使用 Dplyr 包连接 R 中的数据
在本文中,我们将研究在 R 编程语言中使用 dplyr 连接数据的不同方法。
我们需要加载 dplyr 包。键入以下命令 -
Install - install.packages("dplyr")
Load - library("dplyr") 方法一:使用内连接
在这种连接数据的方法中,用户调用 inner_join函数,这将导致连接数据与 R 编程语言中两个表中具有匹配值的记录。
inner_join()函数:
此函数包括 `x` 和 `y` 中的所有行。
Syntax:
inner_join(x, y, by = NULL, on = NULL)
Parameters:
- x: A data.table
- y: A data.table
- by: A character vector of variables to join by.
- on: Indicate which columns in x should be joined with which columns in y.
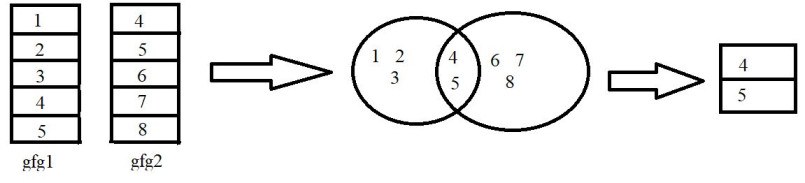
例子:
在此示例中,我们将使用 dplyr 包中的 inner_join()函数以 R 编程语言连接两个不同的数据,如上图所示。
R
# load the library
library("dplyr")
# create dataframe with 1 to 5 integers
gfg1 < -data.frame(ID=c(1: 5))
# create dataframe with 4 to 8 integers
gfg2 < -data.frame(ID=c(4: 8))
# perform inner join
inner_join(gfg1, gfg2, by="ID")R
# load the library
library("dplyr")
# create the dataframes
gfg1<-data.frame(ID=c(1:5))
gfg2<-data.frame(ID=c(4:8))
# perform left join
left_join(gfg1,gfg2, by = "ID")R
# load the library
library("dplyr")
# create dataframes
gfg1<-data.frame(ID=c(1:5))
gfg2<-data.frame(ID=c(4:8))
# perform right join
right_join(gfg1,gfg2, by = "ID")R
# load library
library("dplyr")
# create dataframe
gfg1<-data.frame(ID=c(1:5))
gfg2<-data.frame(ID=c(4:8))
# perform full join
full_join(gfg1,gfg2, by = "ID")R
# load the library
library("dplyr")
# create the dataframes
gfg1<-data.frame(ID=c(1:5))
gfg2<-data.frame(ID=c(4:8))
# perform semijoin
semi_join(gfg1,gfg2, by = "ID")R
# load the library
library("dplyr")
# create the dataframes
gfg1<-data.frame(ID=c(1:5))
gfg2<-data.frame(ID=c(4:8))
# perform anti join
anti_join(gfg1,gfg2, by = "ID")输出:
ID
1 4
2 5 方法2:使用左连接
在这种连接数据的方法中,用户调用 left_join函数,这将导致连接数据包括将第一个数据帧中的所有行与 R 编程语言中 second.s 上的相应值匹配。
left_join()函数:
此函数包括 `x` 中的所有行。
Syntax:
left_join(x, y, by = NULL, on = NULL)
Parameters:
- x: A data.table
- y: A data.table
- by: A character vector of variables to join by.
- on: Indicate which columns in x should be joined with which columns in y.
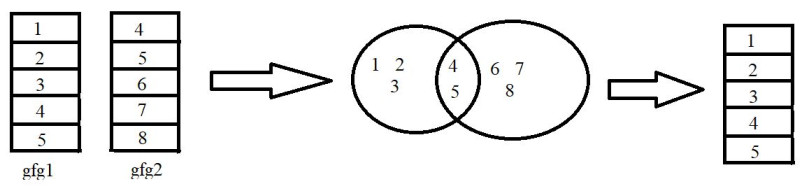
例子:
在此示例中,我们将使用 dplyr 包中的 left_join()函数以 R 编程语言连接两个不同的数据,如上图所示。
R
# load the library
library("dplyr")
# create the dataframes
gfg1<-data.frame(ID=c(1:5))
gfg2<-data.frame(ID=c(4:8))
# perform left join
left_join(gfg1,gfg2, by = "ID")
输出:
ID
1 1
2 2
3 3
4 4
5 5方法3:使用右连接
在这种连接数据的方法中,用户调用 right_join函数,这将导致连接数据包括将第二个数据帧中的所有行与 R 编程语言中第一个数据帧中的相应值匹配。
right_join()函数:
此函数包括“y”中的所有行和“x”的相应行。
Syntax:
right_join(x, y, by = NULL, on = NULL)
Parameters:
- x: A data.table
- y: A data.table
- by: A character vector of variables to join by.
- on: Indicate which columns in x should be joined with which columns in y.
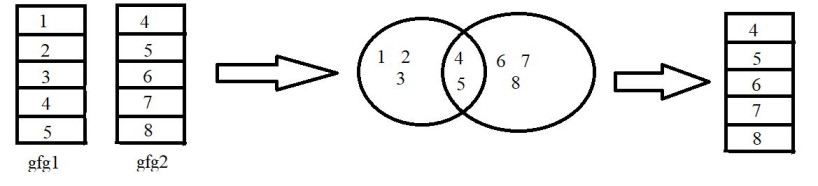
例子:
在此示例中,我们将使用 dplyr 包中的 right_join()函数以 R 编程语言连接两个不同的数据,如上图所示。
R
# load the library
library("dplyr")
# create dataframes
gfg1<-data.frame(ID=c(1:5))
gfg2<-data.frame(ID=c(4:8))
# perform right join
right_join(gfg1,gfg2, by = "ID")
输出:
ID
1 4
2 5
3 6
4 7
5 8方法 4:使用完全连接
在这种连接数据的方法中,用户调用 right_join函数,这将导致连接表中所有行的连接数据,
full_join()函数:
此函数包括所有行。
Syntax:
full_join(x, y, by = NULL, on = NULL)
Parameters:
- x: A data.table
- y: A data.table
- by: A character vector of variables to join by.
- on: Indicate which columns in x should be joined with which columns in y.
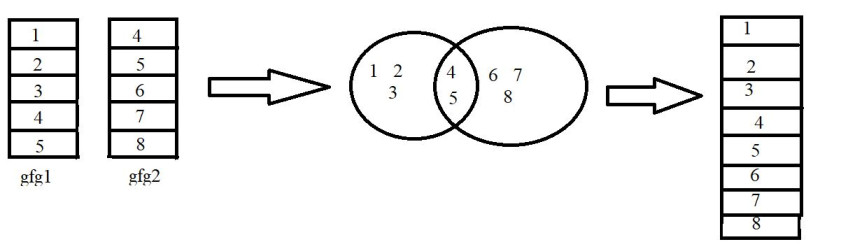
例子:
在此示例中,我们将使用 dplyr 包中的 full_join()函数以 R 编程语言连接两个不同的数据,如上图所示。
R
# load library
library("dplyr")
# create dataframe
gfg1<-data.frame(ID=c(1:5))
gfg2<-data.frame(ID=c(4:8))
# perform full join
full_join(gfg1,gfg2, by = "ID")
输出:
ID
1 1
2 2
3 3
4 4
5 5
6 6
7 7
8 8方法5:使用半连接
在这种连接数据的方法中,用户调用 right_join函数,这将返回第一个表中至少找到一个匹配项的每一行的一个副本。
semi_join()函数:
此函数返回 x 中在 y 中有匹配值的所有行,只保留 x 中的列。
Syntax:
semi_join(x, y, by = NULL, on = NULL)
Parameters:
- x: A data.table
- y: A data.table
- by: A character vector of variables to join by.
- on: Indicate which columns in x should be joined with which columns in y.
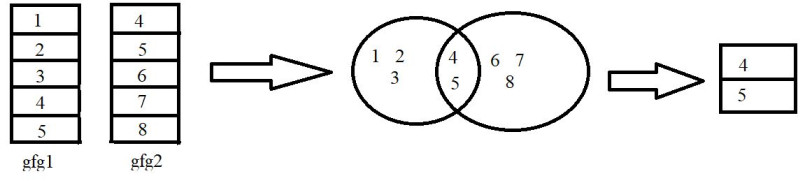
例子:
在此示例中,我们将使用 dplyr 包中的 semi_join()函数以 R 编程语言连接两个不同的数据,如上图所示。
R
# load the library
library("dplyr")
# create the dataframes
gfg1<-data.frame(ID=c(1:5))
gfg2<-data.frame(ID=c(4:8))
# perform semijoin
semi_join(gfg1,gfg2, by = "ID")
输出:
ID
1 4
2 5方法六:使用反连接
在这种连接数据的方法中,用户调用 right_join函数,这将返回 x 中在 y 中没有匹配值的所有行,只保留 x 中的列。
anti_join()函数:
此函数返回 x 中在 y 中没有匹配值的所有行,只保留 x 中的列。
Syntax:
anti_join(x, y, by = NULL, on = NULL)
Parameters:
- x: A data.table
- y: A data.table
- by: A character vector of variables to join by.
- on: Indicate which columns in x should be joined with which columns in y.
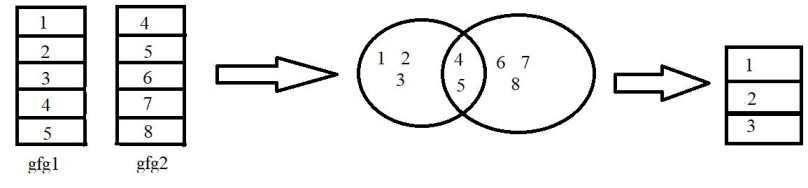
例子:
在此示例中,我们将使用 dplyr 包中的 anti_join()函数以 R 编程语言连接两个不同的数据,如上图所示。
R
# load the library
library("dplyr")
# create the dataframes
gfg1<-data.frame(ID=c(1:5))
gfg2<-data.frame(ID=c(4:8))
# perform anti join
anti_join(gfg1,gfg2, by = "ID")
输出:
ID
1 1
2 2
3 3