Python – 使用 Tkinter 的复利 GUI 计算器
先决条件: tkinter 简介 |计算复利的程序
Python为开发 GUI(图形用户界面)提供了多种选择。在所有的 GUI 方法中,Tkinter 是最常用的方法。在本文中,我们将学习如何使用 Tkinter 创建一个复利 GUI 计算器应用程序,并提供分步指南。
创建 Tkinter:
- 导入模块 – tkinter
- 创建主窗口(容器)
- 将任意数量的小部件添加到主窗口。
- 在小部件上应用事件触发器。
下面是 GUI 的样子:
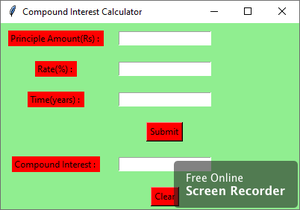
让我们创建一个基于 GUI 的复利计算器应用程序。
下面是实现:
Python3
# import all classes / functions from the tkinter
from tkinter import *
# Function for clearing the
# contents of all entry boxes
def clear_all() :
# whole content of entry boxes is deleted
principle_field.delete(0, END)
rate_field.delete(0, END)
time_field.delete(0, END)
compound_field.delete(0, END)
# set focus on the principle_field entry box
principle_field.focus_set()
# Function to find compound interest
def calculate_ci():
# get a content from entry box
principle = int(principle_field.get())
rate = float(rate_field.get())
time = int(time_field.get())
# Calculates compound interest
CI = principle * (pow((1 + rate / 100), time))
# insert method inserting the
# value in the text entry box.
compound_field.insert(10, CI)
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
# Create a GUI window
root = Tk()
# Set the background colour of GUI window
root.configure(background = 'light green')
# Set the configuration of GUI window
root.geometry("400x250")
# set the name of tkinter GUI window
root.title("Compound Interest Calculator")
# Create a Principle Amount : label
label1 = Label(root, text = "Principle Amount(Rs) : ",
fg = 'black', bg = 'red')
# Create a Rate : label
label2 = Label(root, text = "Rate(%) : ",
fg = 'black', bg = 'red')
# Create a Time : label
label3 = Label(root, text = "Time(years) : ",
fg = 'black', bg = 'red')
# Create a Compound Interest : label
label4 = Label(root, text = "Compound Interest : ",
fg = 'black', bg = 'red')
# grid method is used for placing
# the widgets at respective positions
# in table like structure .
# padx keyword argument used to set padding along x-axis .
# pady keyword argument used to set padding along y-axis .
label1.grid(row = 1, column = 0, padx = 10, pady = 10)
label2.grid(row = 2, column = 0, padx = 10, pady = 10)
label3.grid(row = 3, column = 0, padx = 10, pady = 10)
label4.grid(row = 5, column = 0, padx = 10, pady = 10)
# Create a entry box
# for filling or typing the information.
principle_field = Entry(root)
rate_field = Entry(root)
time_field = Entry(root)
compound_field = Entry(root)
# grid method is used for placing
# the widgets at respective positions
# in table like structure .
# padx keyword argument used to set padding along x-axis .
# pady keyword argument used to set padding along y-axis .
principle_field.grid(row = 1, column = 1, padx = 10, pady = 10)
rate_field.grid(row = 2, column = 1, padx = 10, pady = 10)
time_field.grid(row = 3, column = 1, padx = 10, pady = 10)
compound_field.grid(row = 5, column = 1, padx = 10, pady = 10)
# Create a Submit Button and attached
# to calculate_ci function
button1 = Button(root, text = "Submit", bg = "red",
fg = "black", command = calculate_ci)
# Create a Clear Button and attached
# to clear_all function
button2 = Button(root, text = "Clear", bg = "red",
fg = "black", command = clear_all)
button1.grid(row = 4, column = 1, pady = 10)
button2.grid(row = 6, column = 1, pady = 10)
# Start the GUI
root.mainloop()输出 :