反向级别顺序遍历
我们在上一篇文章中讨论了树的级别顺序遍历。这个想法是首先打印最后一层,然后是倒数第二层,依此类推。与级别顺序遍历一样,每个级别都是从左到右打印的。
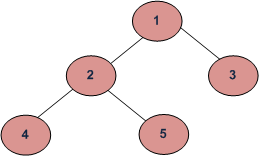
上述树的反向层序遍历为“4 5 2 3 1”。
正常级别顺序遍历的两种方法都可以轻松修改为反向级别顺序遍历。
方法 1(打印给定级别的递归函数)
我们可以很方便的修改普通级别顺序遍历的方法一。在方法 1 中,我们有一个 printGivenLevel() 方法,它打印给定的级别编号。我们唯一需要改变的是,不是从第一级调用 printGivenLevel() 到最后一级,而是从最后一级调用到第一级。
C++
// A recursive C++ program to print
// REVERSE level order traversal
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data,
pointer to left and right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
/*Function prototypes*/
void printGivenLevel(node* root, int level);
int height(node* node);
node* newNode(int data);
/* Function to print REVERSE
level order traversal a tree*/
void reverseLevelOrder(node* root)
{
int h = height(root);
int i;
for (i=h; i>=1; i--) //THE ONLY LINE DIFFERENT FROM NORMAL LEVEL ORDER
printGivenLevel(root, i);
}
/* Print nodes at a given level */
void printGivenLevel(node* root, int level)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (level == 1)
cout << root->data << " ";
else if (level > 1)
{
printGivenLevel(root->left, level - 1);
printGivenLevel(root->right, level - 1);
}
}
/* Compute the "height" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int height(node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
else
{
/* compute the height of each subtree */
int lheight = height(node->left);
int rheight = height(node->right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lheight > rheight)
return(lheight + 1);
else return(rheight + 1);
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return(Node);
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Level Order traversal of binary tree is \n";
reverseLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra C
// A recursive C program to print REVERSE level order traversal
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left and right child */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/*Function prototypes*/
void printGivenLevel(struct node* root, int level);
int height(struct node* node);
struct node* newNode(int data);
/* Function to print REVERSE level order traversal a tree*/
void reverseLevelOrder(struct node* root)
{
int h = height(root);
int i;
for (i=h; i>=1; i--) //THE ONLY LINE DIFFERENT FROM NORMAL LEVEL ORDER
printGivenLevel(root, i);
}
/* Print nodes at a given level */
void printGivenLevel(struct node* root, int level)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (level == 1)
printf("%d ", root->data);
else if (level > 1)
{
printGivenLevel(root->left, level-1);
printGivenLevel(root->right, level-1);
}
}
/* Compute the "height" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int height(struct node* node)
{
if (node==NULL)
return 0;
else
{
/* compute the height of each subtree */
int lheight = height(node->left);
int rheight = height(node->right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lheight > rheight)
return(lheight+1);
else return(rheight+1);
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("Level Order traversal of binary tree is \n");
reverseLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
} Java
// A recursive java program to print reverse level order traversal
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* Function to print REVERSE level order traversal a tree*/
void reverseLevelOrder(Node node)
{
int h = height(node);
int i;
for (i = h; i >= 1; i--)
//THE ONLY LINE DIFFERENT FROM NORMAL LEVEL ORDER
{
printGivenLevel(node, i);
}
}
/* Print nodes at a given level */
void printGivenLevel(Node node, int level)
{
if (node == null)
return;
if (level == 1)
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
else if (level > 1)
{
printGivenLevel(node.left, level - 1);
printGivenLevel(node.right, level - 1);
}
}
/* Compute the "height" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int height(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return 0;
else
{
/* compute the height of each subtree */
int lheight = height(node.left);
int rheight = height(node.right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lheight > rheight)
return (lheight + 1);
else
return (rheight + 1);
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
// Let us create trees shown in above diagram
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Level Order traversal of binary tree is : ");
tree.reverseLevelOrder(tree.root);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank JaiswalPython
