牛顿第三运动定律
毫无疑问,你知道将球扔到墙上会导致球对墙上施加力。同样,墙壁对球施加力,使其从墙壁反弹。同样,地球的万有引力将你推倒。你可能不明白的是,你也在为地面施加同等的力量。这个惊人的统计数据是牛顿第三定律的结果。
牛顿第三定律指出,如果物体 A 对另一个物体 B 施加力,则物体 B 必须对物体 A 施加大小相等且方向相反的力。这条规则代表了自然界中特定的对称性:力总是成对存在,一个物体不能对另一个人施加一种力量,而不会受到一种力量的影响。
让我们深入探索牛顿第三定律,
什么是牛顿运动定律?
处理宇宙中所有大型和熟悉物体的模拟运动的物理学分支,例如汽车、行星和人类,属于牛顿规定的经典力学。相比之下,微小的原子和亚原子物体的运动则属于欧拉规定的量子力学分支。
以下是牛顿运动定律:
- 惯性定律——牛顿第一定律指出,如果物体静止或匀速直线运动,除非受到外力作用,否则它将保持静止或匀速直线运动。作用力。
- 第二定律指出,物体动量的变化率与施加在任何质量恒定的物体上的力成正比。
- 第三定律指出,当一个物体对第二个物体施加力时,第二个物体对第一个物体施加大小相等但方向相反的力。
牛顿第三运动定律
Newton’s Third Law of Motion states that: “To every action there is always an equal and opposite reaction.” Action and reaction forces are applied on different bodies at the same instance time frame. The system maintains its equilibrium.
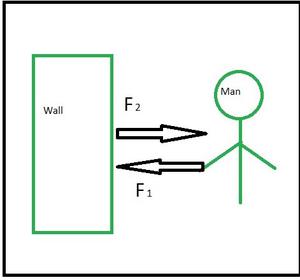
根据牛顿第三定律,当两个物体接触时,它们会相互施加大小相等、方向相反的力。第三定律也称为作用-反应定律。该定律可用于评估所有力平衡的静态平衡问题,但它也适用于恒定或加速运动的物体。
它解释的力量是真实的,而不仅仅是技术。例如,坐在桌子上的一本书会施加与其在桌子上的重量相等的向下力。根据第三定律,桌子对书施加相等且相反的力。书的重量使桌子稍微弯曲,使它像螺旋弹簧一样压在书上。
在数学上,牛顿第三运动定律也可以写成如下所示:
这里,F 12是物体 1 施加在物体 2 上的力,F 21是物体 2 施加在物体 1 上的力。负号表示两个力的施加方向相互相反。
力总是成对出现。如果系统中存在两个物体 A 和 B,则 A 对 B 的力以及 B 和 A 的力成为系统的内力,并且它们相互抵消,因为它们方向相反且相等。结果,系统保持平衡。
牛顿第三自然运动定律
- 鱼在水中的推进——鱼用鳍将水向后推以模拟其运动。反过来,水通过推动鱼向前施加相等的反作用力,推动鱼在水中移动。
- 鱼对水面施加的力的大小,就等于对鱼施加的力的大小。
- 自然界中向后的水的力的方向与鱼的向前的力的方向相反。
- 鸟儿在空中飞翔——鸟儿的飞行运动是由鸟儿用它们的翅膀向下推空气来控制的,而空气反过来又把它们的翅膀向上推并赋予它们升力。
- 自然界中向后的空气力的方向与鸟类的向前力的方向相反。
- 作用-反作用力对使鸟类能够飞行。
Proof that Action and Reaction are Equal and Opposite
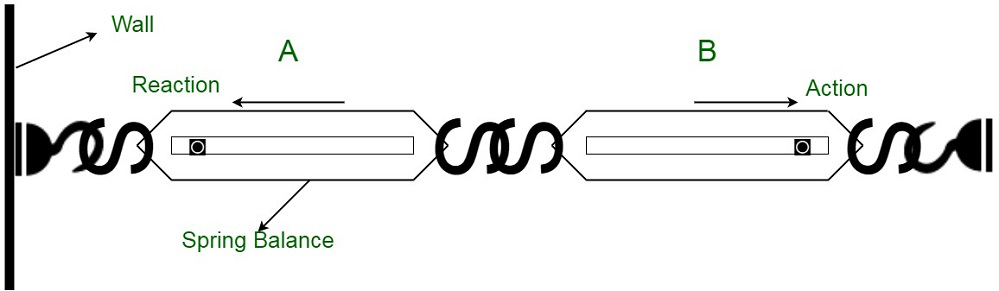
To understand the concept of the action and reaction forces, let us consider a system of two spring balances A and B connected together.
