第 10 类 RD Sharma 解 – 第 3 章两变量线性方程组 – 练习 3.2 |设置 2
问题 14. 用图解法求解下列方程
X – 2y + 11 = 0
3x + 6y + 33 = 0
解决方案:
Given that, x – 2y + 11 = 0 and 3x + 6y + 33 = 0
Now, x – 2y + 11 = 0
x = 2y -11
When y = 5, we get x = -1
When y = 4, we get x = -3
So, the following table giving points on the line x – 2y + 11 = 0x -1 -3 y 5 -4
Now, 3x – 6y + 33 = 0
x = (6y – 33)/3
When y = 6, we get x = -1
When y = 5, we get x = -1
So, the following table giving points on the line 3x – 6y + 33 = 0x 1 -1 y 6 5
So, the graph of the equations x – 2y + 11 = 0 and 3x + 6y + 33 = 0:
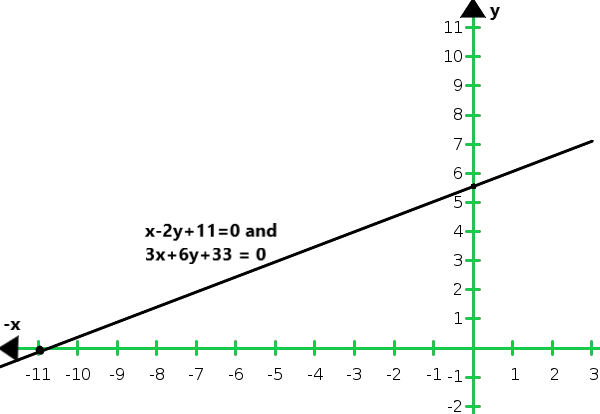
From the graph we conclude that the graphs of the two equations are coincident
Hence, the system of equations has infinitely many solutions.
问题 15. 用图解法求解下列方程
3x – 5y = 20
6x – 10y = – 40
解决方案:
Given that, 3x – 5y = 20 and 6x – 10y = – 40
Now, 3x – 5y = 20
x = (5y + 20)/3
When y = -1, we get x = 5
When y = – 4, we get x = 0
So, the following table giving points on the line 3x – 5y = 20x 5 0 y -1 -4
Now, 6x – 10y = – 40
x = (6y – 40)/6
When y = 4, we get x = 0
When y = 1, we get x = – 5
So, the following table giving points on the line 6x – 10y = – 40x 0 -5 y 4 1
So, the graph of the equations 3x – 5y = 20 and 6x – 10y = – 40:

From the graph we conclude that there is no common point between these two lines.
Hence, given systems of equations is in consistent.
问题 16. 用图解法求解下列方程
x – 2y = 6
3x – 6y = 0
解决方案:
Given that, x – 2y = 6 and 3x – 6y = 0
Now, x – 2y = 6
x = 6 + 2y
When y = 0, we get x = 6
When y = -2, we get x = 2
So, the following table giving points on the line x – 2y = 6x 6 2 y 0 -2
Now, 3x – 6y = 0
= x = 2y
When y = 0, we get x = 0
When y = 1, we get x = 2
So, the following table giving points on the line 3x – 6y = 0x 0 2 y 0 1
So, the graph of the equations x – 2y = 6 and 3x – 6y = 0:

From the graph we conclude that both the lines are parallel. So, the two lines have no common point.
Hence, the given system of equations is in-consistent.
问题 17. 用图解法求解下列方程
2y – x = 9
6y – 3x = 21
解决方案:
Given that, 2y – x = 9 and 6y – 3x = 21
Now, 2y – x = 9
x = -9 + 2y
When y = 3, we get x = -3
When y = 4, we get x = -1
So, the following table giving points on the line 2y – x = 9x -3 -1 y 3 4
Now, 6y – 3x = 21
x = 2y – 7
When y = 2, we get x = -3
When y = 3, we get x = -1
So, the following table giving points on the line 6y – 3x = 21x -3 -1 y 2 3
Graph of the given equations 2y – x = 9 and 6y – 3x = 21:
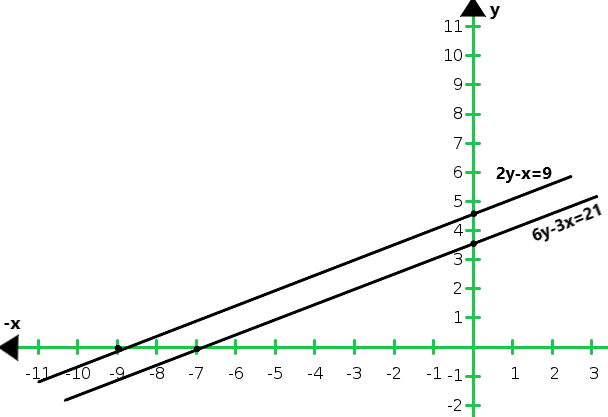
From the graph we conclude that both the lines are parallel. So, the two lines have no common point.
Hence, the given system of equations is in-consistent.
问题 18. 用图解法求解下列方程
3x – 4y – 1 = 0,
2x – 8/3y + 5 = 0
解决方案:
Given that, 3x – 4y – 1 = 0 and 2x – 8/3y + 5 = 0
Now,
3x – 4y -1 = 0
x = (4y + 1)/3
When y = 2, we get x = 3
When y = -1, we get x = -1
So, the following table giving points on the line 3x – 4y – 1 = 0x -1 3 y -1 2
Now,
2x – 8/3y + 5 = 0
x = (8y – 15)/6
When y = 0, we get x = – 2.5
When y = 3, we get x = 1.5
So, the following table giving points on the line 2x – 8/3y + 5 = 0x -2.5 1.5 y 0 3
Graph of the given equations 3x – 4y – 1 = 0 and 2x – 8/3y + 5 = 0:
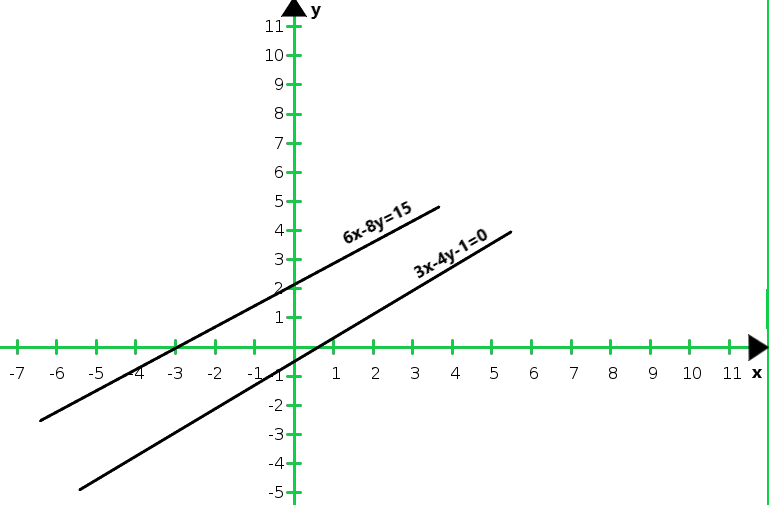
From the graph we conclude that both the lines are parallel. So, the two lines have no common point.
Hence, the given system of equations is inconsistent.
问题 19. 以图形方式确定三角形的顶点,其边的方程如下所示,
(i) 2y – x = 8、5y – x = 14 和 y – 2x = 1
(ii) y = x, y = 0 和 3x + 3y = 10
解决方案:
(i) 2y – x = 8
5y – x = 14
y – 2x = 1
Now, 2y – x = 8
x = 2y – 8
When y = 2, we get x = – 4
When y = 4, we get x = 0
So, the following table giving points on the line 2y – x = 8x -4 0 y 2 4
Now, 5y – x = 14
x = 5y – 14
When y = 2, we get x = 1
When y = 3, we get x = 1
So, the following table giving points on the line 5y – x = 14x -4 1 y 2 3
We have,
y – 2x = 1
x = (y-1)/2
When y = – 1, we get x = 1
When y = 3, we get x = 1
So, the following table giving points on the line y – 2x = 1x -1 1 y 1 3
So, the graph of the equation 2y – x = 8, 5y – x = 14 and y – 2x = 1:
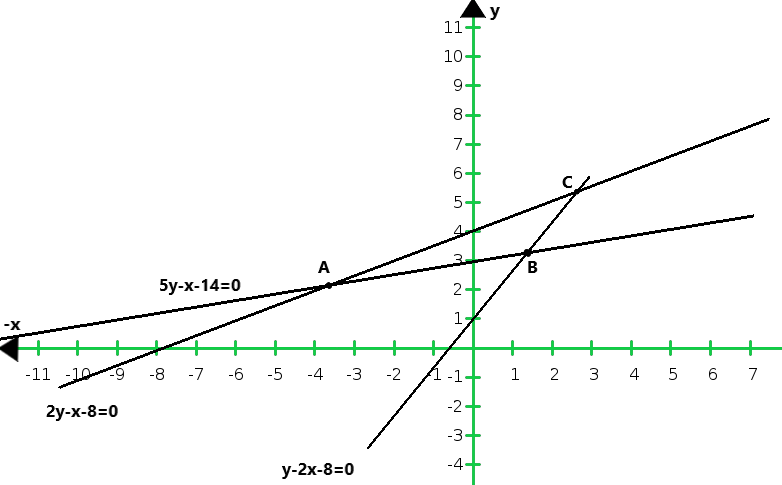
From the graph of the lines represent by the given equation, we conclude that the lines taken in pairs intersect at points A (- 4, 2) B(1, 3) and C(2, 5)
Hence, the vertices of the triangle are A(- 4, 2) B(1, 3) and C(2, 5)
(ii) The given systems of equations are:
y = x
y = 0
3x + 3y = 10
We have, y = x
When x = 1, we get y = 1
When x = -2, we get y = – 2
So, the following table giving points on the line y = xx 1 -2 y 3/7 3/4
So, the graph of the equations y = x, y = 0 and 3x + 3y = 10:
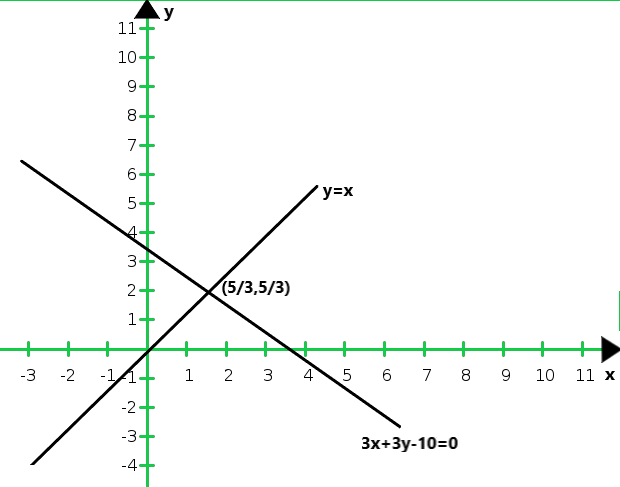
From the graph of the lines represent by the given equation, we conclude that the lines taken in pairs intersect at points
A(0, 0) B(10/3, 0) and C(5/3, 5/3)
Hence, the vertices of the triangle are A(0, 0), B(10/3, 0) and C(5/3, 5/3).
问题 20. 以图形方式确定方程组 x – 2y = 2、4x – 2y = 5 是一致的还是不一致的
解决方案:
Given that, x – 2y = 2 and 4x – 2y = 5
Now, x – 2y = 2
x = 2 + 2y
When y = 0 then, x = 2
When y = -1 then, x = 0
So, the following table giving points on the line x – 2y = 2x 2 0 y 0 -1
Now, 4x – 2y = 5
x = (5+2y)/4
When y = 0, then x = 5/4
When y = 1, then x = 7/4
So, the following table giving points on the line 4x – 2y = 5x 5/4 7/4 y 0 1
So, the graph of the equations x – 2y = 2 and 4x – 2y = 5:
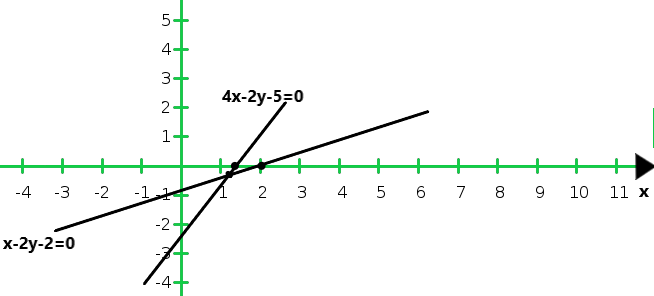
From the graph we conclude that the two lines intersect at (1, 0)
Hence, the system of equations is consistent.
问题 21. 画图判断下列线性方程组是否有唯一解:
(i) 2x – 3y = 6 和 x + y = 1
(ii) 2y = 4x – 6 和 2x = y + 3
解决方案:
(i) Given that, 2x – 3y = 6 and x + y = 1
Now, 2x – 3y = 6
x = (6 + 3y)/2
When y = 0, we get x = 3
When y = – 2, we get x = 0
So, the following table giving points on the line 2x – 3y = 6x 3 0 y 0 -2
Now, x + y = 1
x = 1 – y
When y = 0, we get x = 1
When y = 1, we get n x = 0
So, the following table giving points on the line x + y = 1x 0 1 y 1 0
So, the graph of the given equations 2x – 3y = 6 and x + y = 1:
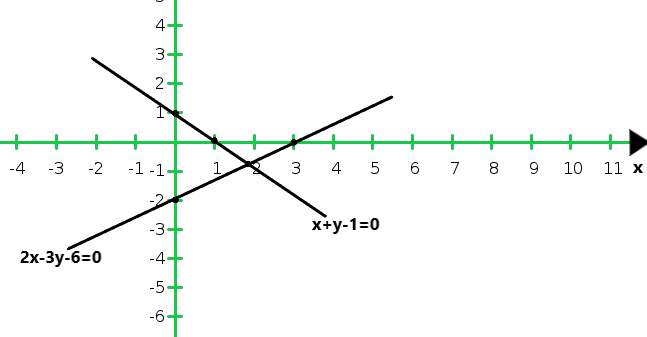
(ii) Given that, 2y = 4x – 6 and 2x = y + 3
x = (6 + 2y)/4
Now, 2y = 4x – 6
When y = -1, we get x = 1
When y = 5, we get x = 4
So, the following table giving points on the line 2y = 4x – 6x 1 4 y -1 5
Now, 2x = y + 3
x = (y + 3)/2
When y = 1, we get x = 2
When y = 3, we get x = 3
So, the following table giving points on the line 2x = y + 3x 2 3 y 1 3
So, the graph of the given equations 2y = 4x – 6 and 2x = y + 3:

From the graph we conclude that the graphs of the two equations are consistent.
Hence, the system of equations has infinitely many solutions.
问题 22. 以图形方式求解以下每个线性方程组。另外,求直线与 y 轴相交点的坐标。
(i) 2x – 5y + 4 = 0 和 2x + y – 8 = 0
解决方案:
Given that, 2x – 5y + 4 = 0 and 2x + y – 8 = 0
Now, 2x – 5y + 4 = 0
x = (5y – 4)/2
When y = 2, we get x = 3
When y = 4, we get x = 8
So, the following table giving points on the line 2x – 5y + 4 = 0x 3 8 y 2 4
Now, 2x + y – 8 = 0
x = (-y + 8)/2
When y = 4, we get x = 2
When y = 2, we get x = 3
So, the following table giving points on the line 2x = y + 3x 3 8 y 2 4
So, the graph of the given equations 2x – 5y + 4 = 0 and 2x + y – 8 = 0
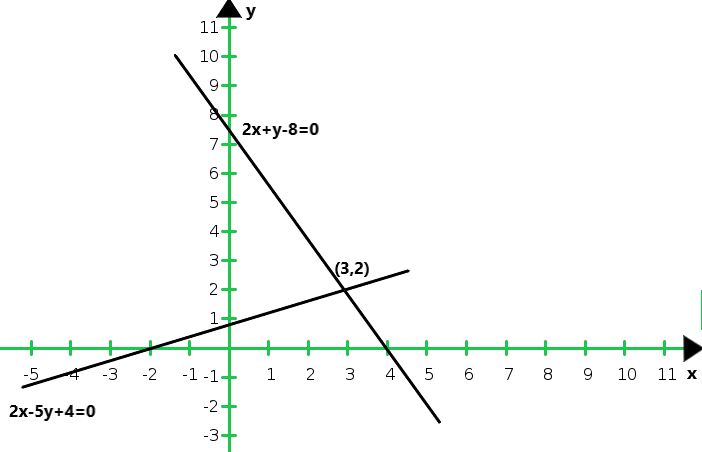
From the graph we conclude that the two intersect at P(3, 2)
Hence, x = 3 and y = 2 is the solution of the given system of equations.
We also observe that the lines represented by 2x – 5y + 4 = 0 and 2x + y – 8 = 0 meet y-axis at A(0, 4/5) and B(0, 8) respectively.
(ii) 3x + 2y = 12 和 5x – 2y = 4
解决方案:
Given that, 3x + 2y = 12 and 5x – 2y = 4
Now, 3x + 2y = 12
x = (12 – 2y)/3
When y = 3, we get x = 2
When y = -3, we get x = 6
So, the following table giving points on the line 3x + 2y = 12x 2 6 y 3 -3
Now, 5x – 2y = 4
x = (4 + 2y)/5
When y = 3, we get x = 2
When y = -7, we get x = -2
So, the following table giving points on the line 5x – 2y = 4x 2 -2 y 3 -7
So, the graph of the given equations 3x + 2y = 12 and 5x – 2y = 4:

From the graph we conclude that the two intersect at P(2, 3)
Hence, x = 2 and y = 3 is the solution of the given system of equations.
We also observe that the lines represented by 3x + 2y = 12 and 5x – 2y = 4 meet y-axis at A(0, 6) and B(0,-2) respectively.
(iii) 2x + y – 11 = 0 和 x – y – 1 = 0
解决方案:
Given that, 2x + y – 11 = 0 and x – y – 1 = 0
Now, 2x + y = 11
y = 11 – 2x
When y = 4, we get x = 3
When y = – 5, we get x = 1
So, the following table giving points on the line 2x + y = 11x 4 5 y 3 1
Now, x – y = 1
y = x – 1
When x = 2, we get y = 1
When y = 3, we get y = 2
So, the following table giving points on the line x – y = 1x 2 3 y 1 2
So, the graph of the given equations 2x + y – 11 = 0 and x – y – 1 = 0:
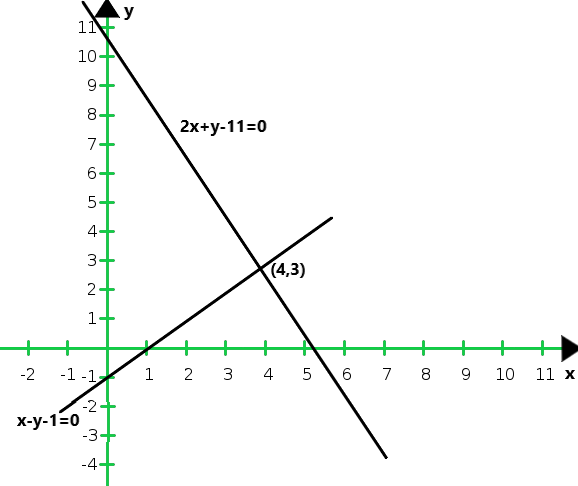
From the graph we conclude that the two intersect at P (4, 3)
Hence, x = 4 and y = 3 is the solution of the given system of equations.
We also observe that the lines represented by 2x + y = 11 and x – y = 1 meet y-axis at A(0, 11) and B(0,-1) respectively.
(iv) x + 2y – 7 = 0 和 2x – y – 4 = 0
解决方案:
Given that, x + 2y – 7 = 0 and 2x – y – 4 = 0
Now, 2x – y – 4 = 0
X = 7 – 2y
When y = 1, we get x = 5
When y = -2, we get x = 3
So, the following table giving points on the line 2x + y = 11x 5 3 y 1 2
Now, 2x – y – 4 = 0
y = 2x – 4
When x = 2, we get y = 0
When y = 0, we get y = -4
So, the following table giving points on the line 2x – y – 4 = 0x 2 0 y 0 -4
So, the graph of the given equations x + 2y – 7 = 0 and 2x – y – 4 = 0:
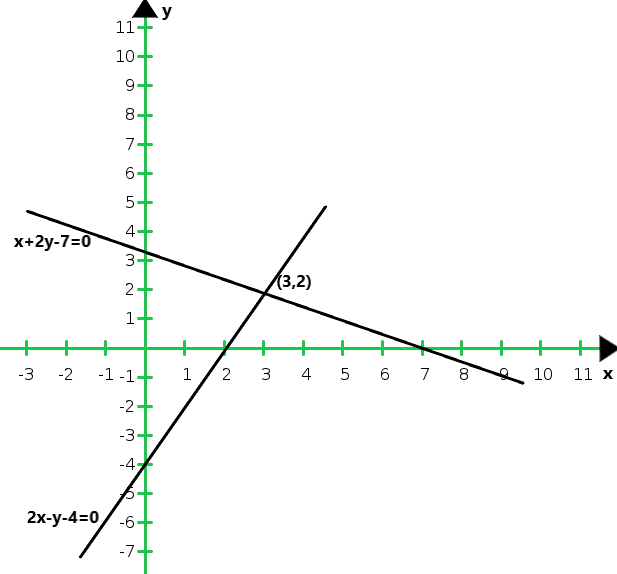
From the graph we conclude that the two intersect at P (3, 2)
Hence, x = 3 and y = 2 is the solution of the given system of equations.
We also observe that the lines meet y-axis at A(0, 3.5) and B(0,- 4) respectively.
(v) 3x + y – 5 = 0 和 2x – y – 5 = 0
解决方案:
Given that, 3x + y – 5 = 0 and 2x – y – 5 = 0
Now, 3x + y – 5 = 0
y = 5 – 3x
When x = 1, we get y = 2
When x = 2, we get y = -1
So, the following table giving points on the line 3x + y – 5 = 0x 1 2 y 2 -1
Now, 2x – y – 5 = 0
y = 2x – 5
When x = 0, we get y = -5
When x = 2, we get y = -1
So, the following table giving points on the line 2x – y – 5 = 0x 0 2 y -5 -1
So, the graph of the given equations 3x + y – 5 = 0 and 2x – y – 5 = 0:
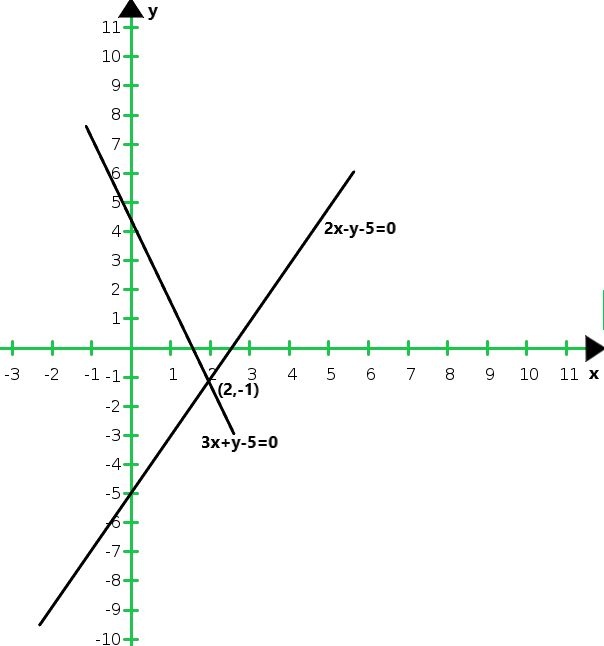
From the graph we conclude that the two intersect at P (2,-1)
Hence, x = 2 and y = -1 is the solution of the given system of equations.
We also observe that the lines meet y-axis at A(0, 5) and B(0, – 5) respectively.
(vi) 2x – y – 5 = 0 和 x – y – 3 = 0
解决方案:
Given that,
2x – y – 5 = 0 ……(i)
x – y – 3 = 0 ……(ii)
The two points satisfying (i) can be listed in a table as,x 1 3 y -3 1
The two points satisfying (ii) can be listed in a table as,x 1 5 y -2 -2
Now, the graph of equations (i) and (ii) can be drawn as,

Graph of the equation (i) and (ii) It is seen that the solution of the given system of equation is given by x = 2, y = -1.
Also, it is observed that the lines (i) and (ii) meet the y-axis at the points (0, – 3) and (0, – 5) respectively.