路径数与顶点v的路径数相加。
- 最后,打印路径[N]。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
const int INF = 1e9;
const int MAXN = 1e5 + 1;
vector > > g(MAXN);
vector dist(MAXN);
vector route(MAXN);
// Function to count number of shortest
// paths from node 1 to node N
void countDistinctShortestPaths(
int n, int m, int edges[][3])
{
// Storing the graph
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int u = edges[i][0],
v = edges[i][1],
c = edges[i][2];
g[u].push_back({ v, c });
}
// Initializing dis array to a
// large value
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
dist[i] = INF;
}
// Initialize a priority queue
priority_queue,
vector >,
greater > >
pq;
pq.push({ 0, 1 });
// Base Cases
dist[1] = 0;
route[1] = 1;
// Loop while priority queue is
// not empty
while (!pq.empty()) {
int d = pq.top().first;
int u = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
// if d is greater than distance
// of the node
if (d > dist[u])
continue;
// Traversing all its neighbours
for (auto e : g[u]) {
int v = e.first;
int c = e.second;
if (c + d > dist[v])
continue;
// Path found of same distance
if (c + d == dist[v]) {
route[v] += route[u];
}
// New path found for lesser
// distance
if (c + d < dist[v]) {
dist[v] = c + d;
route[v] = route[u];
// Pushing in priority
// queue
pq.push({ dist[v], v });
}
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Input
int n = 4;
int m = 5;
int edges[m][3] = { { 1, 4, 5 },
{ 1, 2, 4 },
{ 2, 4, 5 },
{ 1, 3, 2 },
{ 3, 4, 3 } };
// Function Call
countDistinctShortestPaths(n, m, edges);
cout << route[n] << endl;
return 0;
} 输出:
2
时间复杂度: O(MLogN)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。