# A recursive Python program to print REVERSE level order traversal
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to print reverse level order traversal
def reverseLevelOrder(root):
h = height(root)
for i in reversed(range(1, h+1)):
printGivenLevel(root,i)
# Print nodes at a given level
def printGivenLevel(root, level):
if root is None:
return
if level ==1 :
print root.data,
elif level>1:
printGivenLevel(root.left, level-1)
printGivenLevel(root.right, level-1)
# Compute the height of a tree-- the number of
# nodes along the longest path from the root node
# down to the farthest leaf node
def height(node):
if node is None:
return 0
else:
# Compute the height of each subtree
lheight = height(node.left)
rheight = height(node.right)
# Use the larger one
if lheight > rheight :
return lheight + 1
else:
return rheight + 1
# Driver program to test above function
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print "Level Order traversal of binary tree is"
reverseLevelOrder(root)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// A recursive C# program to print
// reverse level order traversal
using System;
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* Function to print REVERSE
level order traversal a tree*/
void reverseLevelOrder(Node node)
{
int h = height(node);
int i;
for (i = h; i >= 1; i--)
// THE ONLY LINE DIFFERENT
// FROM NORMAL LEVEL ORDER
{
printGivenLevel(node, i);
}
}
/* Print nodes at a given level */
void printGivenLevel(Node node, int level)
{
if (node == null)
return;
if (level == 1)
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
else if (level > 1)
{
printGivenLevel(node.left, level - 1);
printGivenLevel(node.right, level - 1);
}
}
/* Compute the "height" of a tree --
the number of nodes along the longest
path from the root node down to the
farthest leaf node.*/
int height(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return 0;
else
{
/* compute the height of each subtree */
int lheight = height(node.left);
int rheight = height(node.right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lheight > rheight)
return (lheight + 1);
else
return (rheight + 1);
}
}
// Driver Code
static public void Main(String []args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
// Let us create trees shown
// in above diagram
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Level Order traversal " +
"of binary tree is : ");
tree.reverseLevelOrder(tree.root);
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by Arnab KunduJavascript
C++
// A C++ program to print REVERSE level order traversal using stack and queue
// This approach is adopted from following link
// http://tech-queries.blogspot.in/2008/12/level-order-tree-traversal-in-reverse.html
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left and right children */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in reverse level order */
void reverseLevelOrder(node* root)
{
stack S;
queue Q;
Q.push(root);
// Do something like normal level order traversal order. Following are the
// differences with normal level order traversal
// 1) Instead of printing a node, we push the node to stack
// 2) Right subtree is visited before left subtree
while (Q.empty() == false)
{
/* Dequeue node and make it root */
root = Q.front();
Q.pop();
S.push(root);
/* Enqueue right child */
if (root->right)
Q.push(root->right); // NOTE: RIGHT CHILD IS ENQUEUED BEFORE LEFT
/* Enqueue left child */
if (root->left)
Q.push(root->left);
}
// Now pop all items from stack one by one and print them
while (S.empty() == false)
{
root = S.top();
cout << root->data << " ";
S.pop();
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* temp = new node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
cout << "Level Order traversal of binary tree is \n";
reverseLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
} Java
// A recursive java program to print reverse level order traversal
// using stack and queue
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left and right children */
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in reverse level order */
void reverseLevelOrder(Node node)
{
Stack S = new Stack();
Queue Q = new LinkedList();
Q.add(node);
// Do something like normal level order traversal order.Following
// are the differences with normal level order traversal
// 1) Instead of printing a node, we push the node to stack
// 2) Right subtree is visited before left subtree
while (Q.isEmpty() == false)
{
/* Dequeue node and make it root */
