毫升 |逻辑回归与决策树分类
逻辑回归和决策树分类是当今使用的两种最流行和最基本的分类算法。没有一种算法比另一种更好,一个算法的卓越性能通常归功于正在处理的数据的性质。
我们可以在不同的类别上比较这两种算法——Criteria Logistic Regression Decision Tree Classification Interpretability Less interpretable More interpretable Decision Boundaries Linear and single decision boundary Bisects the space into smaller spaces Ease of Decision Making A decision threshold has to be set Automatically handles decision making Overfitting Not prone to overfitting Prone to overfitting Robustness to noise Robust to noise Majorly affected by noise Scalability Requires a large enough training set Can be trained on a small training set
作为一个简单的实验,我们在同一个数据集上运行这两个模型并比较它们的性能。
第 1 步:导入所需的库
Python3
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifierPython3
cd C:\Users\Dev\Desktop\Kaggle\Sinking Titanic
# Changing the working location to the location of the file
df = pd.read_csv('_train.csv')
y = df['Survived']
X = df.drop('Survived', axis = 1)
X = X.drop(['Name', 'Ticket', 'Cabin', 'Embarked'], axis = 1)
X = X.replace(['male', 'female'], [2, 3])
# Hot-encoding the categorical variables
X.fillna(method ='ffill', inplace = True)
# Handling the missing valuesPython3
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size = 0.3, random_state = 0)
lr = LogisticRegression()
lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(lr.score(X_test, y_test))Python3
criteria = ['gini', 'entropy']
scores = {}
for c in criteria:
dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion = c)
dt.fit(X_train, y_train)
test_score = dt.score(X_test, y_test)
scores = test_score
print(scores)
第 2 步:读取和清理数据集
Python3
cd C:\Users\Dev\Desktop\Kaggle\Sinking Titanic
# Changing the working location to the location of the file
df = pd.read_csv('_train.csv')
y = df['Survived']
X = df.drop('Survived', axis = 1)
X = X.drop(['Name', 'Ticket', 'Cabin', 'Embarked'], axis = 1)
X = X.replace(['male', 'female'], [2, 3])
# Hot-encoding the categorical variables
X.fillna(method ='ffill', inplace = True)
# Handling the missing values
第 3 步:训练和评估逻辑回归模型
Python3
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size = 0.3, random_state = 0)
lr = LogisticRegression()
lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(lr.score(X_test, y_test))
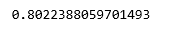
第 4 步:训练和评估决策树分类器模型
Python3
criteria = ['gini', 'entropy']
scores = {}
for c in criteria:
dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion = c)
dt.fit(X_train, y_train)
test_score = dt.score(X_test, y_test)
scores = test_score
print(scores)

在比较分数时,我们可以看到逻辑回归模型在当前数据集上的表现更好,但情况可能并非总是如此。