简谐运动
振荡运动的研究是物理学的基础;它的概念是理解许多物理现象所必需的。振动的字符串在西塔琴、吉他和小提琴等乐器中产生悦耳的声音。电话和扬声器系统中的鼓膜和振膜围绕它们的平均位置振动。让我们简要讨论振荡运动和简谐运动。
什么是振荡运动?
The to and fro motion of an object from its mean position is defined as oscillatory motion. The ideal condition is for the object to remain in oscillatory motion in the absence of friction indefinitely, but this is not possible in the real world, and the object must settle into equilibrium. The term vibration, which is found in a swinging pendulum, is used to describe mechanical oscillation. Similarly, the human heartbeat is an example of oscillation in dynamic systems.
- 振荡运动被定义为粒子围绕平均位置来回移动。振荡运动被定义为粒子在平衡(或)平均位置的任一侧移动。
- 它是一种具有两个极值点的周期性运动。例如,考虑简单摆的振荡和弹簧质量系统。
- 物体将继续围绕一个固定点在两个极值点之间移动,该固定点被称为沿任何路径的平均位置(或平衡位置)。 (请注意,路径不是约束。)
- 将有一个指向平衡(或平均)位置的恢复力。
- 振荡运动中粒子的净力在平均位置为零。
- 平均位置是稳定的平衡位置。
振荡运动的一些例子是:
- 简单的钟摆振荡。
- 乐器的振动字符串是振动运动的机械例子。
- 弹簧运动。
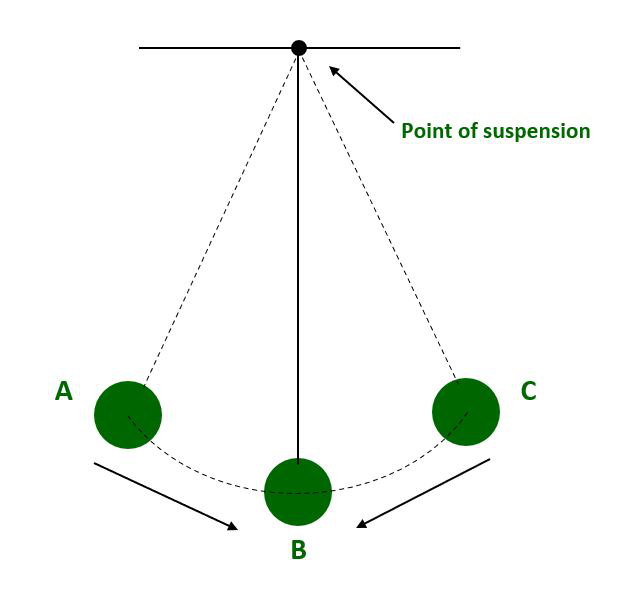
单摆的振荡。
什么是周期性运动?
In general, we describe the motion of bodies in terms of how they move. The motion of an object is said to be periodic if it moves in such a way that it repeats its path at regular intervals of time.
- 在相等的时间间隔之后,运动重复自身。考虑匀速圆周运动。
- 没有所谓的平衡位置。
- 没有恢复力这样的东西。
- 没有稳定的平衡位置。
周期性运动的一些例子是:
- 时钟指针的运动。时针的运动周期为 12 小时,分针的运动周期为 1 小时,时钟秒针的运动周期为 1 分钟。
- 当一个简单的钟摆从静止位置拉到一侧并释放时,它被称为是周期性的,从而导致来回运动(摆动运动)。
- 月球绕地球运动。
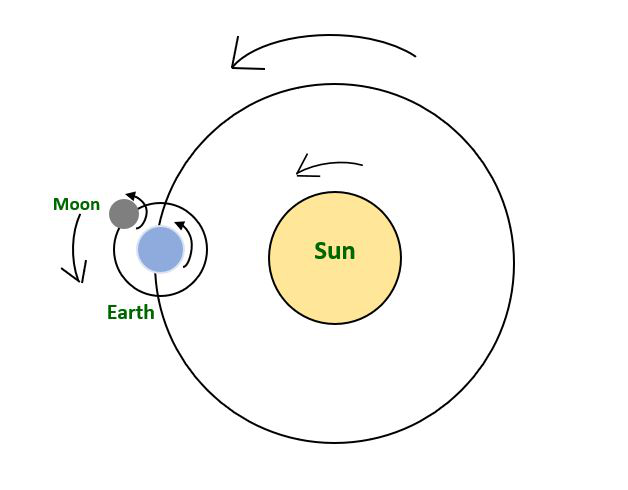
地球围绕太阳的周期性运动
简谐运动 (SHM)
Simple harmonic motion is an oscillatory motion in which the particle’s acceleration at any position is directly proportional to its displacement from the mean position. It is an example of oscillatory motion.
