使用 C 进行离散傅立叶变换及其逆变换
几十年来,人们一直无法找到计算傅立叶变换的最完美方法。早在 1800 年代,高斯就已经提出了他的想法,一个世纪后,一些研究人员也是如此,但解决方案在于必须解决离散傅立叶变换。这是一个相当好的近似值,通过它可以真正接近描述连续时间信号并且它工作得很好(计算机和整个经济一直在使用它)即使它是有限的并且不受时间限制或频带限制同时。更重要的是,它没有考虑信号中的所有样本。尽管如此,它还是有效的,并且是公认的成功。
离散傅里叶变换(DFT):理解离散傅里叶变换是这里的基本目标。逆只是另一个的数学重排,非常简单。傅立叶变换正在将函数从时域转换为频率。人们可能会断言,离散傅立叶变换的作用相同,但离散化信号除外。但是,不要将其与离散时间傅立叶变换混淆。差异解释如下:
- DFT 是针对有限长度的序列计算的,而 DTFT 是针对无限长度的。这就是 DTFT 中的总和范围从 -∞ 到 +∞ 的原因。
- DTFT的特征在于本质上是连续的输出频率,即ω 。另一方面,DFT 给出具有离散频率的输出。
- DTFT 仅对于ω 的采样值等于 DFT。这是我们从另一个中推导出一个的唯一方法。
DFT 和 IDFT 的一般表达式如下。请注意,k 的整数值是从 0 开始计算到 N-1 的。 k 只是一个变量,用于引用函数的采样值。但是,由于 IDFT 是 DFT 的倒数,因此不使用 k。相反,使用“n”。许多人感到困惑的是哪个是哪个。将 DFT 与大写字母“X”和 IDFT 与小写字母“x”关联起来,将其视为一种无压力的活动。
DFT 方程:
IDFT 方程:
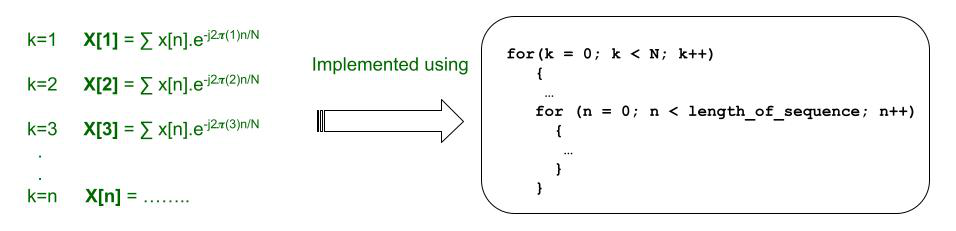
对上述表达式进行编码时首先想到的是从求和开始。实际上,这是通过运行循环并迭代n (在 DFT 中)和k (在 IDFT 中)的不同值来实现的。请注意如何还必须找到不同的输出值。当 k=1 时,可以很容易地计算出 X[k=1]。但是,在其他应用中,例如绘制幅度谱,也必须针对不同的 k 值计算相同的值。因此,必须引入两个循环或一对嵌套循环。
另一个问题是如何翻译表达式的后半部分,即欧拉常数的复数指数。读者必须回忆一下这个公式,该公式有助于用正弦和余弦来描述将欧拉常数提升为复数的公式。这是如下——
这让我们将求和项的后半部分解释如下:
可以导入库(在 C 的情况下),在编写此表达式时可能会在确保代码易读性方面遇到问题。然而,一点数学洞察力和简单的转换是这里的完美要求。许多人会同意。请注意,这会产生表达式的虚部和实部——余弦项是实数,正弦项都是虚数。也可以实现一个相当直观的观点——将序列表示为矩阵,并使用 DFT 和 IDFT 的向量形式进行计算。这最好在 MATLAB 中解决。
算法(DFT):
- 初始化所有需要的库。
- 提示用户在 DFT 中输入点数。
- 现在您可以初始化数组并相应地要求输入序列。这纯粹是由于无法在 C 中声明空数组。动态内存分配是解决方案之一。但是,简单地重新排序提示本身就是一个公平的解决方案。
- 实现 2 个循环,为特定的 k 和 n 值计算 X(k) 的值。请记住,欧拉公式将用于替代e -j2kπn/N 。这需要一个除法,我们分别计算表达式的实部和虚部。
- 运行计算时显示结果。
下面是实现上述方法的 C 程序:
C
// C program for the above approach
#include
#include
// Function to calculate the DFT
void calculateDFT(int len)
{
int xn[len];
float Xr[len];
float Xi[len];
int i, k, n, N = 0;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
printf("Enter the value "
"of x[%d]: ",
i);
scanf("%d", &xn[i]);
}
printf("Enter the number of "
"points in the DFT: ");
scanf("%d", &N);
for (k = 0; k < N; k++) {
Xr[k] = 0;
Xi[k] = 0;
for (n = 0; n < len; n++) {
Xr[k]
= (Xr[k]
+ xn[n] * cos(2 * 3.141592 * k * n / N));
Xi[k]
= (Xi[k]
+ xn[n] * sin(2 * 3.141592 * k * n / N));
}
printf("(%f) + j(%f)\n",
Xr[k], Xi[k]);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int len = 0;
printf("Enter the length of "
"the sequence: ");
scanf("%d4", &len);
calculateDFT(len);
return 0;
} C
// C program for the above approach
#include
#include
// Function to calculate the inverse
// discrete fourier transformation
void calculate_IDFT(int len)
{
int x[len];
float Xr[len];
float Xi[len];
int i, k, n, N = 0;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
