给定一个马尔可夫链G,如果我们在时间t = 0时从状态S开始,则可以找到在时间t = T时到达状态F的概率。
马尔可夫链是一个随机过程,由各种状态和从一种状态转移到另一种状态的概率组成。我们可以使用有向图来表示它,其中节点代表状态,边缘代表从一个节点到另一个节点的概率。从一个节点移动到另一个节点需要花费单位时间。对于每个节点,出局边缘的关联概率之和为1。
考虑给定的马尔可夫链(G),如下图所示:
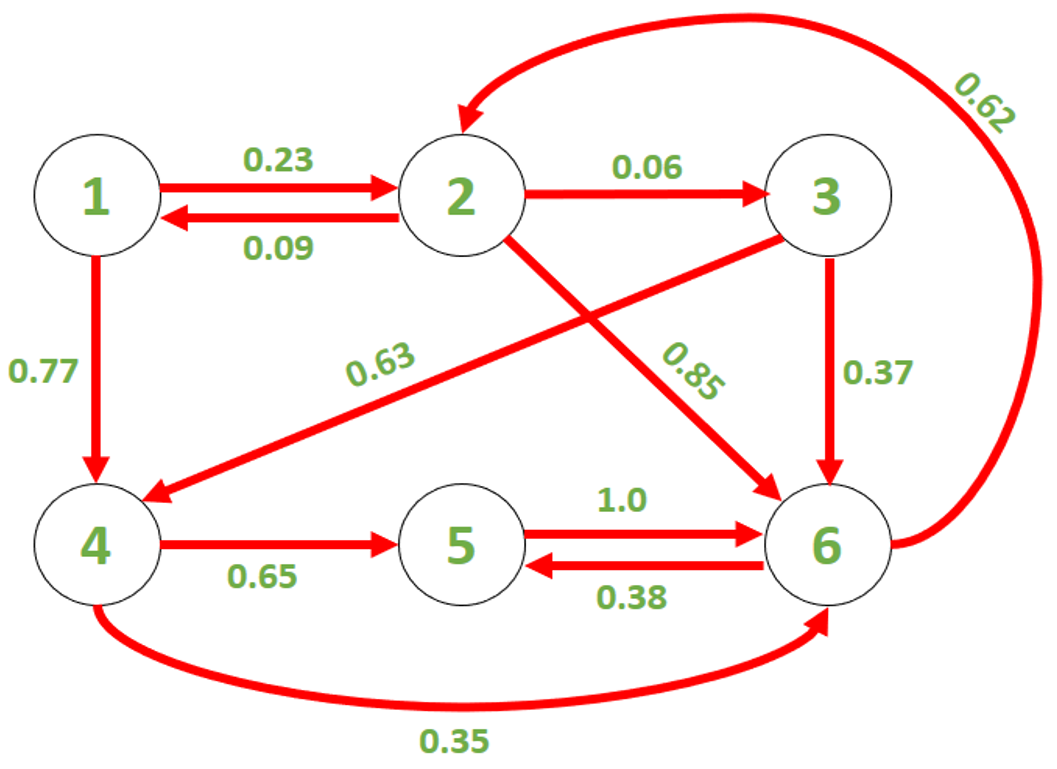
例子:
Input : S = 1, F = 2, T = 1
Output: 0.23
We start at state 1 at t = 0,
so there is a probability of 0.23
that we reach state 2 at t = 1.
Input: S = 4, F = 2, T = 100
Output: 0.284992在上一篇文章中,讨论了一种动态编程方法,其时间复杂度为O(N 2 T),其中N是状态数。
矩阵求幂方法:我们可以为马尔可夫链建立一个邻接矩阵,以表示状态之间转移的概率。例如,上面给出的图的邻接矩阵为:
![由QuickLaTeX.com渲染 \[ M= \left[ {\begin{array}{cccccc} 0 & 0.09 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0.23 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0.62 \\ 0 & 0.06 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0.77 & 0 & 0.63 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0.65 & 0 & 0.38 \\ 0 & 0.85 & 0.37 & 0.35 & 1.0 & 0 \\ \end{array} } \right] \]](https://mangdo-1254073825.cos.ap-chengdu.myqcloud.com//front_eng_imgs/geeksforgeeks2021/Finding%20the%20probability%20of%20a%20state%20at%20a%20given%20time%20in%20a%20Markov%20chain%20%7C%20Set%202_1.jpg)
我们可以观察到,在时间t处的概率分布由P(t)= M * P(t – 1)给出,初始概率分布P(0)是零向量,第S个元素为1。使用这些结果,我们可以求解P(t)的递归表达式。例如,如果我们将S设为3,则P(t)由下式给出:
![由QuickLaTeX.com渲染 \[ P(t)= M^t \left[ {\begin{array}{c} 0 \\ 0 \\ 1 \\ 0 \\ 0 \\ 0 \\ \end{array} } \right] \]](https://mangdo-1254073825.cos.ap-chengdu.myqcloud.com//front_eng_imgs/geeksforgeeks2021/Finding%20the%20probability%20of%20a%20state%20at%20a%20given%20time%20in%20a%20Markov%20chain%20%7C%20Set%202_2.jpg)
如果我们使用有效的矩阵求幂技术,则该方法的时间复杂度为O(N 3 * log T)。如果T的值大大高于状态数(即N),则此方法的性能优于动态编程方法。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Macro to define a vector of float
#define vf vector
// Function to multiply two matrices A and B
vector multiply(vector A, vector B, int N)
{
vector C(N, vf(N, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
for (int k = 0; k < N; ++k)
C[i][j] += A[i][k] * B[k][j];
return C;
}
// Function to calculate the power of a matrix
vector matrix_power(vector M, int p, int n)
{
vector A(n, vf(n, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
A[i][i] = 1;
while (p) {
if (p % 2)
A = multiply(A, M, n);
M = multiply(M, M, n);
p /= 2;
}
return A;
}
// Function to calculate the probability of
// reaching F at time T after starting from S
float findProbability(vector M, int N, int F,
int S, int T)
{
// Storing M^T in MT
vector MT = matrix_power(M, T, N);
// Returning the answer
return MT[F - 1][S - 1];
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Adjacency matrix
// The edges have been stored in the row
// corresponding to their end-point
vector G{ { 0, 0.09, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0.23, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0.62 },
{ 0, 0.06, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0.77, 0, 0.63, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0.65, 0, 0.38 },
{ 0, 0.85, 0.37, 0.35, 1.0, 0 }};
// N is the number of states
int N = 6;
int S = 4, F = 2, T = 100;
cout << "The probability of reaching " << F << " at time "
<< T << "\nafter starting from " << S << " is "
<< findProbability(G, N, F, S, T);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the above approach
class GFG
{
// Function to multiply two matrices A and B
static double[][] multiply(double[][] A,
double[][] B, int N)
{
double[][] C = new double[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
for (int k = 0; k < N; ++k)
C[i][j] += A[i][k] * B[k][j];
return C;
}
// Function to calculate the power of a matrix
static double[][] matrix_power(double[][] M, int p, int n)
{
double[][] A = new double[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
A[i][i] = 1;
while (p > 0)
{
if (p % 2 == 1)
A = multiply(A, M, n);
M = multiply(M, M, n);
p /= 2;
}
return A;
}
// Function to calculate the probability of
// reaching F at time T after starting from S
static double findProbability(double[][] M,
int N, int F, int S, int T)
{
// Storing M^T in MT
double[][] MT = matrix_power(M, T, N);
// Returning the answer
return MT[F - 1][S - 1];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Adjacency matrix
// The edges have been stored in the row
// corresponding to their end-point
double[][] G = { { 0, 0.09, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0.23, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0.62 },
{ 0, 0.06, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0.77, 0, 0.63, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0.65, 0, 0.38 },
{ 0, 0.85, 0.37, 0.35, 1.0, 0 } };
// N is the number of states
int N = 6;
int S = 4, F = 2, T = 100;
System.out.printf(
"The probability of reaching " + F +
" at time " + T + "\nafter starting from " +
S + " is %f",
findProbability(G, N, F, S, T));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiPython3
# Python implementation of the above approach
from typing import List
# Function to multiply two matrices A and B
def multiply(A: List[List[float]], B: List[List[float]],
N: int) -> List[List[float]]:
C = [[0 for _ in range(N)] for _ in range(N)]
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
for k in range(N):
C[i][j] += A[i][k] * B[k][j]
return C
# Function to calculate the power of a matrix
def matrix_power(M: List[List[float]], p: int, n: int) -> List[List[float]]:
A = [[0 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
A[i][i] = 1
while (p):
if (p % 2):
A = multiply(A, M, n)
M = multiply(M, M, n)
p //= 2
return A
# Function to calculate the probability of
# reaching F at time T after starting from S
def findProbability(M: List[List[float]], N: int, F: int, S: int,
T: int) -> float:
# Storing M^T in MT
MT = matrix_power(M, T, N)
# Returning the answer
return MT[F - 1][S - 1]
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Adjacency matrix
# The edges have been stored in the row
# corresponding to their end-point
G = [[0, 0.09, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0.23, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0.62],
[0, 0.06, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0.77, 0, 0.63, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0.65, 0, 0.38], [0, 0.85, 0.37, 0.35, 1.0, 0]]
# N is the number of states
N = 6
S = 4
F = 2
T = 100
print(
"The probability of reaching {} at time {}\nafter starting from {} is {}\n"
.format(F, T, S, findProbability(G, N, F, S, T)))
# This code is contributed by sanjeev2552C#
// C# implementation of the above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to multiply two matrices A and B
static double[,] multiply(double[,] A,
double[,] B, int N)
{
double[,] C = new double[N, N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
for (int k = 0; k < N; ++k)
C[i, j] += A[i, k] * B[k, j];
return C;
}
// Function to calculate the power of a matrix
static double[,] matrix_power(double[,] M, int p, int n)
{
double[,] A = new double[n,n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
A[i, i] = 1;
while (p > 0)
{
if (p % 2 == 1)
A = multiply(A, M, n);
M = multiply(M, M, n);
p /= 2;
}
return A;
}
// Function to calculate the probability of
// reaching F at time T after starting from S
static double findProbability(double[,] M,
int N, int F, int S, int T)
{
// Storing M^T in MT
double[,] MT = matrix_power(M, T, N);
// Returning the answer
return MT[F - 1, S - 1];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Adjacency matrix
// The edges have been stored in the row
// corresponding to their end-point
double[,] G = { { 0, 0.09, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0.23, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0.62 },
{ 0, 0.06, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0.77, 0, 0.63, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0.65, 0, 0.38 },
{ 0, 0.85, 0.37, 0.35, 1.0, 0 } };
// N is the number of states
int N = 6;
int S = 4, F = 2, T = 100;
Console.Write("The probability of reaching " + F +
" at time " + T + "\nafter starting from " +
S + " is {0:F6}",
findProbability(G, N, F, S, T));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar输出:
The probability of reaching 2 at time 100
after starting from 4 is 0.284991时间复杂度:O(N 3 * logT)
空间复杂度:O(N 2 )