N叉树的ZigZag级别顺序遍历
给定一个由N个节点组成的通用树,任务是找到给定树的 ZigZag 级别顺序遍历。
例子:
Input:
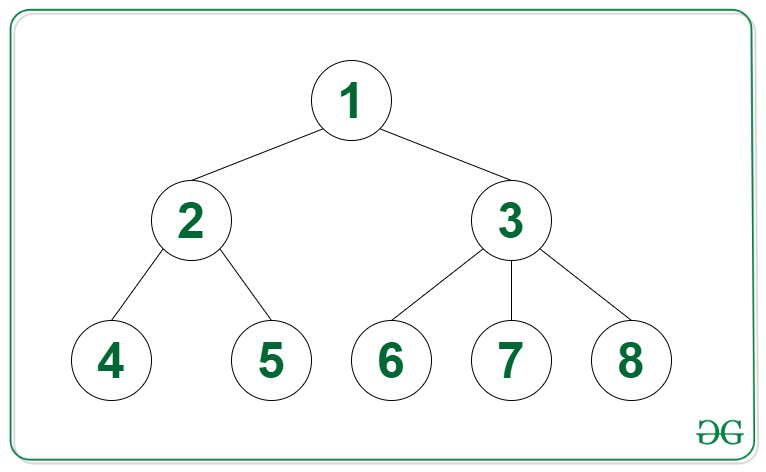
Output:
1
3 2
4 5 6 7 8
方法:给定的问题可以通过使用 BFS 遍历来解决。该方法与 N-ary Tree 的 Level Order Traversal 非常相似。可以观察到,在 Level Order Traversal 期间颠倒偶数级别的顺序时,获得的序列是 ZigZag 遍历。基于这些观察,以下是要遵循的步骤:
- 在 BFS 遍历期间,将每个级别的节点存储到一个向量中,比如curLevel[] 。
- 对于每个相应的级别,将curLevel存储到一个向量向量中,比如result[] 。
- 反转出现在result[]中偶数位置的向量。
- 完成以上步骤后,所有的向量都存储在result[]中需要的结果。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a tree node
struct Node {
int val;
vector child;
};
// Function to create a new node
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->val = key;
return temp;
}
// Function to perform zig zag traversal
// of the given tree
void zigzagLevelOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Stores the vectors containing nodes
// in each level of tree respectively
vector > result;
// Create a queue for BFS
queue q;
// Enqueue Root of the tree
q.push(root);
// Standard Level Order Traversal
// code using queue
while (!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
// Stores the element in the
// current level
vector curLevel;
// Iterate over all nodes of
// the current level
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* node = q.front();
q.pop();
curLevel.push_back(node->val);
// Insert all children of the
// current node into the queue
for (int j = 0;
j < node->child.size(); j++) {
q.push(node->child[j]);
}
}
// Insert curLevel into result
result.push_back(curLevel);
}
// Loop to Print the ZigZag Level order
// Traversal of the given tree
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
// If i+1 is even reverse the order
// of nodes in the current level
if ((i + 1) % 2 == 0) {
reverse(result[i].begin(),
result[i].end());
}
// Print the node of ith level
for (int j = 0;
j < result[i].size(); j++) {
cout << result[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(1);
(root->child).push_back(newNode(2));
(root->child).push_back(newNode(3));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode(4));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode(5));
(root->child[1]->child).push_back(newNode(6));
(root->child[1])->child.push_back(newNode(7));
(root->child[1]->child).push_back(newNode(8));
// Function Call
zigzagLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
// Class containing left and
// right child of current
// node and key value
static class Node {
public int val;
public Vector child;
public Node(int key)
{
val = key;
child = new Vector();
}
}
// Function to create a new node
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node(key);
return temp;
}
// Function to perform zig zag traversal
// of the given tree
static void zigzagLevelOrder(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
// Stores the vectors containing nodes
// in each level of tree respectively
Vector> result = new Vector>();
// Create a queue for BFS
Vector q = new Vector();
// Enqueue Root of the tree
q.add(root);
// Standard Level Order Traversal
// code using queue
while(q.size() > 0)
{
int size = q.size();
// Stores the element in the
// current level
Vector curLevel = new Vector();
// Iterate over all nodes of
// the current level
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
Node node = q.get(0);
q.remove(0);
curLevel.add(node.val);
// Insert all children of the
// current node into the queue
for(int j = 0; j < (node.child).size(); j++)
q.add(node.child.get(j));
}
// Insert curLevel into result
result.add(curLevel);
}
// Loop to Print the ZigZag Level order
// Traversal of the given tree
for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++)
{
// If i+1 is even reverse the order
// of nodes in the current level
if ((i + 1) % 2 == 0)
{
Collections.reverse(result.get(i));
}
// Print the node of ith level
for(int j = 0; j < result.get(i).size(); j++)
System.out.print(result.get(i).get(j) + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root = newNode(1);
(root.child).add(newNode(2));
