Cramer法则:在线性代数中,Cramer法则是一个求解线性方程组的明式,该系统具有与未知变量一样多的方程。它以系数矩阵和从矩阵中获得的矩阵的行列式表示解决方案,方法是用等式右侧的列向量替换一列。对于包含两个或三个以上方程的系统,Cramer规则在计算上效率低下。
假设我们必须解决以下等式:
a 1 x + b 1 y + c 1 z = d 1
a 2 x + b 2 y + c 2 z = d 2
a 3 x + b 3 y + c 3 z = d 3
遵循Cramer法则,首先找到所有四个矩阵的行列式值。
 [Tex] D_1 = \ begin {vmatrix} d_1&b_1&c_1 \\ d_2&b_2&c_2 \\ d_3&b_3&c_3 \\ \ end {vmatrix} [/ Tex]
[Tex] D_1 = \ begin {vmatrix} d_1&b_1&c_1 \\ d_2&b_2&c_2 \\ d_3&b_3&c_3 \\ \ end {vmatrix} [/ Tex] 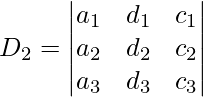 [Tex] D_3 = \ begin {vmatrix} a_1&b_1&d_1 \\ a_2&b_2&d_2 \\ a_3&b_3&d_3 \\ \ end {vmatrix} [/ Tex]
[Tex] D_3 = \ begin {vmatrix} a_1&b_1&d_1 \\ a_2&b_2&d_2 \\ a_3&b_3&d_3 \\ \ end {vmatrix} [/ Tex]
There are 2 cases:
Case I : When D ≠ 0 In this case we have,
x = D1/D
y = D2/D
z = D3/D
Hence unique value of x, y, z will be obtained.
Case II : When D = 0
(a) When at least one of D1, D2 and D3 is non zero: Then no solution is possible and hence system of equations will be inconsistent.
(b) When D = 0 and D1 = D2 = D3 = 0: Then the system of equations will be consistent and it will have infinitely many solutions.
例子
Consider the following system of linear equations.
[2x – y + 3z = 9], [x + y + z = 6], [x – y + z = 2]
 [Tex]D_1 = \begin{vmatrix} 9 & -1 & 3\\ 6 & 1 & 1\\ 2 & -1 & 1\\ \end{vmatrix} [/Tex]
[Tex]D_1 = \begin{vmatrix} 9 & -1 & 3\\ 6 & 1 & 1\\ 2 & -1 & 1\\ \end{vmatrix} [/Tex] [Tex]D_3 = \begin{vmatrix} 2 & -1 & 9\\ 1 & 1 & 6\\ 1 & -1 & 2\\ \end{vmatrix} [/Tex]
[Tex]D_3 = \begin{vmatrix} 2 & -1 & 9\\ 1 & 1 & 6\\ 1 & -1 & 2\\ \end{vmatrix} [/Tex]
[x = D1/D = 1], [y = D2/D = 2], [z = D3/D = 3]
下面是实现。
C++
// CPP program to calculate solutions of linear
// equations using cramer's rule
#include
using namespace std;
// This functions finds the determinant of Matrix
double determinantOfMatrix(double mat[3][3])
{
double ans;
ans = mat[0][0] * (mat[1][1] * mat[2][2] - mat[2][1] * mat[1][2])
- mat[0][1] * (mat[1][0] * mat[2][2] - mat[1][2] * mat[2][0])
+ mat[0][2] * (mat[1][0] * mat[2][1] - mat[1][1] * mat[2][0]);
return ans;
}
// This function finds the solution of system of
// linear equations using cramer's rule
void findSolution(double coeff[3][4])
{
// Matrix d using coeff as given in cramer's rule
double d[3][3] = {
{ coeff[0][0], coeff[0][1], coeff[0][2] },
{ coeff[1][0], coeff[1][1], coeff[1][2] },
{ coeff[2][0], coeff[2][1], coeff[2][2] },
};
// Matrix d1 using coeff as given in cramer's rule
double d1[3][3] = {
{ coeff[0][3], coeff[0][1], coeff[0][2] },
{ coeff[1][3], coeff[1][1], coeff[1][2] },
{ coeff[2][3], coeff[2][1], coeff[2][2] },
};
// Matrix d2 using coeff as given in cramer's rule
double d2[3][3] = {
{ coeff[0][0], coeff[0][3], coeff[0][2] },
{ coeff[1][0], coeff[1][3], coeff[1][2] },
{ coeff[2][0], coeff[2][3], coeff[2][2] },
};
// Matrix d3 using coeff as given in cramer's rule
double d3[3][3] = {
{ coeff[0][0], coeff[0][1], coeff[0][3] },
{ coeff[1][0], coeff[1][1], coeff[1][3] },
{ coeff[2][0], coeff[2][1], coeff[2][3] },
};
// Calculating Determinant of Matrices d, d1, d2, d3
double D = determinantOfMatrix(d);
double D1 = determinantOfMatrix(d1);
double D2 = determinantOfMatrix(d2);
double D3 = determinantOfMatrix(d3);
printf("D is : %lf \n", D);
printf("D1 is : %lf \n", D1);
printf("D2 is : %lf \n", D2);
printf("D3 is : %lf \n", D3);
// Case 1
if (D != 0) {
// Coeff have a unique solution. Apply Cramer's Rule
double x = D1 / D;
double y = D2 / D;
double z = D3 / D; // calculating z using cramer's rule
printf("Value of x is : %lf\n", x);
printf("Value of y is : %lf\n", y);
printf("Value of z is : %lf\n", z);
}
// Case 2
else {
if (D1 == 0 && D2 == 0 && D3 == 0)
printf("Infinite solutions\n");
else if (D1 != 0 || D2 != 0 || D3 != 0)
printf("No solutions\n");
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// storing coefficients of linear equations in coeff matrix
double coeff[3][4] = {
{ 2, -1, 3, 9 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 6 },
{ 1, -1, 1, 2 },
};
findSolution(coeff);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to calculate solutions of linear
// equations using cramer's rule
class GFG
{
// This functions finds the determinant of Matrix
static double determinantOfMatrix(double mat[][])
{
double ans;
ans = mat[0][0] * (mat[1][1] * mat[2][2] - mat[2][1] * mat[1][2])
- mat[0][1] * (mat[1][0] * mat[2][2] - mat[1][2] * mat[2][0])
+ mat[0][2] * (mat[1][0] * mat[2][1] - mat[1][1] * mat[2][0]);
return ans;
}
// This function finds the solution of system of
// linear equations using cramer's rule
static void findSolution(double coeff[][])
{
// Matrix d using coeff as given in cramer's rule
double d[][] = {
{ coeff[0][0], coeff[0][1], coeff[0][2] },
{ coeff[1][0], coeff[1][1], coeff[1][2] },
{ coeff[2][0], coeff[2][1], coeff[2][2] },
};
// Matrix d1 using coeff as given in cramer's rule
double d1[][] = {
{ coeff[0][3], coeff[0][1], coeff[0][2] },
{ coeff[1][3], coeff[1][1], coeff[1][2] },
{ coeff[2][3], coeff[2][1], coeff[2][2] },
};
// Matrix d2 using coeff as given in cramer's rule
double d2[][] = {
{ coeff[0][0], coeff[0][3], coeff[0][2] },
{ coeff[1][0], coeff[1][3], coeff[1][2] },
{ coeff[2][0], coeff[2][3], coeff[2][2] },
};
// Matrix d3 using coeff as given in cramer's rule
double d3[][] = {
{ coeff[0][0], coeff[0][1], coeff[0][3] },
{ coeff[1][0], coeff[1][1], coeff[1][3] },
{ coeff[2][0], coeff[2][1], coeff[2][3] },
};
// Calculating Determinant of Matrices d, d1, d2, d3
double D = determinantOfMatrix(d);
double D1 = determinantOfMatrix(d1);
double D2 = determinantOfMatrix(d2);
double D3 = determinantOfMatrix(d3);
System.out.printf("D is : %.6f \n", D);
System.out.printf("D1 is : %.6f \n", D1);
System.out.printf("D2 is : %.6f \n", D2);
System.out.printf("D3 is : %.6f \n", D3);
// Case 1
if (D != 0)
{
// Coeff have a unique solution. Apply Cramer's Rule
double x = D1 / D;
double y = D2 / D;
double z = D3 / D; // calculating z using cramer's rule
System.out.printf("Value of x is : %.6f\n", x);
System.out.printf("Value of y is : %.6f\n", y);
System.out.printf("Value of z is : %.6f\n", z);
}
// Case 2
else
{
if (D1 == 0 && D2 == 0 && D3 == 0)
System.out.printf("Infinite solutions\n");
else if (D1 != 0 || D2 != 0 || D3 != 0)
System.out.printf("No solutions\n");
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// storing coefficients of linear
// equations in coeff matrix
double coeff[][] = {{ 2, -1, 3, 9 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 6 },
{ 1, -1, 1, 2 }};
findSolution(coeff);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992Python3
# Python3 program to calculate
# solutions of linear equations
# using cramer's rule
# This functions finds the
# determinant of Matrix
def determinantOfMatrix(mat):
ans = (mat[0][0] * (mat[1][1] * mat[2][2] -
mat[2][1] * mat[1][2]) -
mat[0][1] * (mat[1][0] * mat[2][2] -
mat[1][2] * mat[2][0]) +
mat[0][2] * (mat[1][0] * mat[2][1] -
mat[1][1] * mat[2][0]))
return ans
# This function finds the solution of system of
# linear equations using cramer's rule
def findSolution(coeff):
# Matrix d using coeff as given in
# cramer's rule
d = [[coeff[0][0], coeff[0][1], coeff[0][2]],
[coeff[1][0], coeff[1][1], coeff[1][2]],
[coeff[2][0], coeff[2][1], coeff[2][2]]]
# Matrix d1 using coeff as given in
# cramer's rule
d1 = [[coeff[0][3], coeff[0][1], coeff[0][2]],
[coeff[1][3], coeff[1][1], coeff[1][2]],
[coeff[2][3], coeff[2][1], coeff[2][2]]]
# Matrix d2 using coeff as given in
# cramer's rule
d2 = [[coeff[0][0], coeff[0][3], coeff[0][2]],
[coeff[1][0], coeff[1][3], coeff[1][2]],
[coeff[2][0], coeff[2][3], coeff[2][2]]]
# Matrix d3 using coeff as given in
# cramer's rule
d3 = [[coeff[0][0], coeff[0][1], coeff[0][3]],
[coeff[1][0], coeff[1][1], coeff[1][3]],
[coeff[2][0], coeff[2][1], coeff[2][3]]]
# Calculating Determinant of Matrices
# d, d1, d2, d3
D = determinantOfMatrix(d)
D1 = determinantOfMatrix(d1)
D2 = determinantOfMatrix(d2)
D3 = determinantOfMatrix(d3)
print("D is : ", D)
print("D1 is : ", D1)
print("D2 is : ", D2)
print("D3 is : ", D3)
# Case 1
if (D != 0):
# Coeff have a unique solution.
# Apply Cramer's Rule
x = D1 / D
y = D2 / D
# calculating z using cramer's rule
z = D3 / D
print("Value of x is : ", x)
print("Value of y is : ", y)
print("Value of z is : ", z)
# Case 2
else:
if (D1 == 0 and D2 == 0 and
D3 == 0):
print("Infinite solutions")
elif (D1 != 0 or D2 != 0 or
D3 != 0):
print("No solutions")
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# storing coefficients of linear
# equations in coeff matrix
coeff = [[2, -1, 3, 9],
[1, 1, 1, 6],
[1, -1, 1, 2]]
findSolution(coeff)
# This code is contributed by ChitranayalC#
// C# program to calculate solutions of linear
// equations using cramer's rule
using System;
class GFG
{
// This functions finds the determinant of Matrix
static double determinantOfMatrix(double [,]mat)
{
double ans;
ans = mat[0,0] * (mat[1,1] * mat[2,2] - mat[2,1] * mat[1,2])
- mat[0,1] * (mat[1,0] * mat[2,2] - mat[1,2] * mat[2,0])
+ mat[0,2] * (mat[1,0] * mat[2,1] - mat[1,1] * mat[2,0]);
return ans;
}
// This function finds the solution of system of
// linear equations using cramer's rule
static void findSolution(double [,]coeff)
{
// Matrix d using coeff as given in cramer's rule
double [,]d = {
{ coeff[0,0], coeff[0,1], coeff[0,2] },
{ coeff[1,0], coeff[1,1], coeff[1,2] },
{ coeff[2,0], coeff[2,1], coeff[2,2] },
};
// Matrix d1 using coeff as given in cramer's rule
double [,]d1 = {
{ coeff[0,3], coeff[0,1], coeff[0,2] },
{ coeff[1,3], coeff[1,1], coeff[1,2] },
{ coeff[2,3], coeff[2,1], coeff[2,2] },
};
// Matrix d2 using coeff as given in cramer's rule
double [,]d2 = {
{ coeff[0,0], coeff[0,3], coeff[0,2] },
{ coeff[1,0], coeff[1,3], coeff[1,2] },
{ coeff[2,0], coeff[2,3], coeff[2,2] },
};
// Matrix d3 using coeff as given in cramer's rule
double [,]d3 = {
{ coeff[0,0], coeff[0,1], coeff[0,3] },
{ coeff[1,0], coeff[1,1], coeff[1,3] },
{ coeff[2,0], coeff[2,1], coeff[2,3] },
};
// Calculating Determinant of Matrices d, d1, d2, d3
double D = determinantOfMatrix(d);
double D1 = determinantOfMatrix(d1);
double D2 = determinantOfMatrix(d2);
double D3 = determinantOfMatrix(d3);
Console.Write("D is : {0:F6} \n", D);
Console.Write("D1 is : {0:F6} \n", D1);
Console.Write("D2 is : {0:F6} \n", D2);
Console.Write("D3 is : {0:F6} \n", D3);
// Case 1
if (D != 0)
{
// Coeff have a unique solution. Apply Cramer's Rule
double x = D1 / D;
double y = D2 / D;
double z = D3 / D; // calculating z using cramer's rule
Console.Write("Value of x is : {0:F6}\n", x);
Console.Write("Value of y is : {0:F6}\n", y);
Console.Write("Value of z is : {0:F6}\n", z);
}
// Case 2
else
{
if (D1 == 0 && D2 == 0 && D3 == 0)
Console.Write("Infinite solutions\n");
else if (D1 != 0 || D2 != 0 || D3 != 0)
Console.Write("No solutions\n");
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// storing coefficients of linear
// equations in coeff matrix
double [,]coeff = {{ 2, -1, 3, 9 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 6 },
{ 1, -1, 1, 2 }};
findSolution(coeff);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarOutput:
D is : -2.000000
D1 is : -2.000000
D2 is : -4.000000
D3 is : -6.000000
Value of x is : 1.000000
Value of y is : 2.000000
Value of z is : 3.000000