给定一个加权的无向图,走道长度N和成本X。任务是计算长度为N的不同走道W的数量,以使Cost(W)= X。
我们将步行的成本W定义为步行沿边缘的权重中的最大值。
节点从1到n编号。该图不包含任何多个边或自环。
例子:
Input:
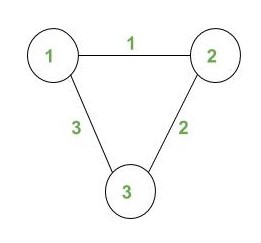
.
N = 4, X = 2
Output: 10
Explanation :
A walk W on the graph is a sequence of vertices (with repetitions of vertices and edges allowed) such that every adjacent pair of vertices in the sequence is an edge of the graph.
For X = 2, all possible 10 walks are listed below :
- 1 -> 2 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3
- 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
- 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 2 -> 3
- 2 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 2
- 2 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 2
- 2 -> 3 -> 2 -> 3 -> 2
- 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 2 -> 1
- 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3
- 3 -> 2 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
- 3 -> 2 -> 3 -> 2 -> 3
Input:
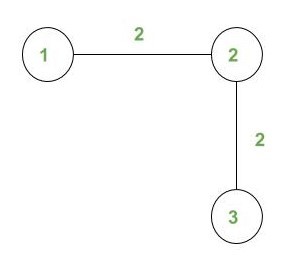
N = 4, X = 2
Output: 12
- 这个想法是要预先计算编号。将所有可能成本的每个顶点的长度N的步长(N)并存储在2-D矩阵中。我们将此矩阵称为B.这些值可以通过在给定的无向图上运行DFS来计算。
例如,
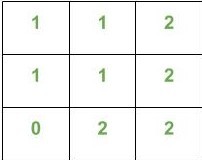
矩阵B的给定快照显示了存储在其中的值。这里B(i,j)表示不。从顶点i开始的长度为N的步数具有步数j的步数。
- 我们维护一维数组Maxedge,在其中保留长度为N的步行成本。当步行长度小于N且有一些与edge(u,v)相关的成本X时,我们调用相同的函数。
我们为长度== N设置了一个基本条件,为此我们更新了数组B并返回了调用。 - 在计算出矩阵B之后,我们只需将成本= x的所有vextex的步数相加即可计算出步数的总和。
Ans += B[i][x];
Here i ranges from 1 to n where n is the no of vertices.
下面是上述方法的实现
C++
// C++ program to count the number of walks
// of length N where cost of each walk is
// equal to k
#include
using namespace std;
int G[250][250] = {0};
int Maxedge[250] = {0};
int B[250][250] = {0};
int l = 0, n, m;
// Function return total
// walk of length N
int TotalWalks(int cost)
{
int ans=0;
// Add values of all
// node with cost X
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
ans+=B[i][cost];
}
return ans;
}
// Function to precompute array B
// meantioned above
void DFS(int u, int v,int len)
{
// Base condition
if (l == len)
{
// Updating the matrix B when
// we get a walk of length N.
B[u][ Maxedge[len]]++;
return ;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (G[v][i] !=0)
{
// Incrementing the length
// of the walk
l++;
// Updating the cost of the walk
Maxedge[l] = max(Maxedge[l - 1],
G[v][i]);
DFS(u, i, len);
l--;
}
}
}
// Function to calculate total
// number of walks of length N
void NumberOfWalks(int cost,int len)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// Calling the function DFS
DFS(i, i, len);
}
int ans = TotalWalks(cost);
// Print the answer
cout<< ans << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int Cost = 2;
n = 3, m = 3;
int length = 4;
// Create a graph given in
// the above diagram
G[1][2] = 1;
G[2][1] = 1;
G[2][3] = 2;
G[3][2] = 2;
G[1][3] = 3;
G[3][1] = 3;
NumberOfWalks(Cost, length) ;
} Java
// Java program to count the number of walks
// of length N where cost of each walk is
// equal to k
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int [][]G = new int[250][250];
static int []Maxedge = new int[250];
static int [][]B = new int[250][250];
static int l = 0, n, m;
// Function return total
// walk of length N
static int TotalWalks(int cost)
{
int ans = 0;
// Add values of all
// node with cost X
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
ans += B[i][cost];
}
return ans;
}
// Function to precompute array B
// meantioned above
static void DFS(int u, int v, int len)
{
// Base condition
if (l == len)
{
// Updating the matrix B when
// we get a walk of length N.