The spring balance B is fixed to any rigid support. A force is then applied in the loose and free end, by pulling the spring balance A. As an effect of the application of force, both the spring balances show the same readings.
This concludes that both the spring balances witness equal magnitude forces. It also shows that the force exerted by both the spring balances, A on B is equal but opposite in direction to the force exerted by spring balance B on A.
Here, he force exerted on the acting body (the spring balance A on B) is termed as action, and the force exerted by the reacting body (spring balance B on A) can be termed as reaction.
牛顿第三运动定律的应用
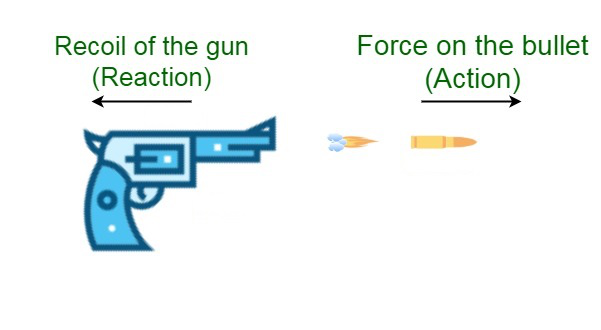
- Bullet Reconcile :当子弹从枪中射出时,它对子弹施加一个向前的力(作用),而子弹对枪施加一个相等和相反的力(反应),枪会后坐。反作用力在射击者的手上受到。
- 当一名水手从船上跳下时,他通过施加船的向后力(动作)将船向后推,然后向前跳跃。因此,船对水手施加一个相等且相反的力,称为反作用力。

- 当我们释放一个充满空气的气球时,从气球中出来的空气(气体)的作用力就是作用力,它通过向上移动对气球施加相等且相反的力,称为反作用力。

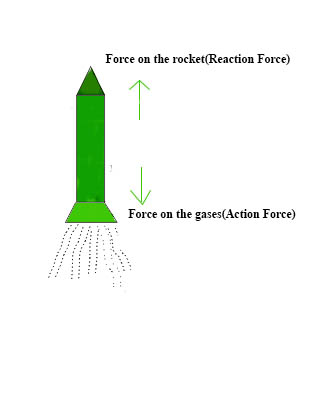
- 当火箭发射时,燃烧气体排出的力(作用)对火箭施加相等且相反的力(反应)并向上移动。
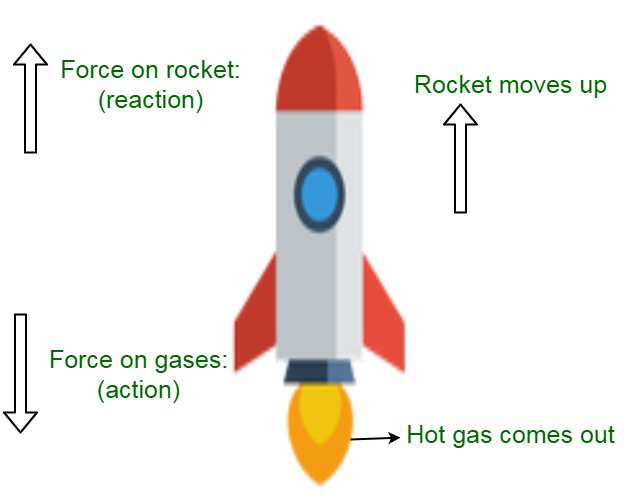
不同种类的燃料在火箭发动机中燃烧,产生热气。这些气体推向火箭的内管。通过内管点燃和燃烧后,气体从火箭底部逸出。随着这些气体向下流动,火箭在天空中朝着向上的方向升起。因此,当气体和火箭相互向相反方向移动时。火箭的反应是运动第三定律的应用。
牛顿第三运动定律的数学解释
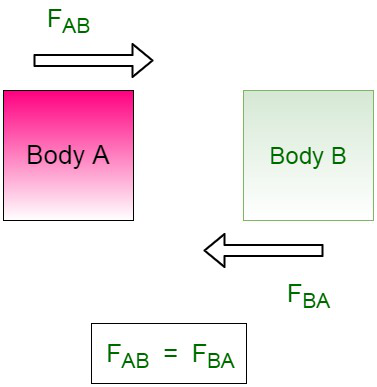
Newton’s third law of motion states that every action has equal and opposite reaction.
