卢瑟福的原子模型
由于 JJ Thomson 的原子模型存在缺陷并且存在重大缺陷,因此 Ernest Rutherford 提出了一个更新的模型,作为以下原子模型的基础。为了寻找有关原子内电子排列的答案,卢瑟福进行了一项实验,在该实验中,快速移动的 α 粒子撞击了薄金箔。
卢瑟福的 Alpha (α) 粒子散射实验
为了确定电子在原子中的排列方式,卢瑟福组织了 Alpha (α) 粒子散射实验。快速移动的 α 粒子被引导轰击薄薄的金片。
- 选择金箔以获得极薄的层。金箔的厚度约为 1000 个原子。
- 双电荷氦离子被称为α粒子。快速移动的 α 粒子拥有大量能量,因为它们的质量约为 4 amu。
假设是 α 粒子会被金原子中的亚原子粒子偏转。卢瑟福没想到会出现明显的偏转,因为 α 粒子比质子重得多。然而,该实验产生了完全出乎意料的结果。
观察
卢瑟福从他的 α 粒子散射实验中观察到以下内容:
- 大多数快速移动的α粒子直接穿过金箔。
- 箔片以相当小的角度偏转了一些α粒子。
- 只有少数 α 粒子完全偏转回来(180 度)。

图 1. 卢瑟福的 Alpha 粒子散射实验(上图)
结论
卢瑟福从他的观察中得出以下结论:
- 因为大部分指向金片的α粒子没有任何偏转穿过它,所以原子中的大部分空间是空的。
- 只有少数 α 粒子偏离了它们的路线,这表明原子的正电荷占据的空间相对较小。
- 由于极小百分比的α粒子完全反弹,这意味着原子的质量和正电荷集中在一个小体积中,并且分布不均匀。
卢瑟福的原子模型
Rutherford model of atom is also known as the Nuclear Model of Atom.
卢瑟福原子模型的特点:
卢瑟福根据上述观察和结论假设了元素的原子结构。卢瑟福原子模型指出:
- 带正电的粒子和原子的大部分质量都集中在一个非常小的体积中。他把这部分原子称为原子核。与整个原子的大小相比,这个原子核的大小非常小。
- 根据卢瑟福的说法,带负电的电子环绕着原子核。他相信环绕原子核的电子以高速绕着原子核运动。他将这些圆形路线称为明确定义的轨道。
原子核和电子通过静电引力结合在一起。
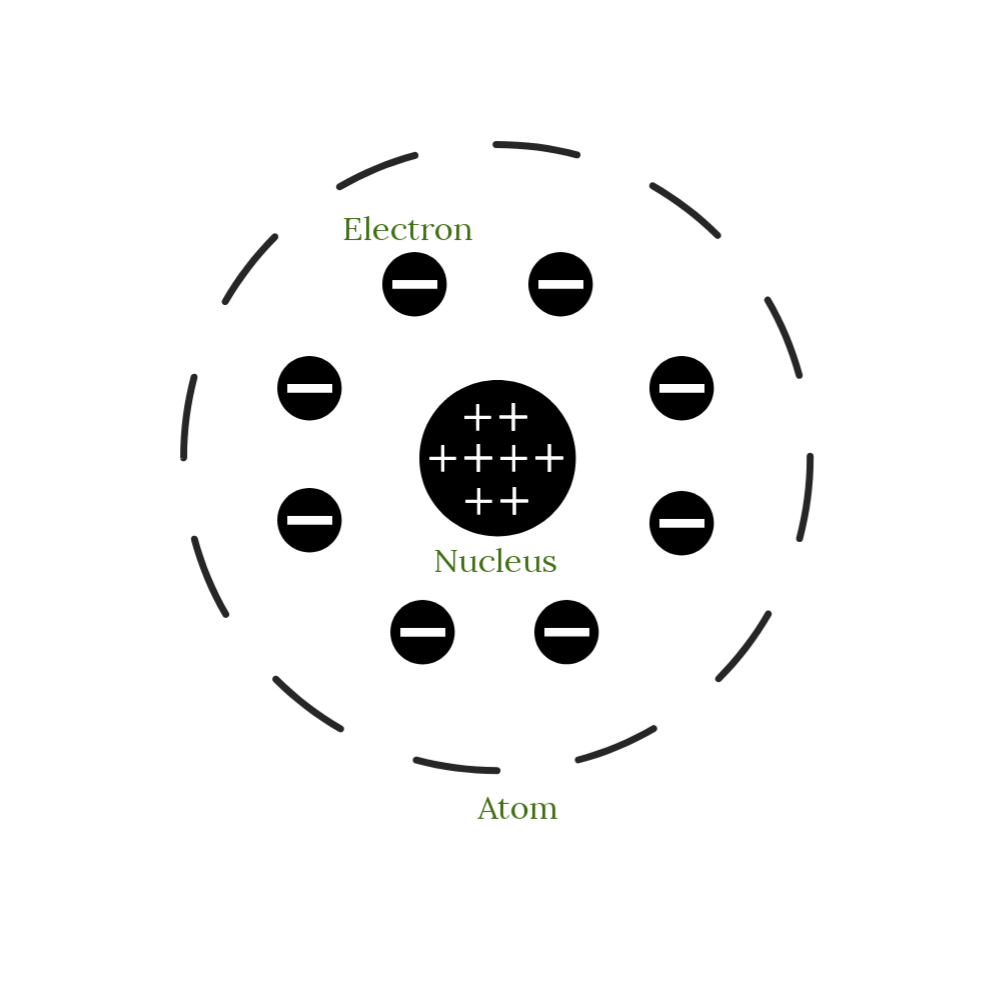
图 2. 卢瑟福的原子模型(上图)
卢瑟福原子模型的缺点
- 卢瑟福模型预测电子将围绕带正电的原子核运行,预计该原子核不会稳定。带电粒子沿圆形路线快速运动,会不断失去能量并最终坍缩到原子核中。这导致原子不稳定,而我们知道原子非常稳定。
- 因为它只是假设原子核中存在质子,所以卢瑟福模型无法解决原子质量问题。

图 3. 卢瑟福原子模型的缺点
示例问题
问题 1:为什么 JJ Thomson 的原子模型存在缺陷?
回答:
Thomson’s atomic model does not explain how the positive charge on the electrons inside the atom is maintained. It also fails to explain the stability of an atom. The nucleus of an atom is not mentioned in the hypothesis. It could not explain Rutherford’s scattering experiment.
问题2:简要解释卢瑟福的散射实验。
回答:
To determine how electrons are arranged in an atom, the Alpha (α) Particle Scattering Experiment was organized by Rutherford. Rapidly-moving α-particles were directed to bombard a thin sheet of gold. The gold foil was selected so as to obtain an extremely thin layer. The thickness of the gold foil was about 1000 atoms. Doubly-charged helium ions are known as α-particles. Rapidly-moving α-particles possess a great deal of energy, as they have a mass of about 4 amu.
The hypothesis was that α-particles would be deflected by the sub-atomic particles in the gold atoms. Rutherford didn’t expect to witness significant deflections as the α-particles were considerably heavier than the protons. However, the experiment produced entirely unanticipated results.
问题3:卢瑟福通过阿尔法(α)粒子散射实验发现了哪个亚原子粒子?
回答:
The sub-atomic particle discovered by Rutherford through his Alpha (α) Particle Scattering Experiment was the Nucleus.
问题 4:为什么在 Alpha (α) 粒子散射实验中使用金箔?
回答:
A gold foil was selected so as to obtain an extremely thin layer and as it is the most malleable metal. However, if any other metal foil was used, the results obtained would be consistent.
问题 5:卢瑟福的原子模型的主要缺点是什么?
回答:
Rutherford’s Model predicts that electrons will orbit around the positively charged nucleus, which is not anticipated to be stable. A charged particle in rapid motion along a circular route, would lose energy continually and eventually collapse into the nucleus. This causes an atom to be unstable, whereas we know that atoms are extremely stable.
问题6:散射实验中α粒子偏转了哪些角度?
回答:
The majority of the fast-moving α-particles went directly through the gold foil. The foil deflected some of the α-particles by fairly small angles. Only a few α-particles were completely deflected back (by 180 degrees).
问题 7:卢瑟福是如何定义轨道的?
回答:
According to Rutherford, negatively charged electrons encircle the nucleus of an atom. He believed that the electrons encircling the nucleus travel around it in circular routes at great speeds. He referred to these circular routes as well-defined orbits.