node = Q.peek();
Q.remove();
S.push(node);
/* Enqueue right child */
if (node.right != null)
// NOTE: RIGHT CHILD IS ENQUEUED BEFORE LEFT
Q.add(node.right);
/* Enqueue left child */
if (node.left != null)
Q.add(node.left);
}
// Now pop all items from stack one by one and print them
while (S.empty() == false)
{
node = S.peek();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
S.pop();
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
// Let us create trees shown in above diagram
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(7);
System.out.println("Level Order traversal of binary tree is :");
tree.reverseLevelOrder(tree.root);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal Python
# Python program to print REVERSE level order traversal using
# stack and queue
from collections import deque
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Given a binary tree, print its nodes in reverse level order
def reverseLevelOrder(root):
# we can use a double ended queue which provides O(1) insert at the beginning
# using the appendleft method
# we do the regular level order traversal but instead of processing the
# left child first we process the right child first and the we process the left child
# of the current Node
# we can do this One pass reduce the space usage not in terms of complexity but intuitively
q = deque()
q.append(root)
ans = deque()
while q:
node = q.popleft()
if node is None:
continue
ans.appendleft(node.data)
if node.right:
q.append(node.right)
if node.left:
q.append(node.left)
return ans
# Driver program to test above function
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
print "Level Order traversal of binary tree is"
reverseLevelOrder(root)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// A recursive C# program to print reverse
// level order traversal using stack and queue
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System;
/* A binary tree node has data,
pointer to left and right children */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* Given a binary tree, print its
nodes in reverse level order */
void reverseLevelOrder(Node node)
{
Stack S = new Stack();
Queue Q = new Queue();
Q.Enqueue(node);
// Do something like normal level
// order traversal order.Following
// are the differences with normal
// level order traversal
// 1) Instead of printing a node, we push the node to stack
// 2) Right subtree is visited before left subtree
while (Q.Count>0)
{
/* Dequeue node and make it root */
node = Q.Peek();
Q.Dequeue();
S.Push(node);
/* Enqueue right child */
if (node.right != null)
// NOTE: RIGHT CHILD IS ENQUEUED BEFORE LEFT
Q.Enqueue(node.right);
/* Enqueue left child */
if (node.left != null)
Q.Enqueue(node.left);
}
// Now pop all items from stack
// one by one and print them
while (S.Count>0)
{
node = S.Peek();
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
S.Pop();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
// Let us create trees shown in above diagram
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(7);
Console.WriteLine("Level Order traversal of binary tree is :");
tree.reverseLevelOrder(tree.root);
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */ Javascript
输出:
Level Order traversal of binary tree is
4 5 2 3 1时间复杂度:此方法最坏情况的时间复杂度为 O(n^2)。对于倾斜树, printGivenLevel() 需要 O(n) 时间,其中 n 是倾斜树中的节点数。所以 printLevelOrder() 的时间复杂度是 O(n) + O(n-1) + O(n-2) + .. + O(1),即 O(n^2)。
方法 2(使用队列和堆栈)
正常层序遍历的方法2也可以很方便的修改为逆序打印层序遍历。这个想法是使用双端队列(双端队列)来获得反向级别的顺序。双端队列允许在两端插入和删除。如果我们进行普通级别顺序遍历而不是打印节点,而是将节点压入堆栈,然后打印双端队列的内容,我们得到上述示例树的“5 4 3 2 1”,但输出应该是“ 4 5 2 3 1”。所以为了得到正确的序列(从左到右在每一层),我们以相反的顺序处理节点的子节点,我们首先将右子树推送到双端队列,然后处理左子树。
C++
// A C++ program to print REVERSE level order traversal using stack and queue
// This approach is adopted from following link
// http://tech-queries.blogspot.in/2008/12/level-order-tree-traversal-in-reverse.html
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left and right children */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in reverse level order */
void reverseLevelOrder(node* root)
{
stack S;
queue Q;
Q.push(root);
// Do something like normal level order traversal order. Following are the
// differences with normal level order traversal
// 1) Instead of printing a node, we push the node to stack
// 2) Right subtree is visited before left subtree
while (Q.empty() == false)
{
/* Dequeue node and make it root */
root = Q.front();
Q.pop();
S.push(root);
/* Enqueue right child */
if (root->right)