简单谐波运动 (SHM) 都是振荡和周期性的,但并非所有振荡运动都是 SHM。摆动运动也称为所有摆动运动的谐波运动,其中最重要的是简谐运动(SHM)。
- 它是一种以直线连接两个极值点的振荡类型(SHM 的路径是一个约束)。
- 对象的路径必须是直线。
- 将有一个指向平衡(或平均)位置的恢复力。
- 在简谐运动中,平均位置是一个稳定的平衡。
(1) 线性简谐运动:
当一个粒子沿一条直线围绕一个固定点(称为平衡位置)来回移动时,这称为线性简谐运动。例如,考虑弹簧质量系统。
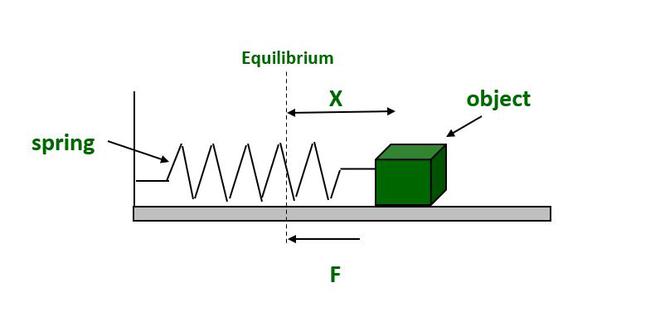
线性简谐运动的条件
作用在粒子上的恢复力或加速度必须始终与粒子的位移成正比并指向平衡位置。
F ∝ – X
or
a ∝ -x
where F is the Restoring force, X is the displacement of particle from equilibrium position and a is the acceleration.
(2) 角简谐运动:
当系统相对于固定轴以一定角度振荡时,就会发生角简谐运动。角简谐运动中粒子的位移是用角位移来测量的。扭摆就是一个例子。
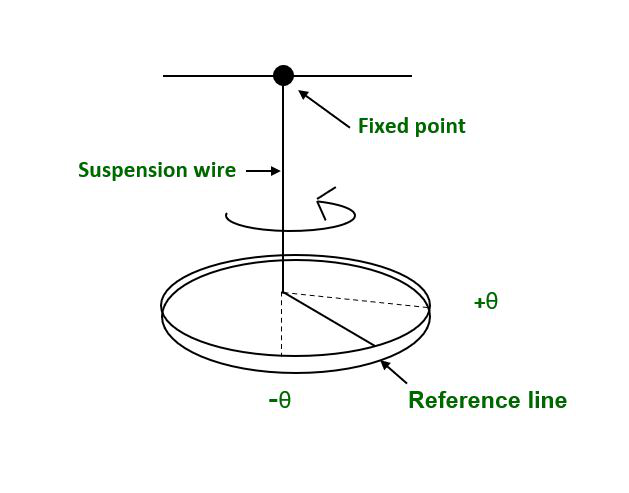
扭摆
角简谐运动的条件:
作用在粒子上的恢复扭矩(或)角加速度应始终与粒子的角位移成正比,并朝向平衡位置。
T ∝ -θ
or
α ∝ -θ
where T is Torque, θ is the Angular displacement and α is the Angular acceleration.
与简谐运动相关的术语
- 振幅:一个粒子的振幅是它从其平衡或平均位置的最大位移,它的方向总是远离平均或平衡位置。米是它的 SI 单位。

- 时间周期:粒子的周期是完成一次振荡所需的时间。因此,SHM 的周期是运动重复之前的最短时间。结果,运动将在 nT 之后重复,其中 n 是整数。

T = 2π/ω
where ω is the Angular frequency and T is the Time period.
- 频率: SHM 的频率是粒子每单位时间执行的振荡次数。赫兹或 rps(每秒转数)是频率的 SI 单位。
Frequency, f = 1/ T and
Angular frequency, ω = 2πf = 2π/T
- 相位:粒子位移的大小和方向代表了SHM的相位,也就是它的振荡状态。
The expression for a particle’s position as a function of time.
x = A sin (ωt + Φ)
where (ωt + Φ) is the particles phase.
- 相位差:相位差定义为以简谐运动运动的两个粒子的总相位角相对于平均位置的差。当两个振动粒子同相时,它们的相位差是π的偶数倍。如果两个振动粒子之间的相位差是 π 的奇数倍,则称它们处于相反相位。
Phase Difference is represented as ΔΦ.
ΔΦ = nπ [for same phase]
ΔΦ = (2n + 1) π [for odd phase]
where n = 0, 1, 2, 3, . . . . .