(root.child).add(newNode(3));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(newNode(4));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(newNode(5));
(root.child.get(1).child).add(newNode(6));
(root.child.get(1)).child.add(newNode(7));
(root.child.get(1).child).add(newNode(8));
// Function Call
zigzagLevelOrder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019. Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Structure of a tree node
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.val = key
self.child = []
# Function to create a new node
def newNode(key):
temp = Node(key)
return temp
# Function to perform zig zag traversal
# of the given tree
def zigzagLevelOrder(root):
if (root == None):
return
# Stores the vectors containing nodes
# in each level of tree respectively
result = []
# Create a queue for BFS
q = []
# Enqueue Root of the tree
q.append(root)
# Standard Level Order Traversal
# code using queue
while len(q) > 0:
size = len(q)
# Stores the element in the
# current level
curLevel = []
# Iterate over all nodes of
# the current level
for i in range(size):
node = q[0]
q.pop(0)
curLevel.append(node.val)
# Insert all children of the
# current node into the queue
for j in range(len(node.child)):
q.append(node.child[j])
# Insert curLevel into result
result.append(curLevel)
# Loop to Print the ZigZag Level order
# Traversal of the given tree
for i in range(len(result)):
# If i+1 is even reverse the order
# of nodes in the current level
if ((i + 1) % 2 == 0):
result[i].reverse()
# Print the node of ith level
for j in range(len(result[i])):
print(result[i][j], end = " ")
print()
root = newNode(1)
(root.child).append(newNode(2))
(root.child).append(newNode(3))
(root.child[0].child).append(newNode(4))
(root.child[0].child).append(newNode(5))
(root.child[1].child).append(newNode(6))
(root.child[1]).child.append(newNode(7))
(root.child[1].child).append(newNode(8))
# Function Call
zigzagLevelOrder(root)
# This code is contributed by decode2207.C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Structure of a tree node
class Node {
public int val;
public List child;
public Node(int key)
{
val = key;
child = new List();
}
}
// Function to create a new node
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node(key);
return temp;
}
// Function to perform zig zag traversal
// of the given tree
static void zigzagLevelOrder(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
// Stores the vectors containing nodes
// in each level of tree respectively
List> result = new List>();
// Create a queue for BFS
List q = new List();
// Enqueue Root of the tree
q.Add(root);
// Standard Level Order Traversal
// code using queue
while(q.Count > 0)
{
int size = q.Count;
// Stores the element in the
// current level
List curLevel = new List();
// Iterate over all nodes of
// the current level
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
Node node = q[0];
q.RemoveAt(0);
curLevel.Add(node.val);
// Insert all children of the
// current node into the queue
for(int j = 0; j < (node.child).Count; j++)
q.Add(node.child[j]);
}
// Insert curLevel into result
result.Add(curLevel);
}
// Loop to Print the ZigZag Level order
// Traversal of the given tree
for(int i = 0; i < result.Count; i++)
{
// If i+1 is even reverse the order
// of nodes in the current level
if ((i + 1) % 2 == 0)
{
result[i].Reverse();
}
// Print the node of ith level
for(int j = 0; j < result[i].Count; j++)
Console.Write(result[i][j] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
static void Main() {
Node root = newNode(1);
(root.child).Add(newNode(2));
(root.child).Add(newNode(3));
(root.child[0].child).Add(newNode(4));
(root.child[0].child).Add(newNode(5));
(root.child[1].child).Add(newNode(6));
(root.child[1]).child.Add(newNode(7));
(root.child[1].child).Add(newNode(8));
// Function Call
zigzagLevelOrder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by suresh07. Javascript
输出:
1
3 2
4 5 6 7 8时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)