牛顿第三运动定律
重要的是要了解,当您将球扔到墙上时,球会在墙上施加力量。同样,墙壁对球施加力,使其从墙壁反弹。同样,地球的万有引力将你推倒。你可能不明白的是,你也在为地面施加同等的力量。这个惊人的现象是牛顿第三定律的结果。
牛顿第三定律指出,如果物体 A 对另一个物体 B 施加一个力,那么物体 B 必须对物体 A 施加一个大小相等且方向相反的力。这条定律代表了自然界中特定的对称性:力总是成对存在,一个物体不能在没有经历过力的情况下对另一个施加力。让我们进一步讨论。
牛顿运动定律
17世纪,艾萨克·牛顿爵士提出了三大运动定律。这些定律通常用于经典力学。它们几乎被普遍接受。法律在此总结为:
- 牛顿第一定律指出,静止或匀速运动的物体将继续保持静止或匀速运动,直到且除非有净外力作用于其上。
- 牛顿第二定律指出,由合力产生的物体加速度与合力的大小成正比,与合力方向相同,与物体的质量成反比。
- 牛顿第三定律指出,对于每一个动作,都有一个相等且相反的反应。
在本文中,仅对运动第三定律进行了适当的解释。该定律讨论了作用力的作用-反应对。
牛顿第三运动定律
该定律表述为:“当一个物体对另一个物体施加力时,第一个物体会感觉到与所施加的力方向相反的力。”根据上述说法,每次相互作用都涉及施加在相互作用对象上的一对力。力的大小相等,第一项上的力与第二项上的力方向相反。
Let’s understand this more clearly with the help of an example:
- While moving on the ground, we push the ground backward by our feet. The ground also exerts a forward force on our feet of equal magnitude in the opposite direction which makes us move forward.
- A book when lying on a table. The book exerts a downward force due to its weight, but it does not fall down, therefore the net force on the book is zero. This is because the table exerts an equal and opposite force on the book in the upward direction.
Explanation: Here in the above examples, we can see that two forces are acting on each of the bodies. In the first example, the force exerted by our feet on the ground is the action force and in response to that, the ground exerts an equal opposite force on our feet. In the second example, the force exerted by the weight of the book is the action force and the force exerted by the table on the book is the reaction force.
现在,让我们了解牛顿第三运动定律中使用的两个术语,称为作用力和反作用力。
作用力:施加在身体上的初始外力称为作用力。
反作用力:身体对反方向的作用力作出反应而施加的力称为反作用力。
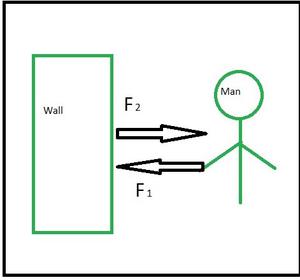
牛顿第三运动定律图解
从上面的例子中,牛顿第三运动定律也可以表述为:
如果两个物体(A 和 B)之间有任何相互作用,则力 F AB (物体 B 施加在物体 A 上的力)等于力 F BA (物体 A 施加在物体 A 上的力),但它们的方向相反.
Note:
- The action and reaction force are exerted by different bodies and not on the same body.
- The action and reaction always occur simultaneously and they are always in pair.
作用-反作用力的例子
自然有广泛的动作反应配对。以下是下面列出的一些示例:
- 动作-反应对的一个例子是鱼在水中的推进。鱼的鳍用来把水向后推。这种推动有助于推动鱼前进。
- 对水的力的大小等于对鱼的力的大小;对水(向后)的力的大小与对鱼(向前)的力的大小相反。
- 鸟的飞行是动作反应对的一个例子。空气被鸟的翅膀向下推。空气被空气推得更高。
- 游泳者向上推水,水向后推。
- 直升机通过迫使空气向下产生升力,从而产生向上的反作用力。
- 登山者使用他们的垂直绳索推动自己向上。
牛顿第三运动定律的应用实例
- 船在水中的运动:在水中,船夫用桨向后推动水(作用力),作为响应,水在向前的方向上对船施加相等的相反力(反作用力)力量)。小船就这样向前移动。
- 用枪发射子弹:当我们用枪发射子弹时,子弹上会施加一个力 F(作用力),而枪在相反方向上会受到相等的后坐力(反作用力)。
- 接球:接球时,球由于其重量和运动对球员的手施加一个力(作用力),球员也对球施加相等的力以使其向相反方向停止。
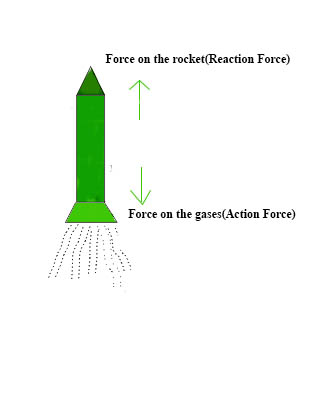
- 火箭的运动:在火箭内部,燃料燃烧,燃烧后的高温高压气体被排出,因此火箭对气体施加力,通过喷嘴(作用力)将气体排出火箭。火箭在向后的方向上,气体也在向上的方向上对火箭施加一个力(反作用力),从而帮助火箭向前移动。
示例问题
问题1:击打后落在地上的一个轻球向上升起,解释。
解决方案:
A light ball when strikes the ground exerts force on the ground (action force) in the downward direction and thus, according to Newton’s third law of motion, the ground in response to it exerts an equal amount of force in opposite direction on the light ball (reaction force) and thus it rises upwards.
问题 2:在以下示例中命名作用力和反作用力:
(a) 放在桌上的一本书
(b) 火箭向上运动
(c) 用枪发射子弹
解决方案:
The given examples are categorized as: Action Force Reaction Force (a) Weight of the book in the downward direction The force exerted by the table on the book in an upward direction (b) Force exerted by the rocket on the burnt gases in the backward direction The force exerted by the gases on the rocket in an upward direction. (c) Force exerted by the gun on the bullet in the forward direction. The force exerted by the bullet on the gun in the backward direction.
问题 3:借助牛顿第三运动定律解释一个人在地面上的行走。
解决方案:
While walking on the ground, a person exerts a force on the ground in a backward direction with his feet (action force) and according to Newton’s third law of motion, the ground exerts an opposite and equal force in the forward direction as a reaction force, and so we can walk on the ground or on floor.
问题 4:一个人用 100N 的力向北推墙。墙对人施加了多大的力?
解决方案:
Given that,
The action force, F is 100 N.
According to Newton’s third law of motion,
Action force = – Reaction force
Therefore, the reaction force = -100 N
That is, the reaction force is equal to 100 N towards south.
问题 5:质量为 500 g 的板球以 20 m/s 的速度行进,被板球棒击中,以 10 m/s 的速度沿原来的路径返回。通过板球棒施加的力计算板球运动中发生的动量变化。
解决方案:
Given that,
The mass of the hockey ball, m is 500 g = 0.5 kg.
The initial velocity of the ball, u is 20 m/s.
The final velocity of the ball after hitting, v is 10 m/s.
The change in momentum = Final momentum – Initial momentum
= mv – mu
= m (v – u)
= 0.5 kg × (20 m/s – 10 m/s)
= 0.5 kg × 10 m/s
= 5 kg m/s
Therefore, change of momentum of the cricket ball by the force applied by the cricket bat is 5 kg m/s.
问题 5:说出牛顿第三运动定律所遵循的原理。另外,说明原理。
解决方案:
Newton’s third law of motion obeys the principle of conservation of momentum. According to the principle of conservation of momentum, when no unbalanced external force acts on the system, the sum of initial momentum is exactly equal to the sum of the final momentum of the system.