printf(
"Enter the real and "
"imaginary bits of X(%d): ",
i);
scanf("%f %f", &Xr[i], &Xi[i]);
}
printf("Enter the number of "
"points in the IDFT: ");
scanf("%d", &N);
for (n = 0; n < N; n++) {
x[n] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < N; k++) {
int theta = (2 * 3.141592 * k * n) / N;
x[n] = x[n] + Xr[k] * cos(theta)
+ Xi[k] * sin(theta);
}
x[n] = x[n] / N;
printf("\n x[%d] = %d\n", n,
x[n]);
}
printf("\n-----------x[n]------------\n\n");
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int len = 0;
printf("Enter the length of "
"the sequence: ");
scanf("%d", &len);
calculate_IDFT(len);
return 0;
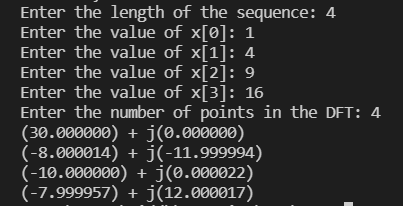
} 输入:
>> Enter the length of the sequence: 4
>> Enter the value of x[0]: 1
>> Enter the value of x[1]: 4
>> Enter the value of x[2]: 9
>> Enter the value of x[3]: 16
>> Enter the number of points in the DFT: 4输出:
算法(IDFT):
- 初始化所有需要的库。
- 提示用户输入序列的长度。这将被替换为 N 的值。初始化负责存储输入的实部和虚部的数组。
- 现在使用“for”循环一一获取序列的实部和虚部。请记住,我们实际上是在颠倒为 DFT 计算定义的过程。
- 定义θ。 Theta 是在 Euler 对 e iθ的转换中 e 升高的指数,即 theta = 2kπn/N。
- 使用余弦和正弦计算 x[n]。使用表达式中涉及的符号时要小心。
- 将得到的输出除以长度或乘以1/N 并打印结果。
下面是实现上述方法的 C 程序:
C
// C program for the above approach
#include
#include
// Function to calculate the inverse
// discrete fourier transformation
void calculate_IDFT(int len)
{
int x[len];
float Xr[len];
float Xi[len];
int i, k, n, N = 0;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
printf(
"Enter the real and "
"imaginary bits of X(%d): ",
i);
scanf("%f %f", &Xr[i], &Xi[i]);
}
printf("Enter the number of "
"points in the IDFT: ");
scanf("%d", &N);
for (n = 0; n < N; n++) {
x[n] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < N; k++) {
int theta = (2 * 3.141592 * k * n) / N;
x[n] = x[n] + Xr[k] * cos(theta)
+ Xi[k] * sin(theta);
}
x[n] = x[n] / N;
printf("\n x[%d] = %d\n", n,
x[n]);
}
printf("\n-----------x[n]------------\n\n");
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int len = 0;
printf("Enter the length of "
"the sequence: ");
scanf("%d", &len);
calculate_IDFT(len);
return 0;
}
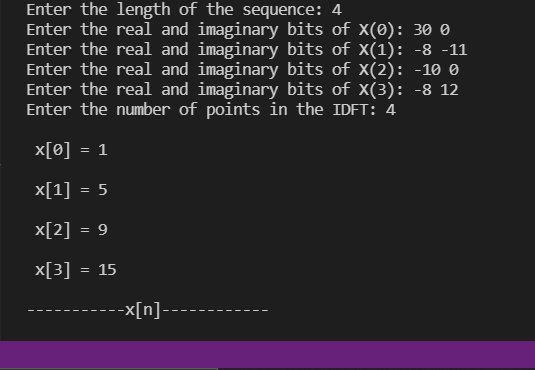
输入:
>> Enter the length of the sequence: 4
>> Enter the real and imaginary bits of X(0): 30 0
>> Enter the real and imaginary bits of X(1): -8 -11
>> Enter the real and imaginary bits of X(2): -10 0
>> Enter the real and imaginary bits of X(3): -8 12
>> Enter the number of points in the IDFT: 4之前获得的 DFT 的输出(不完全是;预计会有一些偏差)用作 IDFT 的输入。
输出: