📌 相关文章
- Python|使用 Tkinter 的距离时间 GUI 计算器(1)
- Python | 使用Tkinter的距离时间GUI计算器(1)
- Python | 使用Tkinter的简单GUI计算器(1)
- Python|使用 Tkinter 的简单 GUI 计算器
- Python | 使用Tkinter的简单GUI计算器
- Python|使用 Tkinter 的简单 GUI 计算器(1)
- 在Python使用 Tkinter 的科学 GUI 计算器
- 在Python使用 Tkinter 的科学 GUI 计算器(1)
- Python - 使用 Tkinter 模块的动态 GUI 计算器(1)
- Python - 使用 Tkinter 模块的动态 GUI 计算器
- Python – 使用 Tkinter 的复利 GUI 计算器
- Python – 使用 Tkinter 的复利 GUI 计算器(1)
- 使用 Tkinter 的比率计算器 GUI
- Python GUI – tkinter
- Python GUI – tkinter(1)
- Python|使用 Tkinter 的简单计算器(1)
- Python|使用 Tkinter 的简单计算器
- Python -GUI编程(Tkinter)(1)
- Python -GUI编程(Tkinter)
- Python 3-GUI编程(Tkinter)
- Python 3-GUI编程(Tkinter)(1)
- Python|使用 Tkinter 的 GUI 日历(1)
- Python|使用 Tkinter 的 GUI 日历
- Python:使用 Tkinter 的年龄计算器(1)
- Python:使用 Tkinter 的年龄计算器
- 基本 tkinter gui - Python (1)
- tkinter 响应式 gui - Python (1)
- 使用 Tkinter 的基于排名的百分位 Gui 计算器(1)
- 使用 Tkinter 的基于排名的百分位 Gui 计算器
📜 Python | 使用Tkinter的距离时间GUI计算器
📅 最后修改于: 2020-04-30 05:36:13 🧑 作者: Mango
Python提供了多种开发GUI(图形用户界面)的选项。在所有GUI方法中,tkinter是最常用的方法。它是Python随附的Tk GUI工具包的标准Python接口。带有tkinter的Python输出了创建GUI应用程序的最快,最简单的方法。使用tkinter创建GUI很容易。
创建一个tkinter:
- 导入模块 tkinter
- 创建主窗口(容器)
- 将任意数量的小部件添加到主窗口
- 将事件触发器应用于小部件。
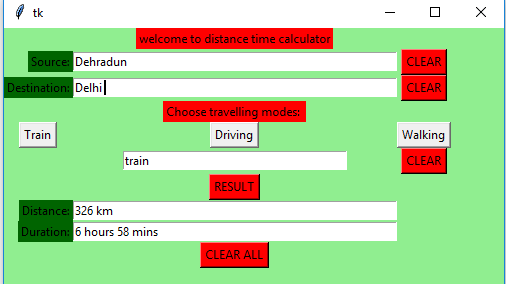
让我们使用Python Tkinter模块创建一个基于GUI的距离时间计算器,该计算器可以判断两个城市/位置之间的距离以及从一个位置到另一位置的旅行时间。
所需模块:
tkinter
requests
json下面是实现:
# Python3程序使用Tkinter创建距离时间GUI计算器
# 从tkinter模块导入所有内容
from tkinter import *
# 导入模块
import requests, json
# 查找两个地方之间的距离和持续时间的功能
def result(source, destination, travel_modes):
# 在此处输入您的API密钥
api_key = 'Your_api_key'
# 用于存储基本URL的基本变量
base = 'https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/distancematrix/json?'
# 检查出行方式
if travel_modes == "train":
# complete_url变量,用于存储完整的URL地址
complete_url = base + 'origins =' + source + \
'&destinations =' + destination + \
'&mode = transit&transit_mode = train' + \
'&key ='+api_key
# 请求模块的get方法返回响应对象
r = requests.get(complete_url)
else:
# complete_url变量,用于存储完整的URL地址
complete_url = base + 'origins =' + source+ \
'&destinations ='+ destination + \
'&mode ='+travel_modes+'&key ='+ api_key
# 请求模块的get方法返回响应对象
r = requests.get(complete_url)
# 响应对象的json方法将json格式的数据转换为Python格式的数据
x = r.json()
# x包含嵌套字典列表
# 我们知道字典包含键值对
# 从x字典中提取有用的信息
row = x['rows'][0]
cell = row['elements'][0]
# 检查对应于单元格字典中状态键的值
if cell['status'] == 'OK' :
# 在文本输入框中插入值的insert方法.
# 从单元格字典中提取有用的信息,然后插入相应的文本字段中
distance_field.insert(10, cell['distance']['text'])
duration_field.insert(10, cell['duration']['text'])
else :
# insert方法在文本输入框中插入值。
# 从单元格字典中提取与状态键对应的值,并将其插入相应的文本字段中。
mode_field.insert(10, cell['status'])
distance_field.insert(10, cell['status'])
# 从相应的文本输入框获取值的函数和调用结果函数。
def find() :
# get方法从文本输入框中以字符串形式返回当前文本
source = source_field.get()
destination = destination_field.get()
travel_modes = mode_field.get()
# 调用result()函数
result(source, destination, travel_modes)
# 在mode_field文本输入框中插入火车字符串的函数
def train() :
mode_field.insert(10, "train")
# 在模式字段输入框中插入驱动字符串的功能
def driving() :
mode_field.insert(10, "driving")
# 用于在mode_field文本输入框中插入步行字符串的函数
def walking() :
mode_field.insert(10, "walking")
# 清除source_field,distance_field,duration_field文本输入框内容的函数.
def del_source() :
source_field.delete(0, END)
distance_field.delete(0, END)
duration_field.delete(0, END)
# 清除destination_field,distance_field,duration_field文字输入框.
def del_destination() :
destination_field.delete(0, END)
distance_field.delete(0, END)
duration_field.delete(0, END)
# 清除mode_field,distance_field,duration_field文本输入框内容的函数.
def del_modes() :
mode_field.delete(0, END)
distance_field.delete(0, END)
duration_field.delete(0, END)
# 清除所有文本输入框的内容的函数
def delete_all() :
source_field.delete(0, END)
destination_field.delete(0, END)
mode_field.delete(0, END)
distance_field.delete(0, END)
duration_field.delete(0, END)
# 驱动程式码
if __name__ == "__main__" :
# 创建一个GUI窗口
root = Tk()
# 设置GUI窗口的背景色
root.configure(background = 'light green')
# 设置GUI窗口的配置
root.geometry("500x300")
# 创建使用距离时间计算器标签
headlabel = Label(root, text = 'welcome to distance time calculator',
fg = 'black', bg = "red")
# 创建源:标签
label1 = Label(root, text = "Source:",
fg = 'black', bg = 'dark green')
# 创建目标:标签
label2 = Label(root, text = "Destination:",
fg = 'black', bg = 'dark green')
# 创建选择旅行方式:标签
label3 = Label(root, text = "Choose travelling modes: ",
fg = 'black', bg = 'red')
# 创建距离:标签
label4 = Label(root, text = "Distance:",
fg = 'black', bg = 'dark green')
# 创建持续时间:标签
label5 = Label(root, text = "Duration:",
fg = 'black', bg = 'dark green')
# 网格方法用于将小部件放置在表格状结构的各个位置.
headlabel.grid(row = 0, column = 1)
label1.grid(row = 1, column = 0, sticky ="E")
label2.grid(row = 2, column = 0, sticky ="E")
label3.grid(row = 3, column = 1)
label4.grid(row = 7, column = 0, sticky ="E")
label5.grid(row = 8, column = 0, sticky ="E")
# 创建一个文本输入框以填充或键入信息.
source_field = Entry(root)
destination_field = Entry(root)
mode_field = Entry(root)
distance_field = Entry(root)
duration_field = Entry(root)
# 网格方法用于将小部件放置在表格状结构的各个位置.
# ipadx关键字参数设置条目空间的宽度 .
source_field.grid(row = 1, column = 1, ipadx ="100")
destination_field.grid(row = 2, column = 1, ipadx ="100")
mode_field.grid(row = 5, column = 1, ipadx ="50")
distance_field.grid(row = 7, column = 1, ipadx ="100")
duration_field.grid(row = 8, column = 1, ipadx ="100")
# 创建一个CLEAR按钮并附加到del_source函数
button1 = Button(root, text = "CLEAR", bg = "red",
fg = "black", command = del_source)
# 创建一个CLEAR按钮并附加到del_destination
button2 = Button(root, text = "CLEAR", bg = "red",
fg = "black", command = del_destination)
# 创建一个RESULT按钮并附加到查找功能
button3 = Button(root, text = "RESULT",
bg = "red", fg = "black",
command = find)
# 创建一个CLEAR ALL按钮并附加到delete_all函数
button4 = Button(root, text = "CLEAR ALL",
bg = "red", fg = "black",
command = delete_all)
# 创建训练按钮并附加到训练功能
button5 = Button(root, text = "Train", command = train)
# 创建驾驶按钮并附加到驾驶功能
button6 = Button(root, text = "Driving", command = driving)
# 创建步行按钮并附加到步行功能
button7 = Button(root, text = "Walking", command = walking)
# 创建一个CLEAR按钮并附加到del_modes函数
button8 = Button(root, text = "CLEAR",
fg = "black", bg = "red",
command = del_modes)
# 网格方法用于将小部件放置在表格状结构的各个位置.
button1.grid(row = 1, column = 2)
button2.grid(row = 2, column = 2)
button3.grid(row = 6, column = 1)
button4.grid(row = 9, column = 1)
button5.grid(row = 4, column = 0)
button6.grid(row = 4, column = 1)
button7.grid(row = 4, column = 2)
button8.grid(row = 5, column = 2)
# 启动GUI
root.mainloop()输出: