从给定集中存在的每个节点中查找所有可达节点
给定一个无向图和一组顶点,从给定集合中存在的每个顶点中找到所有可到达的节点。
考虑下面的无向图,其中包含 2 个断开的组件。
arr[] = {1 , 2 , 5}
Reachable nodes from 1 are 1, 2, 3, 4
Reachable nodes from 2 are 1, 2, 3, 4
Reachable nodes from 5 are 5, 6, 7方法1(简单)
一种直接的解决方案是对集合中存在的每个节点进行 BFS 遍历,然后找到所有可到达的节点。
假设我们需要找到 n 个节点的可达节点,该解决方案的时间复杂度为 O(n*(V+E)),其中 V 是图中的节点数,E 是图中的边数。请注意,我们需要调用 BFS 作为每个节点的单独调用,而不使用先前遍历的已访问数组,因为可能需要多次打印相同的顶点。这似乎是一个有效的解决方案,但考虑当 E = Θ(V 2 ) 和 n = V 的情况,时间复杂度变为 O(V 3 )。
方法二(高效)
由于给定的图是无向的,属于同一组件的所有顶点都具有相同的可达节点集。所以我们跟踪顶点和组件映射。图中的每个组件都分配了一个编号,并且该组件中的每个顶点都分配了这个编号。为此,我们使用访问数组,该数组用于跟踪 BFS 中访问的顶点。
For a node u,
if visit[u] is 0 then
u has not been visited before
else // if not zero then
visit[u] represents the component number.
For any two nodes u and v belonging to same
component, visit[u] is equal to visit[v]要存储可达节点,请使用映射m ,其中键作为组件编号,值作为存储所有可达节点的向量。
要找到节点的可达节点u返回m[visit[u]]
查看下面的伪代码以了解如何分配组件编号。
componentNum = 0
for i=1 to n
If visit[i] is NOT 0 then
componentNum++
// bfs() returns a list (or vector)
// for given vertex 'i'
list = bfs(i, componentNum)
m[visit[i]]] = list对于示例中显示的图表,访问数组将是。
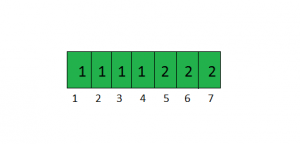
对于节点 1、2、3 和 4,组件编号为 1。对于节点 5、6 和 7,组件编号为 2。
上述想法的实现
C++
// C++ program to find all the reachable nodes
// for every node present in arr[0..n-1].
#include
using namespace std;
// This class represents a directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
class Graph
{
public:
int V; // No. of vertices
// Pointer to an array containing adjacency lists
list *adj;
Graph(int ); // Constructor
void addEdge(int, int);
vector BFS(int, int, int []);
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V+1];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v); // Add w to v’s list.
adj[v].push_back(u); // Add v to w’s list.
}
vector Graph::BFS(int componentNum, int src,
int visited[])
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
// Create a queue for BFS
queue queue;
queue.push(src);
// Assign Component Number
visited[src] = componentNum;
// Vector to store all the reachable nodes from 'src'
vector reachableNodes;
while(!queue.empty())
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
int u = queue.front();
queue.pop();
reachableNodes.push_back(u);
// Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued
// vertex u. If a adjacent has not been visited,
// then mark it visited nd enqueue it
for (auto itr = adj[u].begin();
itr != adj[u].end(); itr++)
{
if (!visited[*itr])
{
// Assign Component Number to all the
// reachable nodes
visited[*itr] = componentNum;
queue.push(*itr);
}
}
}
return reachableNodes;
}
// Display all the Reachable Nodes from a node 'n'
void displayReachableNodes(int n,
unordered_map > m)
{
vector temp = m[n];
for (int i=0; i > m;
// Initialize component Number with 0
int componentNum = 0;
// For each node in arr[] find reachable
// Nodes
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++)
{
int u = arr[i];
// Visit all the nodes of the component
if (!visited[u])
{
componentNum++;
// Store the reachable Nodes corresponding to
// the node 'i'
m[visited[u]] = g.BFS(componentNum, u, visited);
}
// At this point, we have all reachable nodes
// from u, print them by doing a look up in map m.
cout << "Reachable Nodes from " << u <<" are\n";
displayReachableNodes(visited[u], m);
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
int V = 7;
Graph g(V);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(3, 1);
g.addEdge(5, 6);
g.addEdge(5, 7);
// For every ith element in the arr
// find all reachable nodes from query[i]
int arr[] = {2, 4, 5};
// Find number of elements in Set
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int);
findReachableNodes(g, arr, n);
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 program to find all the reachable nodes
# for every node present in arr[0..n-1]
from collections import deque
def addEdge(v, w):
global visited, adj
adj[v].append(w)
adj[w].append(v)
def BFS(componentNum, src):
global visited, adj
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
# Create a queue for BFS
#a = visited
queue = deque()
queue.append(src)
# Assign Component Number
visited[src] = 1
# Vector to store all the reachable
# nodes from 'src'
reachableNodes = []
#print("0:",visited)
while (len(queue) > 0):
# Dequeue a vertex from queue
u = queue.popleft()
reachableNodes.append(u)
# Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued
# vertex u. If a adjacent has not been visited,
# then mark it visited nd enqueue it
for itr in adj[u]:
if (visited[itr] == 0):
# Assign Component Number to all the
# reachable nodes
visited[itr] = 1
queue.append(itr)
return reachableNodes
# Display all the Reachable Nodes
# from a node 'n'
def displayReachableNodes(m):
for i in m:
print(i, end = " ")
print()
def findReachableNodes(arr, n):
global V, adj, visited
# Get the number of nodes in the graph
# Map to store list of reachable Nodes for a
# given node.
a = []
# Initialize component Number with 0
componentNum = 0
# For each node in arr[] find reachable
# Nodes
for i in range(n):
u = arr[i]
# Visit all the nodes of the component
if (visited[u] == 0):
componentNum += 1
# Store the reachable Nodes corresponding
# to the node 'i'
a = BFS(componentNum, u)
# At this point, we have all reachable nodes
# from u, print them by doing a look up in map m.
print("Reachable Nodes from ", u, " are")
displayReachableNodes(a)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
V = 7
adj = [[] for i in range(V + 1)]
visited = [0 for i in range(V + 1)]
addEdge(1, 2)
addEdge(2, 3)
addEdge(3, 4)
addEdge(3, 1)
addEdge(5, 6)
addEdge(5, 7)
# For every ith element in the arr
# find all reachable nodes from query[i]
arr = [ 2, 4, 5 ]
# Find number of elements in Set
n = len(arr)
findReachableNodes(arr, n)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29输出:
Reachable Nodes from 2 are
2 1 3 4
Reachable Nodes from 4 are
2 1 3 4
Reachable Nodes from 5 are
5 6 7时间复杂度分析:
n = 给定集合的大小
E = 边数
V = 节点数
BFS 的 O(V+E)
在最坏的情况下,为给定中存在的每个节点显示所有 V 节点,即图中只有一个组件,因此需要 O(n*V) 时间。
最坏情况时间复杂度:O(V+E) + O(n*V)