强烈建议先查看Van Emde Boas Tree上的先前文章。
插入程序:
- 如果树中没有键,则只需将树的最小值和最大值分配给键。
- 否则,我们将深入树中并执行以下操作:
- 如果要插入的键小于树的当前最小值,则交换两个值,因为新键将是树的实际最小值,并且已经位于最小值处的键将用于进一步的过程。
可以将此概念视为Van Emde Boas Tree中的延迟传播。因为这个旧的最小值实际上是递归Van Emde Boas结构簇中的一个最小值。因此,实际上直到需求出现时,我们才开始深入研究结构。
- 如果我们不在基本情况下,则意味着树的Universe大小大于2,则:
- 如果树的cluster [High(key)]为空,则在摘要上递归调用insert,并且在进行延迟传播时,我们只给键分配最小值和最大值,然后停止递归。
- 否则,我们在存在密钥的群集上调用插入。
- 如果要插入的键小于树的当前最小值,则交换两个值,因为新键将是树的实际最小值,并且已经位于最小值处的键将用于进一步的过程。
- 同样,我们检查最大值,如果密钥大于当前最大值,则将其设置为最大值。
下图表示空的VEB(4)树:
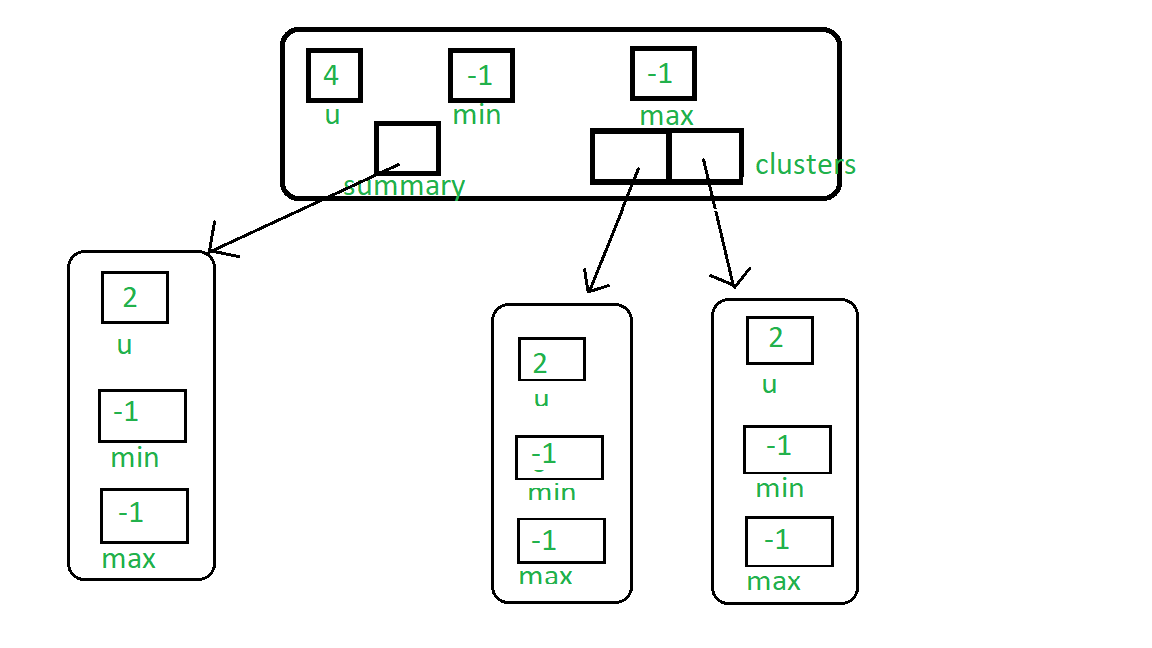
现在我们插入1,然后它将树的最小值和最大值设置为1。您可以看到1的延迟传播:
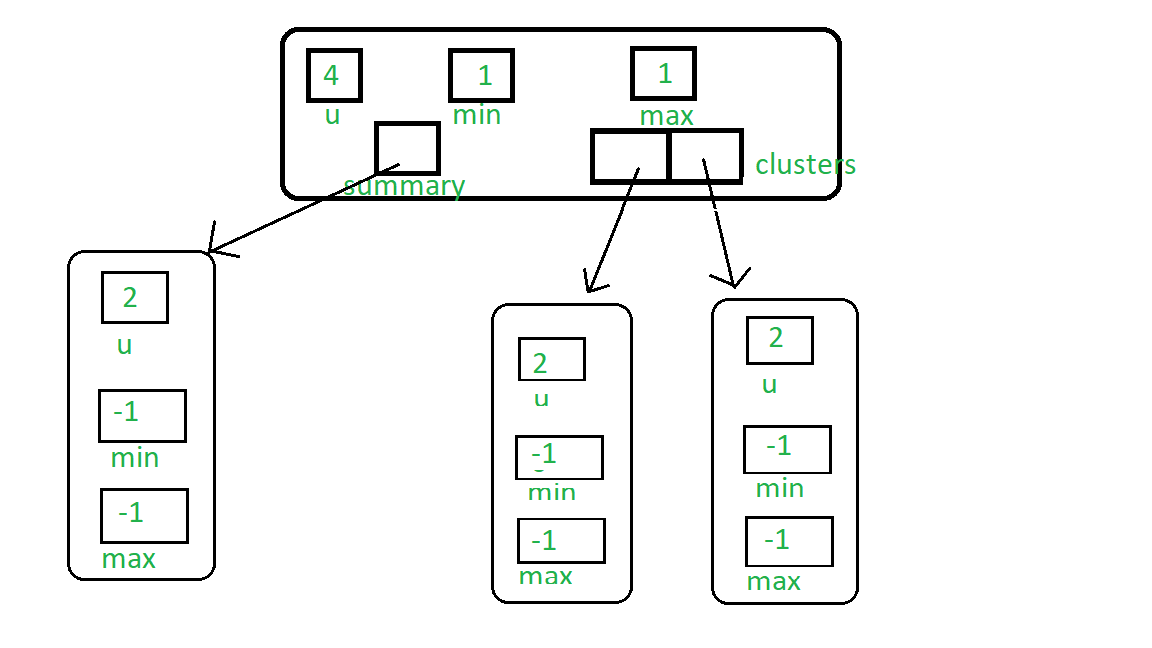
现在,如果我们插入0,则1将传播到第一个簇,零将是新的最小值: 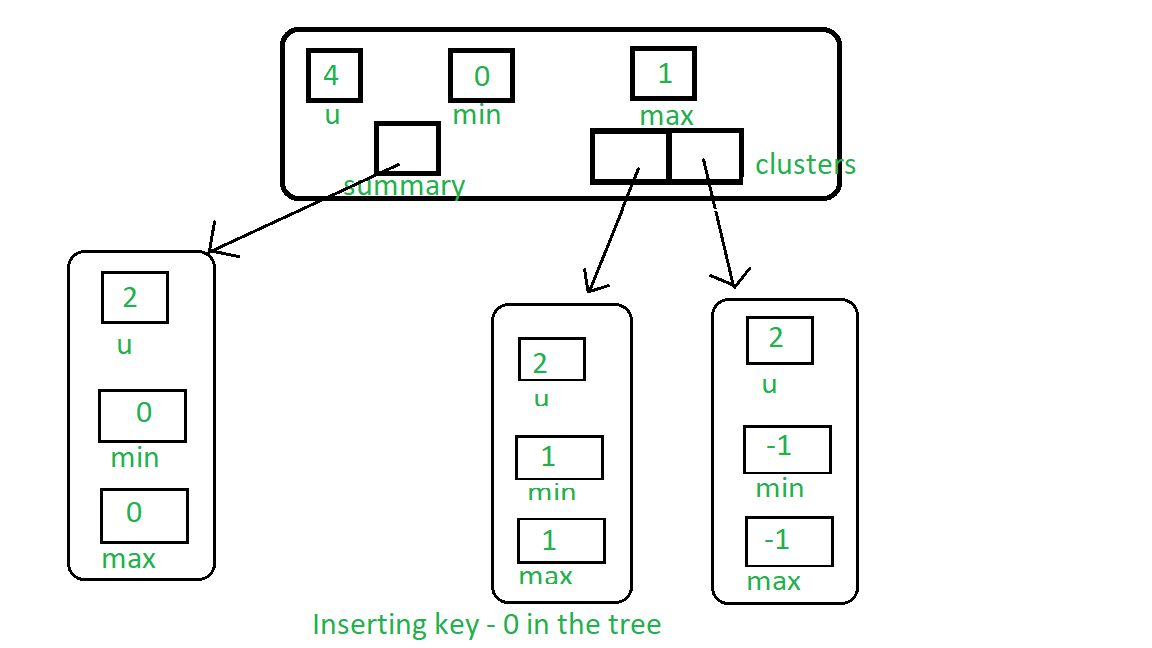
isMember查询的过程:
- 在搜索的任何时候,如果键是树的最小或最大值,这意味着该键存在,则返回true。
- 如果达到基本情况,但以上条件为假,则该键一定不能出现在树中,因此返回true。
- 否则,递归地在键的集群(即High(key))及其在集群的位置(即Low(key))上调用该函数。
- 在这里,我们允许Universe_size为2的任意幂,因此,如果出现Universe_size小于键值的情况,则返回false。
最小和最大值:Van Emde Boas树存储最小值和最大值作为其属性,因此如果存在它,我们可以返回其值,否则返回null。
#include
using namespace std;
class Van_Emde_Boas {
public:
int universe_size;
int minimum;
int maximum;
Van_Emde_Boas* summary;
vector clusters;
// Function to return cluster numbers
// in which key is present
int high(int x)
{
int div = ceil(sqrt(universe_size));
return x / div;
}
// Function to return position of x in cluster
int low(int x)
{
int mod = ceil(sqrt(universe_size));
return x % mod;
}
// Function to return the index from
// cluster number and position
int generate_index(int x, int y)
{
int ru = ceil(sqrt(universe_size));
return x * ru + y;
}
// Constructor
Van_Emde_Boas(int size)
{
universe_size = size;
minimum = -1;
maximum = -1;
// Base case
if (size <= 2) {
summary = nullptr;
clusters = vector(0, nullptr);
}
else {
int no_clusters = ceil(sqrt(size));
// Assigning VEB(sqrt(u)) to summary
summary = new Van_Emde_Boas(no_clusters);
// Creating array of VEB Tree pointers of size sqrt(u)
clusters = vector(no_clusters, nullptr);
// Assigning VEB(sqrt(u)) to all its clusters
for (int i = 0; i < no_clusters; i++) {
clusters[i] = new Van_Emde_Boas(ceil(sqrt(size)));
}
}
}
};
// Function to return the minimum value
// from the tree if it exists
int VEB_minimum(Van_Emde_Boas* helper)
{
return (helper->minimum == -1 ? -1 : helper->minimum);
}
// Function to return the maximum value
// from the tree if it exists
int VEB_maximum(Van_Emde_Boas* helper)
{
return (helper->maximum == -1 ? -1 : helper->maximum);
}
// Function to insert a key in the tree
void insert(Van_Emde_Boas* helper, int key)
{
// If no key is present in the tree
// then set both minimum and maximum
// to the key (Read the previous article
// for more understanding about it)
if (helper->minimum == -1) {
helper->minimum = key;
helper->maximum = key;
}
else {
if (key < helper->minimum) {
// If the key is less than current minimum
// then swap it with the current minimum
// because this minimum is actually
// minimum of one of the internal cluster
// so as we go deeper into the Van Emde Boas
// we need to take that minimum to its real position
// This concept is similar to "Lazy Propagation"
swap(helper->minimum, key);
}
// Not base case then...
if (helper->universe_size > 2) {
// If no key is present in the cluster then insert key into
// both cluster and summary
if (VEB_minimum(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]) == -1) {
insert(helper->summary, helper->high(key));
// Sets the minimum and maximum of cluster to the key
// as no other keys are present we will stop at this level
// we are not going deeper into the structure like
// Lazy Propagation
helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]->minimum = helper->low(key);
helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]->maximum = helper->low(key);
}
else {
// If there are other elements in the tree then recursively
// go deeper into the structure to set attributes accordingly
insert(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)], helper->low(key));
}
}
// Sets the key as maximum it is greater than current maximum
if (key > helper->maximum) {
helper->maximum = key;
}
}
}
// Function that returns true if the
// key is present in the tree
bool isMember(Van_Emde_Boas* helper, int key)
{
// If universe_size is less than the key
// then we can not search the key so returns
// false
if (helper->universe_size < key) {
return false;
}
// If at any point of our traversal
// of the tree if the key is the minimum
// or the maximum of the subtree, then
// the key is present so returns true
if (helper->minimum == key || helper->maximum == key) {
return true;
}
else {
// If after attending above condition,
// if the size of the tree is 2 then
// the present key must be
// maximum or minimum of the tree if it
// is not then it returns false becuase key
// can not be present in the sub tree
if (helper->universe_size == 2) {
return false;
}
else {
// Recursive call over the cluster
// in which the key can be present
// and also pass the new position of the key
// i.e., low(key)
return isMember(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)],
helper->low(key));
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Van_Emde_Boas* veb = new Van_Emde_Boas(8);
// Inserting Keys
insert(veb, 2);
insert(veb, 3);
insert(veb, 6);
cout << boolalpha;
// Checking isMember query
cout << isMember(veb, 3) << endl;
cout << isMember(veb, 4) << endl;
// Maximum of VEB
cout << VEB_maximum(veb) << endl;
// Minimum of VEB
cout << VEB_minimum(veb) << endl;
}
输出:
true
false
6
2