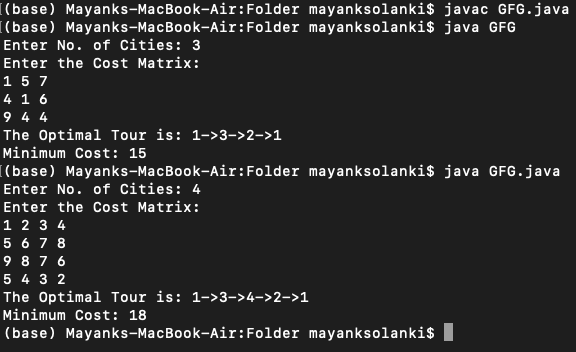
用增量插入法解决旅行商问题的Java程序
增量实际上用于软件开发中,模型以增量方式设计、实现和测试(每次添加一点),直到产品完成。它涉及开发和维护。当产品满足其所有要求时,该产品被定义为成品。
让我们简要讨论旅行商问题。在这里,我们应该找到推销员必须旅行的所有城市之间的最简单或最短的距离,即找到图表节点之间的最短和最佳路线。它也被称为 TSP,是现代世界中最著名的计算机科学优化问题。
算法:
- 从仅包含节点“i”的子图开始。
- 找到节点 r 使得 c ir最小并形成子旅游 iri。
- (选择步骤)给定一个子路径,找到不在子路径中最接近子路径中任何节点 j 的节点 r;即具有最小的 c rj
- (插入步骤)在子循环中找到最小化 c ir + c rj – c ij的弧 (i, j) 在 'i' 和 'j' 之间插入 'r'。
- 如果所有节点都添加到游览中,则停止。否则转到第 3 步
执行:
Java
// Java Program to Solve Travelling Salesman Problem
// Using Incremental Insertion Method
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Importing Scanner class to take input from the user
import java.util.Scanner;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Method 1
// Travelling Salesman Incremental Insertion Method
static int tspdp(int c[][], int tour[], int start,
int n)
{
int mintour[] = new int[10], temp[] = new int[10],
mincost = 999, ccost, i, j, k;
if (start == n - 1)
{
return (c[tour[n - 1]][tour[n]]
+ c[tour[n]][1]);
}
// Logic for implementing the minimal cost
for (i = start + 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
temp[j] = tour[j];
temp[start + 1] = tour[i];
temp[i] = tour[start + 1];
if ((c[tour[start]][tour[i]]
+ (ccost = tspdp(c, temp, start + 1, n)))
< mincost)
{
mincost = c[tour[start]][tour[i]] + ccost;
for (k = 1; k <= n; k++)
mintour[k] = temp[k];
}
}
// Now, iterating over the path (mintour) to
// compute its cost
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
tour[i] = mintour[i];
// Returning the cost of min path
return mincost;
}
// Method 2
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creatingn an object of Scanner class to take user
// input
// 1. Number of cities
// 2. Cost matrix
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// Creating matrices in the main body
int c[][] = new int[10][10], tour[] = new int[10];
// Declaring variables
int i, j, cost;
// Step 1: To read number of cities
// Display message for asking user to
// enter number of cities
System.out.print("Enter No. of Cities: ");
// Reading and storing using nextInt() of Scanenr
int n = in.nextInt();
// Base case
// If the city is 1 then
// path is not possible
// Cost doesnot play any role
if (n == 1) {
// Display on the console
System.out.println("Path is not possible!");
// terminate
System.exit(0);
}
// Case 2
// Many cities
// Again, reading the cost of the matrix
// Display message
System.out.println("Enter the Cost Matrix:");
// Travelling across cities using nested loops
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
c[i][j] = in.nextInt();
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
tour[i] = i;
// Calling the above Method 1 to
cost = tspdp(c, tour, 1, n);
// Now, coming to logic to print the optimal tour
// Display message for better readibility
System.out.print("The Optimal Tour is: ");
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// Printing across which cities should Salesman
// travel
System.out.print(tour[i] + "->");
// Starting off with the city 1->
System.out.println("1");
// Print and display the (minimum)cost of the path
// traversed
System.out.println("Minimum Cost: " + cost);
}
}输出: