拓扑排序
有向无环图 (DAG) 的拓扑排序是顶点的线性排序,因此对于每个有向边 uv,顶点 u 在排序中位于 v 之前。如果图不是 DAG,则无法对图进行拓扑排序。
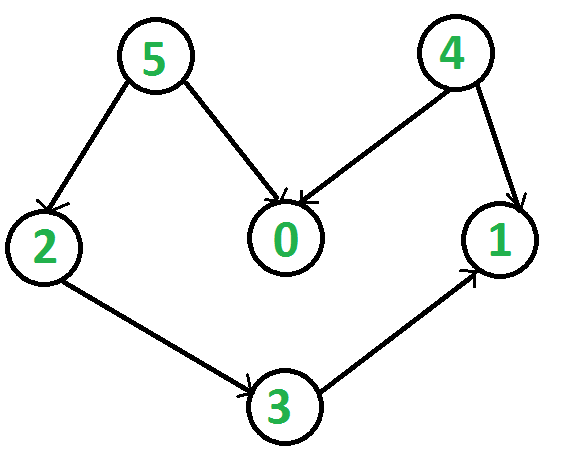
例如,下图的拓扑排序是“5 4 2 3 1 0”。一个图可以有多个拓扑排序。例如,下图的另一种拓扑排序是“4 5 2 3 1 0”。拓扑排序中的第一个顶点始终是入度为 0 的顶点(没有传入边的顶点)。
拓扑排序与深度优先遍历(DFS) :
在 DFS 中,我们打印一个顶点,然后对其相邻顶点递归调用 DFS。在拓扑排序中,我们需要在其相邻顶点之前打印一个顶点。例如,在给定的图中,顶点 '5' 应该打印在顶点 '0' 之前,但与 DFS 不同的是,顶点 '4' 也应该打印在顶点 '0' 之前。所以拓扑排序不同于DFS。例如,所示图的 DFS 是“5 2 3 1 0 4”,但它不是拓扑排序。
查找拓扑排序的算法:
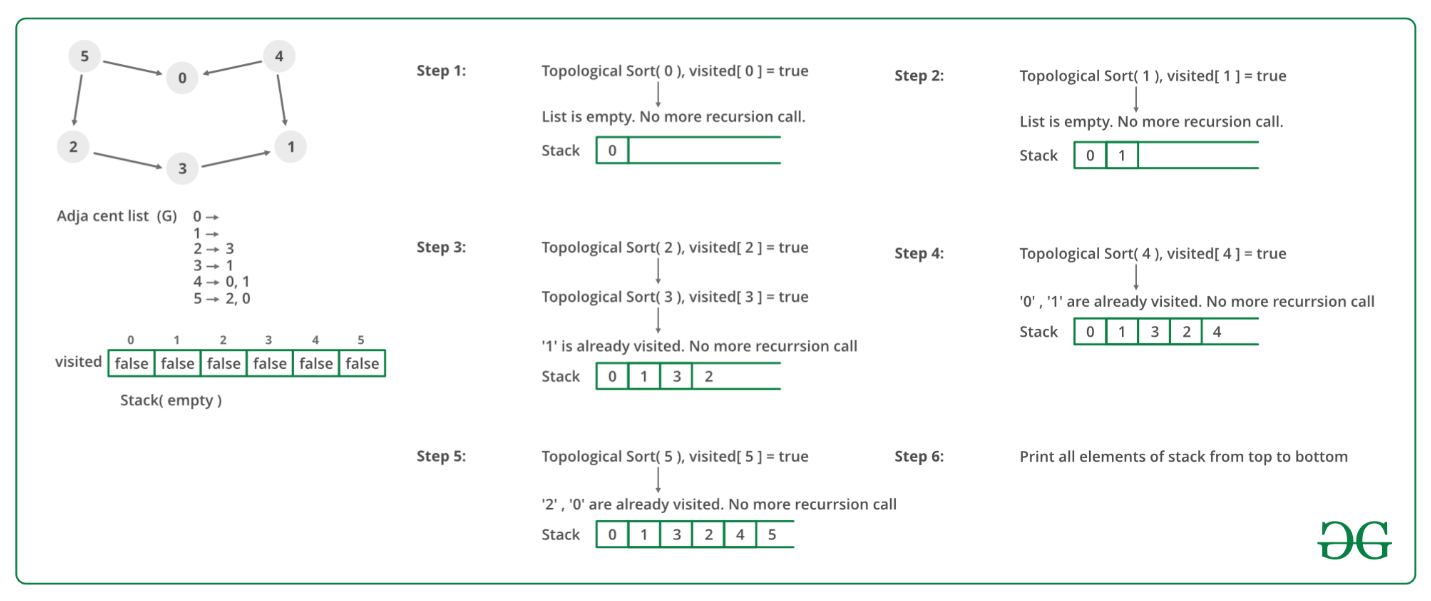
我们建议先看看 DFS 的实现。我们可以修改 DFS 来查找图的拓扑排序。在 DFS 中,我们从一个顶点开始,我们首先打印它,然后递归调用 DFS 为其相邻的顶点。在拓扑排序中,我们使用临时堆栈。我们不会立即打印顶点,我们首先对其所有相邻顶点递归调用拓扑排序,然后将其压入堆栈。最后,打印堆栈的内容。请注意,只有当所有相邻顶点(及其相邻顶点等)都已在堆栈中时,顶点才会被推入堆栈。
下图是上述方法的说明:
以下是拓扑排序的实现。请查看断开连接图的深度优先遍历代码,并注意此处给出的第二个代码与以下代码之间的差异。
C++
// A C++ program to print topological
// sorting of a DAG
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Class to represent a graph
class Graph {
// No. of vertices'
int V;
// Pointer to an array containing adjacency listsList
list* adj;
// A function used by topologicalSort
void topologicalSortUtil(int v, bool visited[],
stack& Stack);
public:
// Constructor
Graph(int V);
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// prints a Topological Sort of
// the complete graph
void topologicalSort();
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
// Add w to v’s list.
adj[v].push_back(w);
}
// A recursive function used by topologicalSort
void Graph::topologicalSortUtil(int v, bool visited[],
stack& Stack)
{
// Mark the current node as visited.
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
topologicalSortUtil(*i, visited, Stack);
// Push current vertex to stack
// which stores result
Stack.push(v);
}
// The function to do Topological Sort.
// It uses recursive topologicalSortUtil()
void Graph::topologicalSort()
{
stack Stack;
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
bool* visited = new bool[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Call the recursive helper function
// to store Topological
// Sort starting from all
// vertices one by one
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
topologicalSortUtil(i, visited, Stack);
// Print contents of stack
while (Stack.empty() == false) {
cout << Stack.top() << " ";
Stack.pop();
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g(6);
g.addEdge(5, 2);
g.addEdge(5, 0);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
g.addEdge(4, 1);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 1);
cout << "Following is a Topological Sort of the given "
"graph \n";
// Function Call
g.topologicalSort();
return 0;
}
Java
// A Java program to print topological
// sorting of a DAG
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// This class represents a directed graph
// using adjacency list representation
class Graph {
// No. of vertices
private int V;
// Adjacency List as ArrayList of ArrayList's
private ArrayList > adj;
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new ArrayList >(v);
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj.add(new ArrayList());
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w) { adj.get(v).add(w); }
// A recursive function used by topologicalSort
void topologicalSortUtil(int v, boolean visited[],
Stack stack)
{
// Mark the current node as visited.
visited[v] = true;
Integer i;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent
// to thisvertex
Iterator it = adj.get(v).iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
i = it.next();
if (!visited[i])
topologicalSortUtil(i, visited, stack);
}
// Push current vertex to stack
// which stores result
stack.push(new Integer(v));
}
// The function to do Topological Sort.
// It uses recursive topologicalSortUtil()
void topologicalSort()
{
Stack stack = new Stack();
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Call the recursive helper
// function to store
// Topological Sort starting
// from all vertices one by one
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
topologicalSortUtil(i, visited, stack);
// Print contents of stack
while (stack.empty() == false)
System.out.print(stack.pop() + " ");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g = new Graph(6);
g.addEdge(5, 2);
g.addEdge(5, 0);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
g.addEdge(4, 1);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 1);
System.out.println("Following is a Topological "
+ "sort of the given graph");
// Function Call
g.topologicalSort();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija Python3
# Python program to print topological sorting of a DAG
from collections import defaultdict
# Class to represent a graph
class Graph:
def __init__(self, vertices):
self.graph = defaultdict(list) # dictionary containing adjacency List
self.V = vertices # No. of vertices
# function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
# A recursive function used by topologicalSort
def topologicalSortUtil(self, v, visited, stack):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[v] = True
# Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
for i in self.graph[v]:
if visited[i] == False:
self.topologicalSortUtil(i, visited, stack)
# Push current vertex to stack which stores result
stack.append(v)
# The function to do Topological Sort. It uses recursive
# topologicalSortUtil()
def topologicalSort(self):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
visited = [False]*self.V
stack = []
# Call the recursive helper function to store Topological
# Sort starting from all vertices one by one
for i in range(self.V):
if visited[i] == False:
self.topologicalSortUtil(i, visited, stack)
# Print contents of the stack
print(stack[::-1]) # return list in reverse order
# Driver Code
g = Graph(6)
g.addEdge(5, 2)
g.addEdge(5, 0)
g.addEdge(4, 0)
g.addEdge(4, 1)
g.addEdge(2, 3)
g.addEdge(3, 1)
print ("Following is a Topological Sort of the given graph")
# Function Call
g.topologicalSort()
# This code is contributed by Neelam YadavC#
// A C# program to print topological
// sorting of a DAG
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// This class represents a directed graph
// using adjacency list representation
class Graph {
// No. of vertices
private int V;
// Adjacency List as ArrayList
// of ArrayList's
private List > adj;
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new List >(v);
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++)
adj.Add(new List());
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
public void AddEdge(int v, int w) { adj[v].Add(w); }
// A recursive function used by topologicalSort
void TopologicalSortUtil(int v, bool[] visited,
Stack stack)
{
// Mark the current node as visited.
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
foreach(var vertex in adj[v])
{
if (!visited[vertex])
TopologicalSortUtil(vertex, visited, stack);
}
// Push current vertex to
// stack which stores result
stack.Push(v);
}
// The function to do Topological Sort.
// It uses recursive topologicalSortUtil()
void TopologicalSort()
{
Stack stack = new Stack();
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
var visited = new bool[V];
// Call the recursive helper function
// to store Topological Sort starting
// from all vertices one by one
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (visited[i] == false)
TopologicalSortUtil(i, visited, stack);
}
// Print contents of stack
foreach(var vertex in stack)
{
Console.Write(vertex + " ");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a graph given
// in the above diagram
Graph g = new Graph(6);
g.AddEdge(5, 2);
g.AddEdge(5, 0);
g.AddEdge(4, 0);
g.AddEdge(4, 1);
g.AddEdge(2, 3);
g.AddEdge(3, 1);
Console.WriteLine("Following is a Topological "
+ "sort of the given graph");
// Function Call
g.TopologicalSort();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Abhinav Galodha Following is a Topological Sort of the given graph
5 4 2 3 1 0 复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(V+E)。
上述算法只是带有额外堆栈的 DFS。因此时间复杂度与 DFS 相同。 - 辅助空间: O(V)。
堆栈需要额外的空间。
注意:在这里,我们也可以使用向量来代替堆栈。如果使用向量,则以相反的顺序打印元素以获得拓扑排序。
应用:
拓扑排序主要用于根据作业之间的给定依赖关系调度作业。在计算机科学中,这种类型的应用出现在指令调度、重新计算电子表格中的公式值时对公式单元求值的排序、逻辑综合、确定要在 make 文件中执行的编译任务的顺序、数据序列化以及解决链接器中的符号依赖性 [ 2]。
相关文章:
Kahn 的拓扑排序算法:另一种 O(V + E) 算法。
有向无环图的所有拓扑排序