给定一个马尔可夫链 G,如果我们从时间 t = 0 的状态 S 开始,我们就有了在时间 t = T 到达状态 F 的概率。
马尔可夫链是由各种状态和从一种状态移动到另一种状态的概率组成的随机过程。我们可以使用有向图来表示它,其中节点表示状态,边表示从一个节点到另一个节点的概率。从一个节点移动到另一个节点需要单位时间。出边的相关概率之和对于每个节点都是一个。
考虑给定的马尔可夫链( G ),如下图所示:
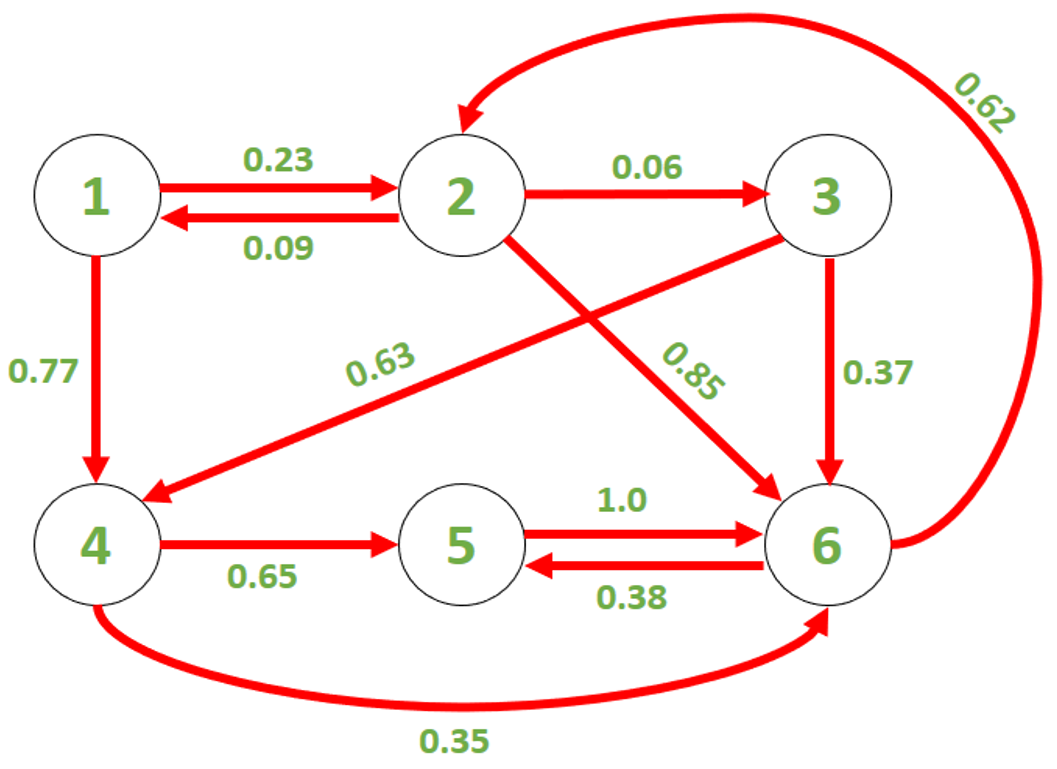
例子:
Input : S = 1, F = 2, T = 1
Output : 0.23
We start at state 1 at t = 0,
so there is a probability of 0.23
that we reach state 2 at t = 1.
Input : S = 4, F = 2, T = 100
Output : 0.284992我们可以使用动态规划和深度优先搜索(DFS)来解决这个问题,将状态和时间作为两个 DP 变量。我们可以很容易地观察到,在时间t从状态 A 到状态 B 的概率等于在时间t – 1处于 A 的概率与连接 A 和 B 的边相关的概率的乘积。因此概率在时间t在 B 的数量是与 B 相邻的所有 A 的数量之和。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Macro for vector of pair to store
// each node with edge
#define vp vector >
// Function to calculate the
// probability of reaching F
// at time T after starting
// from S
float findProbability(vector& G, int N,
int F, int S, int T)
{
// Declaring the DP table
vector > P(N + 1, vector(T + 1, 0));
// Probability of being at S
// at t = 0 is 1.0
P[S][0] = 1.0;
// Filling the DP table
// in bottom-up manner
for (int i = 1; i <= T; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= N; ++j)
for (auto k : G[j])
P[j][i] += k.second * P[k.first][i - 1];
return P[F][T];
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Adjacency list
vector G(7);
// Building the graph
// The edges have been stored in the row
// corresponding to their end-point
G[1] = vp({ { 2, 0.09 } });
G[2] = vp({ { 1, 0.23 }, { 6, 0.62 } });
G[3] = vp({ { 2, 0.06 } });
G[4] = vp({ { 1, 0.77 }, { 3, 0.63 } });
G[5] = vp({ { 4, 0.65 }, { 6, 0.38 } });
G[6] = vp({ { 2, 0.85 }, { 3, 0.37 }, { 4, 0.35 }, { 5, 1.0 } });
// N is the number of states
int N = 6;
int S = 4, F = 2, T = 100;
cout << "The probability of reaching " << F
<< " at time " << T << " \nafter starting from "
<< S << " is " << findProbability(G, N, F, S, T);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class pair
{
int first;
double second;
public pair(int first, double second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Function to calculate the
// probability of reaching F
// at time T after starting
// from S
static float findProbability(Vector[] G,
int N, int F, int S, int T)
{
// Declaring the DP table
float[][] P = new float[N + 1][T + 1];
// Probability of being at S
// at t = 0 is 1.0
P[S][0] = (float) 1.0;
// Filling the DP table
// in bottom-up manner
for (int i = 1; i <= T; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= N; ++j)
for (pair k : G[j])
P[j][i] += k.second * P[k.first][i - 1];
return P[F][T];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Adjacency list
Vector[] G = new Vector[7];
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
{
G[i] = new Vector();
}
// Building the graph
// The edges have been stored in the row
// corresponding to their end-point
G[1].add(new pair(2, 0.09));
G[2].add(new pair(1, 0.23));
G[2].add(new pair(6, 0.62));
G[3].add(new pair(2, 0.06));
G[4].add(new pair(1, 0.77));
G[4].add(new pair(3, 0.63));
G[5].add(new pair(4, 0.65));
G[5].add(new pair(6, 0.38));
G[6].add(new pair(2, 0.85));
G[6].add(new pair(3, 0.37));
G[6].add(new pair(4, 0.35));
G[6].add(new pair(5, 1.0));
// N is the number of states
int N = 6;
int S = 4, F = 2, T = 100;
System.out.print("The probability of reaching " + F +
" at time " + T + " \nafter starting from " +
S + " is "
+ findProbability(G, N, F, S, T));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Python3
# Python3 implementation of the above approach
# Macro for vector of pair to store
# each node with edge
# define vp vector >
# Function to calculate the
# probability of reaching F
# at time T after starting
# from S
def findProbability(G, N, F, S, T):
# Declaring the DP table
P = [[0 for i in range(T + 1)]
for j in range(N + 1)]
# Probability of being at S
# at t = 0 is 1.0
P[S][0] = 1.0;
# Filling the DP table
# in bottom-up manner
for i in range(1, T + 1):
for j in range(1, N + 1):
for k in G[j]:
P[j][i] += k[1] * P[k[0]][i - 1];
return P[F][T]
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
# Adjacency list
G = [0 for i in range(7)]
# Building the graph
# The edges have been stored in the row
# corresponding to their end-point
G[1] = [ [ 2, 0.09 ] ]
G[2] = [ [ 1, 0.23 ], [ 6, 0.62 ] ]
G[3] = [ [ 2, 0.06 ] ]
G[4] = [ [ 1, 0.77 ], [ 3, 0.63 ] ]
G[5] = [ [ 4, 0.65 ], [ 6, 0.38 ] ]
G[6] = [ [ 2, 0.85 ], [ 3, 0.37 ],
[ 4, 0.35 ], [ 5, 1.0 ] ]
# N is the number of states
N = 6
S = 4
F = 2
T = 100
print("The probability of reaching {} at "
"time {}\nafter starting from {} is {}".format(
F, T, S, findProbability(G, N, F, S, T)))
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56 C#
// C# implementation of the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
class pair
{
public int first;
public double second;
public pair(int first, double second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Function to calculate the
// probability of reaching F
// at time T after starting
// from S
static float findProbability(List[] G,
int N, int F, int S, int T)
{
// Declaring the DP table
float[,] P = new float[N + 1, T + 1];
// Probability of being at S
// at t = 0 is 1.0
P[S, 0] = (float) 1.0;
// Filling the DP table
// in bottom-up manner
for (int i = 1; i <= T; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= N; ++j)
foreach (pair k in G[j])
P[j, i] += (float)k.second *
P[k.first, i - 1];
return P[F, T];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Adjacency list
List[] G = new List[7];
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
{
G[i] = new List();
}
// Building the graph
// The edges have been stored in the row
// corresponding to their end-point
G[1].Add(new pair(2, 0.09));
G[2].Add(new pair(1, 0.23));
G[2].Add(new pair(6, 0.62));
G[3].Add(new pair(2, 0.06));
G[4].Add(new pair(1, 0.77));
G[4].Add(new pair(3, 0.63));
G[5].Add(new pair(4, 0.65));
G[5].Add(new pair(6, 0.38));
G[6].Add(new pair(2, 0.85));
G[6].Add(new pair(3, 0.37));
G[6].Add(new pair(4, 0.35));
G[6].Add(new pair(5, 1.0));
// N is the number of states
int N = 6;
int S = 4, F = 2, T = 100;
Console.Write("The probability of reaching " + F +
" at time " + T + " \nafter starting from " +
S + " is "
+ findProbability(G, N, F, S, T));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Javascript
输出:
The probability of reaching 2 at time 100
after starting from 4 is 0.284992时间复杂度:O(N 2 * T)
空间复杂度:O(N * T)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。