简谐运动方程
让我们考虑一个质量为 (m) 的粒子沿路径 A'OA 进行简单谐波运动,平均位置为 O。假设粒子在位置 P(距点 O 一定距离)时的速度为 V 0
当时, t = 0 P 处的粒子(向 A 点移动)
此时, t = t ,如果速度为 V,则粒子此时位于 Q(距点 O 的距离为 X),则:
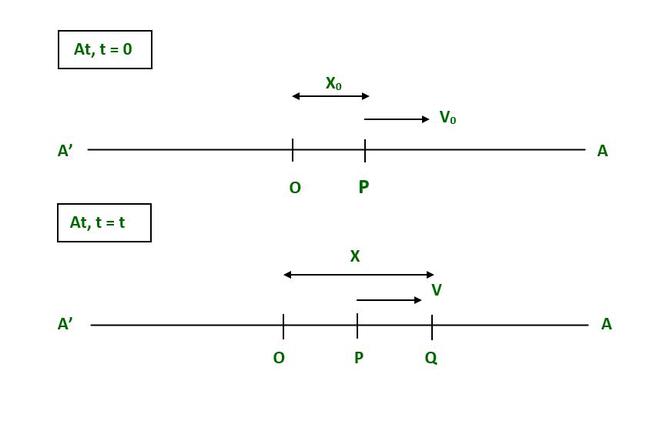
The force F acting on a particle at point p is given as,
F = -K X where, K = positive constant
We know that,
F = m a where, a = Acceleration at Q
m a = -K X
a = -(K/m) X [putting ω2 = K/m]
a = -ω2 X [Since, a = d2X/d2t]
d2X/d2t = -ω2 X
Hence,
d2X/d2t + ω2 X = 0
which is the differential equation for linear simple harmonic motion.
Solutions of Differential Equations of SHM:
The solutions to the differential equation for simple harmonic motion are as follows:
- This solution when the particle is in its mean position at point (O): x = Asinωt.
- When the particle is at the position p (not at mean position): x = Asinϕ.
- When the particle is at position Q (any time t): x = Asin(ωt+ϕ).
示例问题
问题一:为什么谐波运动是周期性的?
解决方案:
The sine wave can represent a harmonic motion. When a spring is stretched from its mean position, it oscillates to and fro about the mean position under the influence of a restoring force that is always directed towards the mean position and whose magnitude at any instant is proportional to the body’s displacement from the mean position at that instant. When there is no friction, the motion tends to be periodic. The harmonic motion is periodic in this case.
问题2:什么是周期性和非周期性变化?
解决方案:
Periodic changes are those that occur at regular intervals of time, such as the occurrence of day and night, or the change of periods in your school. Non-periodic changes are those that do not occur on a regular basis, such as the freezing of ice to water.
问题3:地球绕太阳和绕极轴公转的周期是多少?地球的运动解释是什么?
解决方案:
The earth’s revolution around the sun takes one year, and its revolution around its polar axis takes one day. The motion of earth is periodic because after some interval of time it repeats its path.
问题 4:运动是否可能是振荡的而不是简谐的?
解决方案:
When a ball is dropped from a height onto a perfectly elastic surface, the motion of the ball is oscillatory but not simple harmonic because the restoring force, F = mg = constant.
问题 5:SHM 中的频率是多少。时间段和频率如何相关?
解决方案:
The frequency of SHM is the number of oscillations performed by a particle per unit of time. Hertz, or r.p.s. (rotations per second), is the SI unit of frequency. Frequency and time period are related as:
Frequency, (f) = 1/ Time period (T)
问题 6:简谐运动的角频率是多少?
解决方案:
Angular frequency (ω), also known as radial or circular frequency, is a unit of time for measuring angular displacement. As a result, its units are degrees (or radians) per second.
The angular frequency(ω) is given by the expression,
ω = 2π/T.
问题 7:弹簧常数为 1200 N m–1 的弹簧安装在水平工作台上。一个 3 kg 的质量连接到弹簧的自由端。然后在释放之前将质量块从侧面拉到 2.0 m 的距离。确定以下内容:
(i) 振荡频率,
(ii) 质量的最大加速度,以及
(iii) 质量的最大速度。
解决方案:

Given that,
The spring constant, k = 1200 N/m.
The mass of the object, m = 3 kg.
The displacement, x = 2 m.
(i) The frequency of oscillation:
We know that frequency (f) = 1/Time period (T) [ T = 2π/ω and ω = √k/m]
Therefore,
f = (1/2π)√k/m
= (1/2 × 3,14) √1200/3 = 3.18 Hz.
(ii) Maximum acceleration of the mass:
The Maximum acceleration (a) = ω2x
where, ω = Angular frequency = √k/m
Therefore, a = x(k/m)
a = 2 × (1200/3) = 800 m/s2.
(iii) The maximum speed of the mass:
The maximum speed (V) = ωx
Put, ω = √k/m.
Therefore, V = x(√k/m)
V = 2 × (√1200/3) = 40 m/s.