For a system of two bodies, A and B, let us assume FAB is a force of body A acting on B and FBA is force by B on body A.
The mathematical expression w.r.t the forces is given by,
FAB = – FBA
where, FAB is an action on B while FBA is reaction of body B on A.
The negative sign indicates that force acting on body A is in opposite direction to the force which is acting on body B.
从牛顿第二运动定律推导牛顿第三运动定律
Let us assume an isolated system with no external forces acting upon them, consisting of two massive bodies A & B mutually interacting with each other. Now, Let us consider both bodies to be in effect of a force under the influence of each other, that is, FAB, to be the force exerted on body B by body A and FBA be the force exerted by body B on A.
Due to these forces, FAB and FBA, let us assume dp1/dt and dp2/dt to be the rate of the change of momentum in the effect of these bodies respectively.Then,
FBA = dp1/dt and FAB = dp2/dt
Adding these equations as:
FBA + FAB = dp1/dt + dp2/dt
= d(p1 + p2) / dt
Since, no external force acts on the system, therefore:
d(p1 + p2) / dt = 0
or
FBA + FAB = 0
FBA = -FAB
The above equation represents Newton’s third law of motion (i.e, for every action there, is an equal and opposite reaction).
示例问题
问题 1:一辆质量为 1250 Kg 的汽车以 10 m/s 2的加速度行驶,撞上了一辆自行车。汽车经历了什么力量?
解决方案:
According to Newton’ second law,
The force on the bike, F = m × a
= 1250 kg × 10 m/s2
= 12500 N
Now according to Newton’s third law, for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Thus, the car experiences a force of 10 N.
问题 2:质量为 10 公斤的狗在质量为 60 公斤的桌子上跳跃。当狗在桌子上走动时,桌子对狗施加的平均力是多少?使用 g = 10 m/s 2 。
解决方案:
The force that the dog applies to the table is its weight. As per Newton’s third law, the table also applies a force to the dog of the same magnitude.
The force on the dog from the table is:
Fs = FN = ma = 10 kg × 10 m/s2 = 100 N
问题 3:一个男孩骑着他的滑板车,用脚将地面推开。因此,这导致他以 8 m/s 2的速度加速。男孩的体重是 600 N。他推离地面的力量是多少?使用 g = 10 m/s 2 。
解决方案:
Boy’s weight, F is 600 N.
The formula to calculate the force on an object is,
F = ma
where m is the mass and a is the acceleration.
or
m = F / a
= 600 N / 10 m/s2
= 60 kg
Boy accelerates at 8 m/s2. so, he is pushed by a force of
F = ma = 60 kg × 8 m/s2 = 480 N
问题 4:两个物体相互施力。在 x 方向上作为时间函数的物体之一上的力是 kt + b,其中 k 和 b 是常数。另一个物体在 x 方向上作为时间函数的力是多少?考虑除了物体相互施加的力之外不存在其他力。
解决方案:
According to Newton’s third law, Every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
Thus, the force has an equal and opposite force on the other body.
Mathematically, this just means to negative the force. Therefore, the force as a function of time in the x-direction on the other body is -ky – b.
问题 5:当玩家开枪并且射击的力量导致后坐力时,枪和子弹的力量和加速度的大小会发生什么变化?
解决方案:
According to Newton’s third law, every force has an equal and opposite reaction, the force on the gun is equal to the force on the bullet.
Therefore, the gun has a larger mass, so the magnitude of its acceleration is less than that of the bullet. A player shoots a gun and the force of the shot results in recoil. The magnitude of the force on the gun equals the magnitude of the force on the bullet, and the magnitude of the acceleration of the gun is less than that of the bullet.