B[u][ Maxedge[len]]++;
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (G[v][i] !=0)
{
// Incrementing the length
// of the walk
l++;
// Updating the cost of the walk
Maxedge[l] = Math.max(Maxedge[l - 1],
G[v][i]);
DFS(u, i, len);
l--;
}
}
}
// Function to calculate total
// number of walks of length N
static void NumberOfWalks(int cost,int len)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// Calling the function DFS
DFS(i, i, len);
}
int ans = TotalWalks(cost);
// Print the answer
System.out.print(ans + "\n");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int Cost = 2;
n = 3; m = 3;
int length = 4;
// Create a graph given in
// the above diagram
G[1][2] = 1;
G[2][1] = 1;
G[2][3] = 2;
G[3][2] = 2;
G[1][3] = 3;
G[3][1] = 3;
NumberOfWalks(Cost, length);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# Python3 program to count the number of walks
# of length N where cost of each walk is
# equal to k
G = [[0 for i in range(250)]
for j in range(250)]
Maxedge = [0 for i in range(250)]
B = [[0 for i in range(250)]
for j in range(250)]
l = 0
n = 0
m = 0
# Function return total
# walk of length N
def TotalWalks(cost):
ans = 0
# Add values of all
# node with cost X
for i in range(1, n + 1):
ans += B[i][cost]
return ans
# Function to precompute array B
# meantioned above
def DFS(u, v, len):
global l
# Base condition
if (l == len):
# Updating the matrix B when
# we get a walk of length N.
B[u][ Maxedge[len]] += 1
return
for i in range(1, n + 1):
if (G[v][i] != 0):
# Incrementing the length
# of the walk
l += 1
# Updating the cost of the walk
Maxedge[l] = max(Maxedge[l - 1], G[v][i])
DFS(u, i, len)
l -= 1
# Function to calculate total
# number of walks of length N
def NumberOfWalks(cost, len):
for i in range(1, n + 1):
# Calling the function DFS
DFS(i, i, len)
ans = TotalWalks(cost)
# Print the answer
print(ans)
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
Cost = 2
n = 3
m = 3
length = 4
# Create a graph given in
# the above diagram
G[1][2] = 1
G[2][1] = 1
G[2][3] = 2
G[3][2] = 2
G[1][3] = 3
G[3][1] = 3
NumberOfWalks(Cost, length)
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# program to count the number of walks
// of length N where cost of each walk is
// equal to k
using System;
class GFG{
static int [,]G = new int[250, 250];
static int []Maxedge = new int[250];
static int [,]B = new int[250, 250];
static int l = 0, n;
// Function return total
// walk of length N
static int TotalWalks(int cost)
{
int ans = 0;
// Add values of all
// node with cost X
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
ans += B[i, cost];
}
return ans;
}
// Function to precompute array B
// meantioned above
static void DFS(int u, int v, int len)
{
// Base condition
if (l == len)
{
// Updating the matrix B when
// we get a walk of length N.
B[u, Maxedge[len]]++;
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (G[v, i] != 0)
{
// Incrementing the length
// of the walk
l++;
// Updating the cost of the walk
Maxedge[l] = Math.Max(Maxedge[l - 1],
G[v, i]);
DFS(u, i, len);
l--;
}
}
}
// Function to calculate total
// number of walks of length N
static void NumberOfWalks(int cost, int len)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// Calling the function DFS
DFS(i, i, len);
}
int ans = TotalWalks(cost);
// Print the answer
Console.Write(ans + "\n");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int Cost = 2;
n = 3;
int length = 4;
// Create a graph given in
// the above diagram
G[1, 2] = 1;
G[2, 1] = 1;
G[2, 3] = 2;
G[3, 2] = 2;
G[1, 3] = 3;
G[3, 1] = 3;
NumberOfWalks(Cost, length);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1输出:
10