Q.push(root->right); // NOTE: RIGHT CHILD IS ENQUEUED BEFORE LEFT
/* Enqueue left child */
if (root->left)
Q.push(root->left);
}
// Now pop all items from stack one by one and print them
while (S.empty() == false)
{
root = S.top();
cout << root->data << " ";
S.pop();
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* temp = new node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
cout << "Level Order traversal of binary tree is \n";
reverseLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
}
Java
// A recursive java program to print reverse level order traversal
// using stack and queue
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left and right children */
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in reverse level order */
void reverseLevelOrder(Node node)
{
Stack S = new Stack();
Queue Q = new LinkedList();
Q.add(node);
// Do something like normal level order traversal order.Following
// are the differences with normal level order traversal
// 1) Instead of printing a node, we push the node to stack
// 2) Right subtree is visited before left subtree
while (Q.isEmpty() == false)
{
/* Dequeue node and make it root */
node = Q.peek();
Q.remove();
S.push(node);
/* Enqueue right child */
if (node.right != null)
// NOTE: RIGHT CHILD IS ENQUEUED BEFORE LEFT
Q.add(node.right);
/* Enqueue left child */
if (node.left != null)
Q.add(node.left);
}
// Now pop all items from stack one by one and print them
while (S.empty() == false)
{
node = S.peek();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
S.pop();
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
// Let us create trees shown in above diagram
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(7);
System.out.println("Level Order traversal of binary tree is :");
tree.reverseLevelOrder(tree.root);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal
Python
# Python program to print REVERSE level order traversal using
# stack and queue
from collections import deque
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Given a binary tree, print its nodes in reverse level order
def reverseLevelOrder(root):
# we can use a double ended queue which provides O(1) insert at the beginning
# using the appendleft method
# we do the regular level order traversal but instead of processing the
# left child first we process the right child first and the we process the left child
# of the current Node
# we can do this One pass reduce the space usage not in terms of complexity but intuitively
q = deque()
q.append(root)
ans = deque()
while q:
node = q.popleft()
if node is None:
continue
ans.appendleft(node.data)
if node.right:
q.append(node.right)
if node.left:
q.append(node.left)
return ans
# Driver program to test above function
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
print "Level Order traversal of binary tree is"
reverseLevelOrder(root)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
C#
// A recursive C# program to print reverse
// level order traversal using stack and queue
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System;
/* A binary tree node has data,
pointer to left and right children */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* Given a binary tree, print its
nodes in reverse level order */
void reverseLevelOrder(Node node)
{
Stack S = new Stack();
Queue Q = new Queue();
Q.Enqueue(node);
// Do something like normal level
// order traversal order.Following
// are the differences with normal
// level order traversal
// 1) Instead of printing a node, we push the node to stack
// 2) Right subtree is visited before left subtree
while (Q.Count>0)
{
/* Dequeue node and make it root */
node = Q.Peek();
Q.Dequeue();
S.Push(node);
/* Enqueue right child */
if (node.right != null)
// NOTE: RIGHT CHILD IS ENQUEUED BEFORE LEFT
Q.Enqueue(node.right);
/* Enqueue left child */
if (node.left != null)
Q.Enqueue(node.left);
}
// Now pop all items from stack
// one by one and print them
while (S.Count>0)
{
node = S.Peek();
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
S.Pop();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
// Let us create trees shown in above diagram
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(7);
Console.WriteLine("Level Order traversal of binary tree is :");
tree.reverseLevelOrder(tree.root);
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
Javascript
输出:
Level Order traversal of binary tree is
4 5 6 7 2 3 1时间复杂度: O(n),其中 n 是二叉树中的节点数。
?list=PLqM7alHXFySHCXD7r1J0ky9Zg_GBB1dbk